Abstract
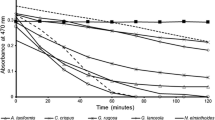
Nutrient composition, total phenolic content (TPC) and in vitro protein digestibility (IVPD) of wild and cultivated seaweeds were determined. Seaweeds had a high range of protein (7–31 % of dry weight (DW)), lipid (3–13 % DW), carbohydrate (32–60 % DW), ash (9–45 % DW) and energy (10–18 MJ kg−1 DW). Seaweeds had favourable amino acid (AA) profiles with moderate (0.77–0.86) to high (0.93–1.07) essential AA indices. Major minerals and trace elements included calcium (0.1–1.1 % DW), magnesium (0.2–0.8 % DW), phosphorous (0.1–0.6 % DW), potassium (2.1–4.6 % DW), sodium (1.1–3.9 % DW), sulphur (0.4–6.5 % DW), copper (1–21 mg kg−1 DW), iron (26–945 mg kg−1 DW), manganese (3–191 mg kg−1 DW) and zinc (28–74 mg kg−1 DW). Red seaweeds contained low TPC (4–5 mg gallic acid equivalents (GAE) g−1 DW) whereas most brown seaweeds contained moderate (11–18 mg GAE g−1 DW) to high levels (47–59 mg GAE g−1 DW). IVPD was mid-range (82–87 %) for Saccharina latissima, Palmaria palmata (W), Palmaria palmata (M-S), Chondrus crispus, Meristotheca papulosa and Sarcodiotheca gaudichaudii and lower (79 %) for Ascophyllum nodosum, Fucus vesiculosus and Alaria esculenta. Despite relatively good AA profiles, estimated digestible protein (DP) levels for seaweeds were generally low (<15 % DW) with exception of moderate levels (16–24 % DW) for P. palmata (W), P. palmata (M-S) and S. gaudichaudii. A highly significant inverse correlation (r = −0.81, R 2 = 0.83, P < 0.001) was found between TPC and IVPD of seaweeds (IVPD = 89.198 × TPC−0.035). The following species-specific nitrogen-to-protein conversion factors were determined: P. palmata (W), 6.28; P. palmata (M-S), 4.54; C. crispus, 4.85; S. gaudichaudii, 5.55.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Angell AR, Mata L, de Nys R, Paul NA (2016) The protein content of seaweeds: a universal nitrogen-to-protein conversion factor of five. J Appl Phycol 28:511–524
Barbarino E, Lourenço SO (2005) An evaluation of methods for extraction and quantification of protein from marine macro- and microalgae. J Appl Phycol 17:447–460
Becker EW (2007) Micro-algae as a source of protein. Biotechnol Adv 25:207–210
Bobin-Dubigeon C, Hoebler C, Lognone V, Dagorn-Scaviner C, Mabeau S, Barry JL, LaHaye M (1997) Chemical composition, physico-chemical properties, enzymatic inhibition and fermentative characteristics of dietary fibres from edible seaweeds. Sci Aliment 17:619–639
Brown MR, Jeffrey SW (1992) Biochemical composition of microalgae from the green algal classes Chlorophyceae and Prasinophyceae. 1. Amino acids, sugars and pigments. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 161:91–113
Brownlee IA, Allen A, Pearson JP, Dettmar PW, Havler ME, Atherton MR, Onsoyen E (2005) Alginate as a source of dietary fiber. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 45:497–510
Cherniack EP (2011) Polyphenols: planting the seeds of treatment for the metabolic syndrome. Nutrition 27:617–623
Chronakis IS (2000) Biosolar proteins from aquatic algae. Dev Food Sci 41:39–75
Diniz GS, Barbarino E, Oiano-Neto J, Pacheco S, Lourenço SO (2011) Gross chemical profile and calculation of nitrogen-to-protein conversion factors for five tropical seaweeds. Am J Plant Sci 2:287–296
Environmental Protection Agency (2007) Test methods for evaluating solid waste physical/chemical methods, methods EPA 6010C and 7471B
Fernández-Garcia E, Lérida-Carvajal I, Pérez-Gálvez A (2009) In vitro bioaccessibility assessment as a prediction tool of nutritional efficiency. Nutr Res 29:751–760
Fleurence J (1999a) Seaweed proteins: biochemical, nutritional aspects and potential uses. Trends Food Sci Technol 10:25–28
Fleurence J (1999b) The enzymatic degradation of algal cell walls: a useful approach for improving protein accessibility? J Appl Phycol 11:313–314
Fleurence J (2004) Seaweed proteins. In: Yada RY (ed) Proteins in food processing. Woodhead Publishing Limited, Cambridge, pp 197–213
Fleurence J, Le Couer C, Mabeau S, Maurice M, Landrein A (1995) Comparison of different extractive procedures for proteins from the edible seaweeds Ulva rigida and Ulva rotundata. J Appl Phycol 7:577–582
Food and Agriculture Organization (2014) The state of world fisheries and aquaculture 2014. Rome, Italy, 223 p
Fujiwara-Arasaki T, Mino N, Kuroda M (1984) The protein value in human nutrition of edible marine algae in Japan. Hydrobiologia 116:513–516
