Abstract
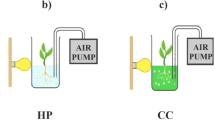
Hydroponic growing systems and the application of natural biostimulant substances are becoming very attractive option for crop cultivation due to their economic relevance since they allow reduction in the use of fertilizer and increase the yield. In order to perform a hydroponic co-cultivation system of microalgae (Chlorella vulgaris or Scenedesmus quadricauda) and tomato plants, grown in Hoagland nutrient solution, their mutual effect and the influence of a natural biostimulant obtained by alkaline extraction from a digestate of agro-livestock residues (DHL) were evaluated. The results showed that the co-cultivation system positively affected the growth of both tomato plants and microalgae. The best option, aimed to a mutual benefit for both cultures, resulted to be the co-cultivation system of tomato plants and S. quadricauda in the presence of DHL, positively affecting the growth of tomato plants along with a great increase in microalgal biomass.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alam MZ, Braun G, Norrie J, Hodges DM (2014) Ascophyllum extract application can promote plant growth and root yield in carrot associated with increased root-zone soil microbial activity. Can J Plant Sci 94:337–348
Bacellar Mendes LB, Vermelho AB (2013) Allelopathy as a potential strategy to improve microalgae cultivation. Biotechnol Biofuels 6:152–165
Baglieri A, Cadili V, Monterumici CM, Gennari M, Tabasso S, Montoneri E, Nardi S, Negre M (2014) Fertilization of bean plants with tomato plants hydrolysates. Effect on biomass production, chlorophyll content and N assimilation. Sci Hortic 176:194–199
Baglieri A, Sidella S, Barone V, Fragalà F, Silkina A, Nègre M, Gennari M (2016) Cultivating Chlorella vulgaris and Scenedesmus quadricauda microalgae to degrade inorganic compounds and pesticides in water. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:18165–18174
Barone V, Baglieri A, Stevanato P, Broccanello C, Bertoldo G, Bertaggia M, Cagnin M, Pizzeghello D, Moliterni VMC, Mandolino G, Fornasier F, Squartini A, Nardi S, Concheri G (2018) Root morphological and molecular responses induced by microalgae extracts in sugar beet (Beta vulgaris L.). J Appl Phycol 30:1061–1071
Bulgari R, Cocetta G, Trivellini A, Vernieri P, Ferrante A (2015) Biostimulants and crop responses: a review. Biol Agric Hortic 31:1–17
Erice G, Louahlia S, Irigoyen JJ, Sanchez-Diaz M, Avice JC (2010) Biomass partitioning, morphology and water status of four alfalfa genotypes submitted to progressive drought and subsequent recovery. J Plant Physiol 167:114–120
Ertani A, Pizzeghello D, Baglieri A, Cadili V, Tambone F (2013) Humic-like substances from agro-industrial residues affect growth and nitrogen assimilation in maize (Zea mays L.) plantlets. J Geochem Explor 129:103–111
Gong Y, Jiang M (2011) Biodiesel production with microalgae as feedstock: from strains to biodiesel. Biotechnol Lett 33:1269–1284
Hickman GW (2011) Greenhouse vegetable production statistics: a review of current data on the international production of vegetables in greenhouses. Cuesta Roble Greenhouse Consultants, Mariposa
Hultberg M, Carlsson AS, Gustafsson S (2013) Treatment of drainage solution from hydroponic greenhouse production with microalgae. Bioresour Technol 136:401–406
Kumar RR, Cho JY (2014) Reuse of hydroponic waste solution. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:9569–9577
Lee YK (2001) Microalgal mass culture systems and methods: their limitation and potential. J Appl Phycol 13:307–315
Mata TM, Martins AA, Caetano NS (2010) Microalgae for biodiesel production and other applications: a review. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 14:217–232
Maurya R, Paliwal C, Chokshi K, Pancha I, Ghosh T, Satpati GG, Pal R, Ghosh A, Mishra S (2016) Hydrolysate of lipid extracted microalgal biomass residue: an algal growth promoter and enhancer. Bioresour Technol 207:197–204
Parrado J, Bautista J, Romero EJ, García-Martínez AM, Friaza V, Tejada M (2008) Production of a carob enzymatic extract: potential use as a biofertilizer. Bioresour Technol 99:2312–2318
Povero G, Mejia JF, Di Tommaso D, Piaggesi A, Warrior P (2016) A systematic approach to discover and characterize natural plant biostimulants. Front Plant Sci 7:435
Puglisi I, Barone V, Sidella S, Coppa M, Broccanello C, Gennari M, Baglieri A (2018) Biostimulant activity of humic-like substances from agro-industrial waste on Chlorella vulgaris and Scenedesmus quadricauda. Eur J Phycol; https://doi.org/10.1080/09670262.2018.1458997
Rice EL (1984) Allelopathy, 2nd edn. Academic Press, Orlando
Stanier RY, Kunisawa R, Mandel M, Cohen-Bazire G (1971) Purification and properties of unicellular blue-green algae (order Chroococcales). Bacteriol Rev 35:171–205
Taiz L, Zeiger E, Møller IM, Murphy A (2015) Plant physiology and development, 6th edn. Sinauer Associates, NY
Vernieri P, Borghesi E, Tognoni F, Serra G, Ferrante A, Piaggesi A (2006) Use of biostimulants for reducing nutrient solution concentration in floating system. Acta Hortic 718:477–484
Zhang J, Wang X, Zhou Q (2017) Co-cultivation of Chlorella spp and tomato in a hydroponic system. Biomass Bioenergy 97:132–138
Funding
This work was supported by the grant “PIANO PER LA RICERCA 2016-2018”—University of Catania (Italy).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barone, V., Puglisi, I., Fragalà, F. et al. Novel bioprocess for the cultivation of microalgae in hydroponic growing system of tomato plants. J Appl Phycol 31, 465–470 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-018-1518-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-018-1518-y