Abstract
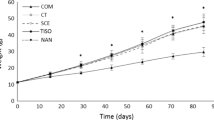
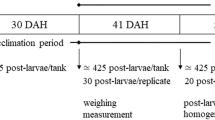
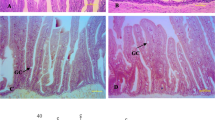
The long-term inclusion of 10% seaweed meal (Ulva rigida and Undaria pinnatifida) was evaluated in diets for Senegalese sole (Solea senegalensis). Triplicate groups of fish with an initial body weight of 23 g were fed the experimental diets (ULVA and UNDARIA) and compared to fish fed a control diet with no seaweed included (CTRL), both in juvenile (after 5 months of feeding, up to 60 g) and on-growing stages (after 9 months of feeding, up to 160 g). In the early juvenile phase, the inclusion of seaweeds did not affect fish growth, but final body weight was significantly lower in on-growing fish fed the UNDARIA diet. Overall, growth performance was also reduced in fish fed the UNDARIA diet, with a significantly lower daily growth index. Whole-body composition and nutrient retention (% intake) remained unaffected by the dietary treatment, but by the end of the growth trial fish fed the UNDARIA diet had a significantly lower protein gain associated with significantly lower intestinal villi width. At the end of the experiment, fish fed the UNDARIA diet had a significantly higher iodine flesh content (375.7 μg kg−1) than those fed the CTRL (187.5 μg kg−1) or ULVA (199.3 μg kg−1) diets, whereas selenium content was similar in all groups of fish. In conclusion, U. rigida seems a valid ingredient for Senegalese sole diets without affecting fish growth or nutrient utilization. Undaria pinnatifida was an effective way of naturally fortifying the nutritional value of sole fillets for human consumption, but resulted in growth impairment, so a lower inclusion level should be further evaluated.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Warith AW, Younis el SM, Al-Asgah NA (2016) Potential use of green macroalgae Ulva lactuca as a feed supplement in diets on growth performance, feed utilization and body composition of the African catfish, Clarias gariepinus. Saudi J Biol Sci 23:404–409
Andreakis N, Schaffelke B (2012) Invasive marine seaweeds: pest or prize? In: Wiencke C, Bischof K (eds) Seaweed biology. Springer, Berlin pp ??
AOAC (2006) Official methods of analysis of AOAC International. Maryland, USA
APROMAR (2016) La acuicultura en España. Asociación Empresarial de Productores de Cultivos Marinos de España (APROMAR)
Araújo M, Rema P, Sousa-Pinto I, Cunha LM, Peixoto MJ, Pires MA, Seixas F, Brotas V, Beltrán C, Valente LMP (2016) Dietary inclusion of IMTA-cultivated Gracilaria vermiculophylla in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) diets: effects on growth, intestinal morphology, tissue pigmentation, and immunological response. J Appl Phycol 28:679–689
Azaza MS, Mensi F, Ksouri J, Dhraief MN, Brini B, Abdelmouleh A, Kraïem MM (2008) Growth of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus L.) fed with diets containing graded levels of green algae ulva meal (Ulva rigida) reared in geothermal waters of southern Tunisia. J Appl Ichthyol 24:202–207
Bell JG, Henderson RJ, Tocher DR, McGhee F, Dick JR, Porter A, Smullen RP, Sargent JR (2002) Substituting fish oil with crude palm oil in the diet of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) affects muscle fatty acid composition and hepatic fatty acid metabolism. J Nutr 132:222–230
Bligh EG, Dyer WJ (1959) A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol 37:911–917
Borges P, Medale F, Veron V, Pires Mdos A, Dias J, Valente LM (2013) Lipid digestion, absorption and uptake in Solea senegalensis. Comp Biochem Physiol A 166:26–35
Borges P, Oliveira B, Casal S, Dias J, Conceicao L, Valente LM (2009) Dietary lipid level affects growth performance and nutrient utilisation of Senegalese sole (Solea senegalensis) juveniles. Br J Nutr 102:1007–1014
Cabral EM, Bacelar M, Batista S, Castro-Cunha M, Ozorio ROA, Valente LMP (2011) Replacement of fishmeal by increasing levels of plant protein blends in diets for Senegalese sole (Solea senegalensis) juveniles. Aquaculture 322:74–81
Cabral EM, Fernandes TJR, Campos SD, Castro-Cunha M, Oliveira MBPP, Cunha LM, Valente LMP (2013) Replacement of fish meal by plant protein sources up to 75% induces good growth performance without affecting flesh quality in ongrowing Senegalese sole. Aquaculture 380-383:130–138
