Abstract
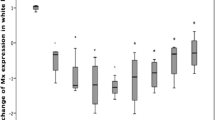
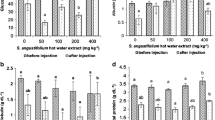
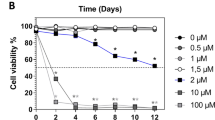
Red macroalgae (Phylum Rhodophyta) are considered to be an important source of biologically active metabolites; their use as functional feed ingredients in fish diets can increase disease resistance and animal growth. Furthermore, red macroalgae can be cultured in a sustainable and environmentally friendly manner. We evaluate the potential antiviral activity against the infectious salmon anemia (ISA) virus of Chilean red macroalgae as a sustainable feed additive in the Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) diet. Lyophilized Chilean red macroalgae concentrates were elaborated and added to a commercial diet. Diets were prepared with 0.1, 1.0, and 10.0 % of Gracilaria chilensis and Pyropia columbina separately, and 0.1 and 1.0 % of a mix of both species in a 1:1 ratio. The diets were fed to S. salar over a period of 2 months. We collected data on production parameters and blood samples. The serum and its constituents were challenged with the ISA virus in the presence of Atlantic salmon kidney cells and tested ex vivo for antiviral capacity using a plaque reduction neutralization assay. Fish fed a diet containing 10 % G. chilensis showed a significantly higher specific growth rate compared with fish fed the control diet. The feed conversion ratio was not significantly affected by treatments. Sera from fish fed the algae diets showed a significant increase in antiviral activity against the ISA virus compared with sera of fish fed the control diet that did not include red macroalgae. Diets including G. chilensis (1.0 and 10 %) exhibited the largest increase in antiviral activity.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arts MT, Kohler CC (2009) Health and condition in fish: the influence of lipids on membrane competency and immune response. In: Kainz M, Brett MT, Arts MT (eds) Lipids in aquatic ecosystems. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 237–256
Bell JG, Sargent JR (2003) Arachidonic acid in aquaculture feeds: current status and future opportunities. Aquaculture 218:491–499
Bourgougnon N, Lahaye M, Quemener B, Chermann J-C, Rimbert M, Cormaci M, Furnari G, Kornprobst J-M (1996) Annual variation in composition and in vitro anti-HIV-1 activity of the sulfated glucuronogalactan from Schizymenia dubyi (Rhodophyta, Gigartinales). J Appl Phycol 8:155–161
Buschmann AH, Correa JA, Westermeier R, del Carmen Hernandez-Gonzalez M, Norambuena R (2001) Red algal farming in Chile: a review. Aquaculture 194:203–220
Buschmann AH, del Carmen Hernandez-Gonzalez M, Varela D (2008) Seaweed future cultivation in Chile: perspectives and challenges. Int J Environ Pollut 33:432–456
Castell JD, Bell JG, Tocher DR, Sargent JR (1994) Effects of purified diets containing different combinations of arachidonic and docosahexaenoic acid on survival, growth and fatty acid composition of juvenile turbot (Scophthalmus maximus). Aquaculture 128:315–333
Collet B, Boudinot P, Benmansour A, Secombes CJ (2004) An Mx1 promoter–reporter system to study interferon pathways in rainbow trout. Dev Comp Immunol 28:793–801
Costas B, Conceição LE, Dias J, Novoa B, Figueras A, Afonso A (2011) Dietary arginine and repeated handling increase disease resistance and modulate innate immune mechanisms of Senegalese sole (Solea senegalensis Kaup, 1858). Fish Shellfish Immunol 31:838–847
Cottet L, Cortez-San Martin M, Tello M, Olivares E, Rivas-Aravena A, Vallejos E, Sandino AM, Spencer E (2010) Bioinformatic analysis of the genome of infectious salmon anemia virus associated with outbreaks with high mortality in Chile. J Virol 84:11916–11928
Dang VT, Li Y, Speck P, Benkendorff K (2011) Effects of micro and macroalgal diet supplementations on growth and immunity of greenlip abalone, Haliotis laevigata. Aquaculture 320:91–98