Galland-Irmouli AV, Fleurence J, Lamghari R, Luçon M, Rouxel C, Barbaroux O, Bronowicki JP, Villaume C, Guéant JL (1999) Nutritional value of proteins from edible seaweed Palmaria palmata (Dulse). J Nutr Biochem 10:353–359
Hafting JT, Craigie JS, Stengel DB, Loureiro RR, Buschmann AH, Yarish C, Edwards MD, Critchley AT (2015) Prospects and challenges for industrial production of seaweed bioactives. J Phycol 51:821–837
Harnedy PA, FitzGerald RJ (2011) Bioactive proteins, peptides, and amino acids from macroalgae. J Phycol 47:218–232
Holdt SL, Kraan S (2011) Bioactive compounds in seaweed: functional food applications and legislation. J Appl Phycol 23:543–597
Hsu HW, Vavak DL, Satterlee LD, Miller GA (1977) A multienzyme technique for estimating protein digestibility. J Food Sci 42:1269–1273
Ito K, Hori K (1989) Seaweed: chemical composition and potential food uses. Food Rev Int 5:101–144
Jamroz D, Orda J, Kamel C, Wiliczkiewicz A, Wertelecki T, Skorupinska J (2003) The influence of phytogenic extracts on performance, nutrient digestibility, carcass characteristics, and gut microbial status in broiler chickens. J Anim Feed Sci 12:583–596
Jimenez-Alvarez D, Giuffrida F, Vanrobaeys F, Golay PA, Cotting C, Lardeau A, Keely BJ (2008) High-throughput methods to assess lipophilic and hydrophilic antioxidant capacity of food extracts in vitro. J Agric Food Chem 56:3470–3477
Julkunen-Tiitto R (1985) Phenolic constituents in the leaves of Northern willows: methods for the analysis of certain phenolics. J Agric Food Chem 33:213–217
Kadam SU, Tiwari BK, O’Sonnell CP (2015) Extraction, structure and biofunctional activities of laminarin from brown algae. Int J Food Sci Technol 50:24–31
Króliczewska B, Miśta D, Zawadzki W, Wypchlo A, Króliczewski J (2011) Effects of a skullcap root supplement on haematology, serum parameters and antioxidant enzymes in rabbits on a high-cholesterol diet. J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr 95:114–124
Laurens LM, Dempster TA, Jones HDT, Wolfrum EJ, Van Wychen S, McAllister JSP, Rencenberger M, Parchert KJ, Gloe LM (2012) Algal biomass constituent analysis: method uncertainties and investigation of the underlying measuring chemistries. Anal Chem 84:1879–1887
Lourenço SO, Barbarino E, De-Paula JC, Pereira LO, Lanfer Marquez UM (2002) Amino acid composition, protein content and calculation of nitrogen-to-protein conversion factors for 19 tropical seaweeds. Phycol Res 50:233–241
Mabeau S, Fleurence J (1993) Seaweeds in food products: biochemical and nutritional aspects. Trends Food Sci Technol 4:103–107
MacArtain P, Gill CIR, Brooks M, Campbell R, Rowland IR (2007) Nutritional value of edible seaweeds. Nutr Rev 65:535–543
Maehre HK, Edvinsen GK, Eilertsen KE, Elvevoll EO (2016) Heat treatment increased the protein bioaccessibility in the red seaweed dulse (Palmaria palmata), but not in the brown seaweed winged kelp (Alaria esculenta). J Appl Phycol 28:581–590
Mariotti F, Tome D, Mirand PP (2008) Converting nitrogen into protein—beyond 6.25 and Jones’ factors. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 48:177–184
Marrion O, Fleurence J, Schwertz A, Guéant JL, Mamelouk L, Ksouri J, Villaume C (2005) Evaluation of protein in vitro digestibility of Palmaria palmata and Gracilaria verrucosa. J Appl Phycol 17:99–102
Marsham S, Scott GW, Tobin ML (2007) Comparison of nutritive chemistry of a range of temperate seaweeds. Food Chem 100:1331–1336
McDermid KJ, Stuercke B (2003) Nutritional composition of edible Hawaiian seaweeds. J Appl Phycol 15:513–524
McDonald P, Edwards RA, Greenhalgh JFD, Morgan CA, Sinclair LA (2010) Animal nutrition, 7th edn. Prentice Hall, New York, 692 p
Morris HJ, Almerales A, Carrillo O, Bermúdez RC (2008) Utilisation of Chlorella vulgaris cell biomass for the production of enzymatic protein hydrolysates. Bioresour Technol 99:7723–7729
Mossé J (1990) Nitrogen to protein conversion factor for ten cereals and six legumes or oilseeds. A reappraisal of its definition and determination. Variation according to species and to seed protein content. J Agric Food Chem 38:18–24
Naidu KA, Tewari A, Joshi HV, Viswanath S, Ramesh HP, Rao SV (1993) Evaluation of nutritional quality and food safety of seaweeds in India. J Food Saf 13:77–90