Castillo-Duran C, Ruz M (2004) Epidemiology of micronutrient deficiencies in developing and developed countries, specifically zinc, copper, selenium and iodine. In: Pettifor JM, Zlotkin S (eds) Micronutrient Deficiencies during the Weaning Period and the First Years of Life. Nestlé Nutrition Workshop Series Pediatric Program, vol 54. Nestec Ltd., Vevey/S. Karger AG, Basel, pp 37–52
Dantagnan P, Hernández A, Borquez A, Mansilla A (2009) Inclusion of macroalgae meal (Macrocystis pyrifera) as feed ingredient for rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss): effect on flesh fatty acid composition. Aquac Res 41:87–94
Dawczynski C, Schubert R, Jahreis G (2007) Amino acids, fatty acids, and dietary fibre in edible seaweed products. Food Chem 103:891–899
Diler I, Tekinay A, Güroy D, Güroy BK, Soyutürk M (2007) Effects of Ulva rigida on the growth, feed intake and body composition of common carp, Cyprinus carpio L. J Biol Sci 7:305–308
Ergün S, Soyutürk M, Güroy B, Güroy D, Merrifield D (2009) Influence of Ulva meal on growth, feed utilization, and body composition of juvenile Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) at two levels of dietary lipid. Aquac Int 17:355–361
FEAP (2016) European Aquaculture Production Report 2007-2015. Fed Eur Aqua Prod (FEAP)
Fernandes TJ, Alves RC, Souza T, Silva JM, Castro-Cunha M, Valente LM, Oliveira MB (2012) Lipid content and fatty acid profile of Senegalese sole (Solea senegalensis Kaup, 1858) juveniles as affected by feed containing different amounts of plant protein sources. Food Chem 134:1337–1342
Fernández-Reiriz MJ, Pérez-Camacho A, Ferreiro MJ, Blanco J, Planas M, Campos MJ, Labarta U (1989) Biomass production and variation in the biochemical profile (total protein, carbohydrates, RNA, lipids and fatty acids) of seven species of marine microalgae. Aquaculture 83:17–37
FishStatJ (2018) FishStatJ—software for fishery statistical time series. http://www.fao.org/fishery/. Accessed 27 February 2018
Fleurence J (2004) Seaweed proteins. In: Yada RY (ed) Proteins in food processing. Woodhead Publishing Limited, pp 197–211. https://doi.org/10.1533/9781855738379.1.197
Fung A, Hamid N, Lu J (2013) Fucoxanthin content and antioxidant properties of Undaria pinnatifida. Food Chem 136:1055–1062
Grammes F, Reveco F, Romarheim O, Landsverk T, Mydland L, Øverland M (2013) Candida utilis and Chlorella vulgaris counteract intestinal inflammation in Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar L.). PLoS One 8:e83213
Güroy B, Ergün S, Merrifield DL, Güroy D (2013) Effect of autoclaved Ulva meal on growth performance, nutrient utilization and fatty acid profile of rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss. Aquac Int 21:605–615
Güroy BK, Cirik Ş, Güroy D, Sanver F, Tekinay AA (2007) Effects of Ulva rigida and Cystoseira barbata meals as a feed additive on growth performance, feed utilization,and body composition of Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. Turk J Vet Anim Sd 31:91–97
Güroy D, Güroy B, Merrifield DL, Ergün S, Tekinay AA, Yigit M (2011) Effect of dietary Ulva and Spirulina on weight loss and body composition of rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum), during a starvation period. J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr (Berl) 95:320–327
Heidarieh M, Mirvaghefi AR, Akbari M, Farahmand H, Sheikhzadeh N, Shahbazfar AA, Behgar M (2012) Effect of dietary Ergosan on growth performance, digestive enzymes, intestinal histology, hematological parameters and body composition of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Fish Physiol Biochem 38:1169–1174
Holdt SL, Kraan S (2011) Bioactive compounds in seaweed: functional food applications and legislation. J Appl Phycol 23:543–597
Julshamn K, Dahl L, Eckhoff K (2001) Determination of iodine in seafood by inductively coupled plasma/mass spectrometry. J AOAC Int 84:1976–1983
Mæhre HK, Malde MK, Eilertsen KE, Elvevoll EO (2014) Characterization of protein, lipid and mineral contents in common Norwegian seaweeds and evaluation of their potential as food and feed. J Sci Food Agric 94:3281–3290