Dawczynski C, Schubert R, Jahreis G (2007) Amino acids, fatty acids, and dietary fibre in edible seaweed products. Food Chem 103:891–899
Divakaran S (2006) Taurine: an amino acid rich in fish meal. VIII Simposium Internacional de Nutricion Acuícola. Universidad Autónoma de Nuevo León, Monterrey, pp 15–17, ISBN970-694-333-5
Duarte ME, Cauduro JP, Noseda DG, Noseda MD, Gonçalves AG, Pujol CA, Damonte EB, Cerezo AS (2004) The structure of the agaran sulfate from Acanthophora spicifera (Rhodomelaceae, Ceramiales) and its antiviral activity. Relation between structure and antiviral activity in agarans. Carbohydr Res 339:335–347
El Gamal AA (2010) Biological importance of marine algae. Saudi Pharm J 18:1–25
Eliassen TM, Frøystad MK, Dannevig BH, Jankowska M, Brech A, Falk K, Romøren K, Gjøen T (2000) Initial events in infectious salmon anemia virus infection: evidence for the requirement of a low-pH step. J Virol 74:218–227
Feldman SC, Reynaldi S, Stortz CA, Cerezo AS, Damont EB (1999) Antiviral properties of fucoidan fractions from Leathesia difformis. Phytomedicine 6:335–340
Gonzalez R, Rodriguez S, Romay C, Ancheta O, González A, Armesto J, Remirez D, Merino N (1999) Anti-inflammatory activity of phycocyanin extract in acetic acid-induced colitis in rats. Pharmacol Res 39:55–59
Haller O, Staeheli P, Kochs G (2007) Interferon-induced Mx proteins in antiviral host defense. Biochimie 89:812–818
Kiron V (2012) Fish immune system and its nutritional modulation for preventive health care. Anim Feed Sci Technol 173:111–133
Lester K, Hall M, Urquhart K, Gahlawat S, Collet B (2012) Development of an in vitro system to measure the sensitivity to the antiviral Mx protein of fish viruses. J Virol Methods 182:1–8
Liland NS, Rosenlund G, Berntssen MHG, Brattelid T, Madsen L, Torstensen BE (2013) Net production of Atlantic salmon (FIFO, fish in fish out <1) with dietary plant proteins and vegetable oils. Aquac Nutr 19:289–300
MacArtain P, Gill CI, Brooks M, Campbell R, Rowland IR (2007) Nutritional value of edible seaweeds. Nutr Rev 65:535–543
Martinez-Rubio L, Morais S, Evensen Ø, Wadsworth S, Vecino JG, Ruohonen K, Bell JG, Tocher DR (2013) Effect of functional feeds on fatty acid and eicosanoid metabolism in liver and head kidney of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) with experimentally induced heart and skeletal muscle inflammation. Fish Shellfish Immunol 34:1533–1545
Matanjun P, Mohamed S, Mustapha NM, Muhammad K (2009) Nutrient content of tropical edible seaweeds, Eucheuma cottonii, Caulerpa lentillifera and Sargassum polycystum. J Appl Phycol 21:75–80
Midtbø LK, Ibrahim MM, Myrmel LS, Aune UL, Alvheim AR, Liland NS, Torstensen BE, Rosenlund G, Liaset B, Brattelid T, Kristiansen K, Madsen L (2013) Intake of farmed Atlantic salmon fed soybean oil increases insulin resistance and hepatic lipid accumulation in mice. PLoS ONE 8, e53094
Mohamed S, Hashim SN, Rahman HA (2012) Seaweeds: a sustainable functional food for complementary and alternative therapy. Trends Food Sci Technol 23:83–96
Morais S, Castanheira F, Martinez-Rubio L, Conceição LE, Tocher DR (2012) Long chain polyunsaturated fatty acid synthesis in a marine vertebrate: ontogenetic and nutritional regulation of a fatty acyl desaturase with Δ4 activity. Biochim Biophys Acta 1821:660–671
Morse ANC, Froyd CA, Morse DE (1984) Molecules from cyanobacteria and red algae that induce larval settlement and metamorphosis in the mollusc Haliotis rufescens. Mar Biol 81:293–298
Russell WC (1962) A sensitive and precise plaque assay for Herpes virus. Nature 195:1028–1029
Sakai DK (1992) Repertoire of complement in immunological defense mechanisms of fish. Annu Rev Fish Dis 2:223–247