Oser BL (1951) Method for integrating essential amino acid content in the nutritional evaluation of protein. J Am Diet Assoc 27:396–402
Palmquist DL, Jenkins TC (2003) Challenges with fats and fatty acid methods. J Anim Sci 81:3250–3254
Ragan MA, Jensen A (1977) Quantitative studies on brown algal phenols. I. Estimation of absolute polyphenol content of Ascophyllum nodosum (L.) Le Jol. and Fucus vesiculosus (L.). J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 30:209–221
Rebours C, Marinho-Soriano E, Zertuche-González JA, Hayashi L, Vásquez JA, Kradolfer P, Soriano G, Ugarte R, Abreu MH, Bay-Larsen I, Hovelsrud G, Rødven R, Robledo D (2014) Seaweeds: an opportunity for wealth and sustainable livelihood for coastal communities. J Appl Phycol 26:1939–1951
Roesijadi G, Huesemann MH, Gill GA, Elliott DC, Magnuson JK (2011) Macroalgae as possible feedstock for biofuels production in the United States. 4th Congress of the International Society for Applied Phycology, Halifax, p 68
Rupérez P, Ahrazem O, Leal JA (2002) Potential antioxidant capacity of sulfated polysaccharides from the edible marine brown seaweed Fucus vesiculosus. J Agric Food Chem 50:840–845
Ryu HS, Satterlee LD, Lee KH (1982) Nitrogen conversion factors and in vitro protein digestibility of some seaweeds. Bull Korean Fish Soc 15:263–270
Shuuluka D, Bolton JJ, Anderson RJ (2013) Protein content, amino acid composition and nitrogen-to-protein conversion factors of Ulva rigida and Ulva capensis from natural populations and Ulva lactuca from an aquaculture system in South Africa. J Appl Phycol 25:677–685
Singleton VL, Orthofer R, Lamuela-Raventós RM (1999) Analysis of total phenols and other oxidation substrates and antioxidants by means of Folin-Ciocalteu reagent. In: Abelson JN, Simon MI (eds) Methods in enzymology. Academic Press, New York, pp 152–178
Sweeney T, Dillon S, Fanning J, Egan J, O’Shea CJ, Figat S, Gutierrez JJM, Mannion C, Leonard F, O’Doherty JV (2011) Evaluation of seaweed-derived polysaccharides on indices of gastrointestinal fermentation and selected populations of microbiota in newly weaned pigs challenged with Salmonella typhimurium. Anim Feed Sci Technol 165:85–94
Tibbetts SM, Milley JE, Lall SP (2015) Chemical composition and nutritional properties of freshwater and marine microalgal biomass cultured in photobioreactors. J Appl Phycol 27:1109–1119
Van Parys A, Boyen F, Dewulf J, Haesebrouck F, Pasmans F (2010) The use of tannins to control Salmonella typhimurium infection in pigs. Zoonoses Public Health 57:423–428
Velioglu YS, Mazza G, Gao L, Oomah BD (1998) Antioxidant activity and total phenolics in selected fruits, vegetables, and grain products. J Agric Food Chem 46:4113–4117
Venugopal V (2009) Seaweed: nutritional value, bioactive properties, and uses. In: Venugopal V (ed) Marine products for healthcare: functional and bioactive nutraceutical compounds from the ocean. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 261–295
Wong KH, Cheung PCK (2001) Nutritional evaluation of some subtropical red and green seaweeds. Part II—in vitro protein digestibility and amino acid profiles of protein concentrates. Food Chem 72:11–17
Yuan YV (2008) Marine algal constituents. In: Barrow C, Shahidi F (eds) Marine nutraceuticals and functional foods. CRC Press Inc., Boca Raton, pp 259–296
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Stephen O’Leary, Shawna MacKinnon, Laura Garrison and Neil Ross for providing valuable logistical and technical assistance and advice during this study and Drs. Alan Critchley and Arjun Banskota for reviewing a draft of this manuscript. We are grateful to Acadian Seaplants Limited for providing samples of P. palmata, M. papulosa and S. gaudichaudii for this study. This is NRCC publication no. 56186.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
This work was supported by the National Bioproducts Program (NBP), a collaborative agreement between Agriculture and Agri-Food Canada (AAFC), Natural Resources Canada (NRCan) and the National Research Council of Canada (NRCC).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tibbetts, S.M., Milley, J.E. & Lall, S.P. Nutritional quality of some wild and cultivated seaweeds: Nutrient composition, total phenolic content and in vitro digestibility. J Appl Phycol 28, 3575–3585 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-016-0863-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-016-0863-y