Marinho G, Nunes C, Sousa-Pinto I, Pereira R, Rema P, Valente LMP (2013) The IMTA-cultivated Chlorophyta Ulva spp. as a sustainable ingredient in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) diets. J Appl Phycol 25:1359–1367 3
McNamara R, Jandacek R, Rider T, Tso P, Straus A, Lipton J (2010) Omega-3 fatty acid deficiency increases constitutive pro-inflammatory cytokine production in rats: relationship with central serotonin turnover. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids 83:185–191
Morais S, Aragão C, Cabrita E, Conceição LEC, Constenla M, Costas B, Dias J, Duncan N, Engrola S, Estevez A, Gisbert E, Mañanós E, Valente LMP, Yúfera M, Dinis MT (2016) New developments and biological insights into the farming of Solea senegalensis reinforcing its aquaculture potential. Rev Aquacult 8:227–263
Mustafa MG, Wakamatsu S, Takeda TA, Umino T, Nakagawa H (1995) Effects of algae meal as feed additive on growth, feed efficiency, and body composition in red sea bream. Fish Sci 61:25–28
Nakagawa H, Nematipour GR, Yamamoto M (1993) Optimum level of Ulva meal diet supplement to minimize weight loss during wintering in black sea bream Acanthopagrus schlegeli (Bleeker). Asian Fish Sci 6:139–148
Niu J, Chen X, Lu X, Jiang S-G, Lin H-Z, Liu Y-J, Huang Z, Wang J, Wang Y, Tian L-X (2015) Effects of different levels of dietary wakame (Undaria pinnatifida) on growth, immunity and intestinal structure of juvenile Penaeus monodon. Aquaculture 435:78–85
Norambuena F, Hermon K, Skrzypczyk V, Emery JA, Sharon Y, Beard A, Turchini GM (2015) Algae in fish feed: performances and fatty acid metabolism in juvenile Atlantic Salmon. PLoS One 10:e0124042
Pereira R, Valente LMP, Sousa-Pinto I, Rema P (2012) Apparent nutrient digestibility of seaweeds by rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) and Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Algal Res 1:77–82
Peteiro C, Freire Ó (2011) Effect of water motion on the cultivation of the commercial seaweed Undaria pinnatifida in a coastal bay of Galicia, Northwest Spain. Aquaculture 314:269–276
Peteiro C, Sánchez N, Martínez B (2016) Mariculture of the Asian kelp Undaria pinnatifida and the native kelp Saccharina latissima along the Atlantic coast of Southern Europe: an overview. Algal Res 15:9–23
Pirarat N, Pinpimai K, Endo M, Katagiri T, Ponpornpisit A, Chansue N, Maita M (2011) Modulation of intestinal morphology and immunity in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) by Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG. Res Vet Sci 91:e92–e97
Ribeiro AR, Gonçalves A, Bandarra N, Nunes ML, Dinis MT, Dias J, Rema P (2017) Natural fortification of trout with dietary macroalgae and selenised-yeast increases the nutritional contribution in iodine and selenium. Food Res Int 99
Ribeiro AR, Gonçalves A, Colen R, Nunes ML, Dinis MT, Dias J (2015) Dietary macroalgae is a natural and effective tool to fortify gilthead seabream fillets with iodine: effects on growth, sensory quality and nutritional value. Aquaculture 437:51–59
Rodiles A, Herrera M, Hachero-Cruzado I, Ruiz-Jarabo I, Mancera JM, Cordero ML, Lall SP, Alarcón FJ (2014) Tissue composition, blood biochemistry and histology of digestive organs in Senegalese sole (Solea senegalensis) juveniles fed diets containing different plant protein ingredients. Aquac Nutr 21:767–779
Rodríguez HP, Rojas SM (2014) Effect of diets enriched with vitamin E and organic selenium on the productive performance and meat quality of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Rev Investig Vet Perú 25
Sánchez-Machado DI, López-Cervantes J, López-Hernández J, Paseiro-Losada P (2004) Fatty acids, total lipid, protein and ash contents of processed edible seaweeds. Food Chem 85:439–444
Schmid S, Ranz D, He ML, Burkard S, Lukowicz MY, reiter R, Arnold R, Le Deit H, David M, Rambeck WA (2003) Marine algae as natural source of iodine in the feeding of freshwater fish—a new possibility to improve iodine supply of man. Revue Méd Vét 154:645–648
Silva DM, Valente LMP, Sousa-Pinto I, Pereira R, Pires MA, Seixas F, Rema P (2015) Evaluation of IMTA-produced seaweeds (Gracilaria, Porphyra, and Ulva) as dietary ingredients in Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus L., juveniles. Effects on growth performance and gut histology J Appl Phycol 27:1s671–1680