Salze GP, Davis DA (2015) Taurine: a critical nutrient for future fish feeds. Aquaculture 437:215–229
Schaeffer DJ, Krylov VS (2000) Anti-HIV activity of extracts and compounds from algae and cyanobacteria. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 45:208–227
Schaeffler A, Gross P, Buettner R, Bollheimer C, Buechler C, Neumeier M, Kopp A, Schoelmerich J, Falk W (2009) Fatty acid-induced induction of toll-like receptor-4/nuclear factor-κB pathway in adipocytes links nutritional signalling with innate immunity. Immunology 126:233–245
Seaborn CD, Briske-Anderson M, Nielsen FH (2002) An interaction between dietary silicon and arginine affects immune function indicated by con-A-induced DNA synthesis of rat splenic T-lymphocytes. Biol Trace Elem Res 87:133–142
Seierstad SL, Seljeflot I, Johansen O, Hansen R, Haugen M, Rosenlund G, Frøyland L, Arnesen H (2005) Dietary intake of differently fed salmon; the influence on markers of human atherosclerosis. Eur J Clin Invest 35:52–59
Stokes WS, Brown K, Kulpa-Eddy J et al (2011) Improving animal welfare and reducing animal use for veterinary vaccine potency testing: state of the science and future directions. Procedia Vaccinol 5:84–105
Sweetman JW, Torrecillas S, Dimitroglou A, Rider S, Davies SJ, Izquieerdo MS (2010) Enhancing the natural defences and barrier protection of aquaculture species. Aquac Res 41:345–355
Tacchi L, Bickerdike R, Douglas A, Secombes CJ, Martin SAM (2011) Transcriptomic responses to functional feeds in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). Fish Shellfish Immunol 31:704–715
Tocher DR, Bell JG, Dick JR, Henderson RJ, McGhee F, Michell D, Morris PC (2000) Polyunsaturated fatty acid metabolism in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) undergoing parr-smolt transformation and the effects of dietary linseed and rapeseed oils. Fish Physiol Biochem 23:59–73
Toledo M, Avila M, Manríquez A, Olivares G, Soto P, Saavedra S, Zertuche J, Bai S (2009) Algas: Insumo alternativo para la alimentación de especies acuícolas. Pontificia Universidad Católica de Valparaiso, Valparaiso, pp 16–18, ISBN 978-956-17-0439-8
Torstensen BE, Bell JG, Rosenlund G, Henderson RJ, Graff IE, Tocher DR, Lie Ø, Sargent JR (2005) Tailoring of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) flesh lipid composition and sensory quality by replacing fish oil with a vegetable oil blend. J Agr Food Chem 53:10166–10178
Trichet VV (2010) Nutrition and immunity: an update. Aquac Res 41:356–372
Vo T-S, Ngo D-H, Ta QV, Kim S-K (2011) Marine organisms as a therapeutic source against herpes simplex virus infection. Eur J Pharm Sci 44:11–20
Watanuki H, Ota K, Tassakka ACMA, Kato T, Sakai M (2006) Immunostimulant effects of dietary Spirulina platensis on carp, Cyprinus carpio. Aquaculture 258:157–163
Zeng K, Xu H, Chen K, Zhu J, Zhou Y, Zhang Q, Mantian M (2010) Effects of taurine on glutamate uptake and degradation in Müller cells under diabetic conditions via antioxidant mechanism. Mol Cell Neurosci 45:192–199
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by BioMar Chile S.A. and Laboratorio de Genética y Biotecnología en Acuicultura, Producción Animal, Facultad de Ciencias Agronómicas, Universidad de Chile. The authors thank BioMar Castro experimental station researcher Victor Vidal for fish care and BioMar Chile S.A. R&D Salmon Division researcher Michael Adler for supervising the analytical work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lozano, I., Wacyk, J.M., Carrasco, J. et al. Red macroalgae Pyropia columbina and Gracilaria chilensis: sustainable feed additive in the Salmo salar diet and the evaluation of potential antiviral activity against infectious salmon anemia virus. J Appl Phycol 28, 1343–1351 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-015-0648-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-015-0648-8