Valente LM, Araújo M, Batista S, Peixoto MJ, Sousa-Pinto I, Brotas V, Cunha LM, Rema P (2016) Carotenoid deposition, flesh quality and immunological response of Nile tilapia fed increasing levels of IMTA-cultivated Ulva spp. J Appl Phycol 28:691–701
Valente LMP, Gouveia A, Rema P, Matos J, Gomes EF, Pinto IS (2006) Evaluation of three seaweeds Gracilaria bursa-pastoris, Ulva rigida and Gracilaria cornea as dietary ingredients in European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) juveniles. Aquaculture 252:85–91
Valente LMP, Linares F, Villanueva JLR, Silva JMG, Espe M, Escórcio C, Pires MA, Saavedra MJ, Borges P, Medale F, Alvárez-Blázquez B, Peleteiro JB (2011) Dietary protein source or energy levels have no major impact on growth performance, nutrient utilisation or flesh fatty acids composition of market-sized Senegalese sole. Aquaculture 318:128–137
Valente LMP, Rema P, Ferraro V, Pintado M, Sousa-Pinto I, Cunha LM, Oliveira MB, Araújo M (2015) Iodine enrichment of rainbow trout flesh by dietary supplementation with the red seaweed Gracilaria vermiculophylla. Aquaculture 446:132–139
Walker AB, Fournier HR, Neefus CD, Nardi GC, Berlinsky DL (2009) Partial replacement of fish meal with laver Porphyra spp. in diets for Atlantic cod. N Am J Aquac 71:39–45
Wassef EA, El-Sayed AFM, Kandeel KM, Sakr EM (2005) Evaluation of Pterocladia (Rhodophyta) and Ulva (Chlorophyta) meals as additives to gilthead seabream Sparus aurata diets. Egypt J Aquat Res 31:321–332
Wassef EA, El-Sayed A-FM, Sakr EM (2013) Pterocladia (Rhodophyta) and Ulva (Chlorophyta) as feed supplements for European seabass, Dicentrarchus labrax L., fry. J Appl Phycol 25:1369–1376
Wassef EA, El Masry MH, Mikhail FR (2001) Growth enhancement and muscle structure of striped mullet, Mugil cephalus L., fingerlings by feeding algal meal-based diets. Aquac Res 32:315–322
WHO (2007) Assessment of iodine deficiency disorders and monitoring their elimination: a guide for programme managers, 3rd edn. World Health Organization, Geneva
Yi Y-H, Chang Y-J (1994) Physiological effects of seamustard supplement diet on the growth and body composition of young rockfish Sebastes schlegeli. Bull Korean Fish Soc 27:69–82
Yildirim Ö, Ergün S, Yaman S, Türker A (2009) Effects of two seaweeds (Ulva lactuca and Enteromorpha linza) as a feed additive in diets on growth performance, feed utilization, and body composition of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Kafkas Univ Vet Fak Derg 15:455–460
Yone Y, Furuichi M, Urano K (1986a) Effects of dietary wakame Undaria penatifida and Ascophyllum nodosum supplements on growth, feed efficiency, and proximate composition of liver and muscle of red sea bream. Bull Jpn Soc Sci Fish 52:1465–1468
Yone Y, Furuichi M, Urano K (1986b) Effects of wakame Undaria pinnatifida and Ascophyllum nodosum on absorption of dietary nutrients, and blood sugar and plasma free amino-n levels of red sea bream. Bull Jpn Soc Sci Fish 52:1817–1819
Zhu D, Wen X, Xuan X, Li S, Li Y (2016) The green alga Ulva lactuca as a potential ingredient in diets for juvenile white spotted snapper Lutjanus stellatus Akazaki. J Appl Phycol 28:703–711
Zimmermann MB, Jooste PL, Pandav CS (2008) Iodine-deficiency disorders. Lancet 372:1251–1262
Funding
This study was partially supported by MARINALGAE4aqua “Improving bio-utilisation of marine algae as sustainable feed ingredients to increase efficiency and quality of aquaculture production” ERA-NET COFASP/004/2015 and by the Structured R&D&I Project INNOVMAR—Innovation and sustainability in the management and exploitation of marine resources (ref. NORTE-01-0145-FEDER-000035) within the research line “INSEAFOOD—Innovation and valorization of seafood products: meeting local challenges and opportunities”, founded by the Northern Regional Operational Programme (NORTE2020) through the European Regional Development Fund (ERDF).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moutinho, S., Linares, F., Rodríguez, J.L. et al. Inclusion of 10% seaweed meal in diets for juvenile and on-growing life stages of Senegalese sole (Solea senegalensis). J Appl Phycol 30, 3589–3601 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-018-1482-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-018-1482-6