Abstract
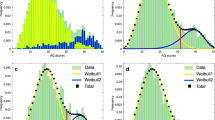
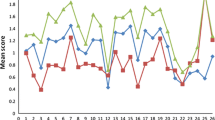
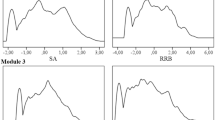
In the present study, factor mixture models (FMMs) were used to examine the latent structure underlying the Autism-Spectrum Quotient (AQ) among a sample of 633 undergraduate students. FMM represents a combination of latent-class, person-centered approaches and common-factor, variable-centered approaches to modeling population heterogeneity. Findings suggest the presence of either two or six latent classes with distinct profiles across the set of 50 AQ items. In addition, within each class, individuals can be further differentiated according to their scores on five latent factors. These results suggest the presence of phenotypical heterogeneity at the sub-clinical level in addition to that which is known to exist at the clinical level.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asparouhov, T., & Muthén, B. (2012). Using Mplus TECH11 and TECH14 to test the number of latent classes (Mplus Web Notes No. 14), 1–17.
Austin, E. J. (2005). Personality correlates of the broader autism phenotype as assessed by the Autism-Spectrum Quotient (AQ). Personality and Individual Differences, 38(2), 451–460.
Baron-Cohen, S., Wheelwright, S., Skinner, R., Martin, J., & Clubley, E. (2001). The Autism-Spectrum Quotient (AQ): Evidence from Asperger syndrome/high functioning autism, males and females, scientists and mathematicians. Journal of Autism Developmental Disorders, 31(1), 5–17.
Clark, S. L., Muthén, B., Kaprio, J., D’Onofrio, B. M., Viken, R., & Rose, R. J. (2013). Models and strategies for factor mixture analysis: An example concerning the structure underlying psychological disorders. Structural Equation Modeling, 20, 681–703.
Gallitto, E., & Leth-Steensen, C. (2015). Autistic traits and adult attachment styles. Personality and Individual Differences, 79, 63–67.
Grove, R., Baillie, A., Allison, C., Baron-Cohen, S., & Hoekstra, R. A. (2015). Exploring the quantitative nature of empathy, systemising and autistic traits using factor mixture modelling. The British Journal of Psychiatry, 207(5), 400–406.
Hirota, T., Deserno, M., & McElroy, E. (2020). The network structure of irritability and aggression in individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorder. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 50, 1210–1220.
Hoekstra, R. A., Bartels, M., Cath, D. C., & Boomsma, D. I. (2008). Factor structure, reliability, and criterion validity of the Autism Spectrum Quotient (AQ): A study in Dutch population and patient groups. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 38, 1555–1566.
Hurley, R. S., Losh, M., Parlier, M., Reznick, J. S., & Piven, J. (2007). The broad autism phenotype questionnaire. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 37, 1679–1690.
Hurst, R. M., Mitchell, J. T., Kimbrel, N. A., Kwapil, T. K., & Nelson-Gray, R. O. (2007). Examination of the reliability and factor structure of the Autism Spectrum Quotient (AQ) in a non-clinical sample. Personality and Individual Differences, 43, 1938–1949.
James, R. J. E., Dubey, I., Smith, D., Ropar, D., & Tunney, R. J. (2016). The latent structure of autistic traits: A taxometric, latent class and latent profile analysis of the adult Autism Spectrum Quotient. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 46, 3712–3728.
Kloosterman, P. H., Keefer, K. V., Kelley, E. A., Summerfeldt, L. J., & Parker, J. D. (2011). Evaluation of the factor structure of the Autism-Spectrum Quotient. Personality and Individual Differences, 50(2), 310–314.
Lai, M-C., Lomobardo, M. V., Chakrabarti, B., & Baron-Cohen, S. (2013). Subgrouping the autism “spectrum”: Reflections on DSM-5. PLoS Biology, 11, e1001544.
Lau, W. Y. P., Kelly, A. B., & Peterson, C. C. (2013). Further evidence on the factorial structure of the Autism Spectrum Quotient (AQ) with and without a clinical diagnosis of Autism. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 43, 2807–2815.
Liss, M., Mailloux, J., & Erchull, M. J. (2008). The relationships between sensory processing sensitivity, alexithymia, autism, depression, and anxiety. Personality and Individual Differences, 45(3), 255–259.
Lubke, G. H., & Muthén, B. (2005). Investigating population heterogeneity with factor mixture models. Psychological Methods, 10(1), 21–39.
Lubke, G. H., & Muthén, B. (2007). Performance of factor mixture models as a function of model size, covariate effects, and class-specific paramters. Structural Equation Modeling, 14(1), 26–47.
Meade, A. W., & Craig, S. B. (2012). Identifying careless responses in psychological data. Psychological Methods, 17, 437–455.
Miettunen, J., Nordström, T., Kaakinen, M., & Ahmed, A. O. (2016). Latent variable mixture modeling in psychiatric research—A review and application. Psychological Medicine, 46(3), 457–467.
Mintah, K. (2011). Autistic traits hamper casual romantic experiences, but do not preclude committed relationships (Unpublished undergraduate thesis). Carleton University, Ottawa, ON, Canada.
Mintah, K. (2014). I cannot see it in their eyes: How autism symptoms hamper dating (Unpublished master’s thesis). Carleton University, Ottawa, ON, Canada.
Morin, A. J. S., Morizot, J., Boudrias, J-S., & Madore, I. (2011). A multi-foci person-centered perspective on workplace commitment: A latent profile/factor mixture analysis. Organizational Research Methods, 14(1), 58–90.
Nyland, K. L., Asparouhov, T., & Muthén, B. (2007). Deciding on the number of classes in latent class analysis and growth mixture modeling: A Monte Carlo simulation study. Structural Equation Modeling, 14(4), 535–569.
Palmer, C. J., Paton, B., Enticott, P. G., & Hohwy, J. (2015). ‘Subtypes’ in the presentation of autistic traits in the general adult population. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 45(5), 1291–1301.
Ring, H., Woodbury-Smith, M., Watson, P., Wheelwright, S., & Baron-Cohen, S. (2008). Clinical heterogeneity among people with high functioning autism spectrum conditions: Evidence favouring a continuous severity gradient. Behavioural and Brain Functions, 4, 11.
Ruzich, E., Allison, C., Smith, P., Watson, P., Auyeung, B., Ring, H., et al. (2015). Measuring autistic traits in the general population: A systematic review of the Autism-Spectrum Quotient (AQ) in a nonclinical population sample of 6,900 typical adult males and females. Molecular Autism, 6(1), 1.
Stewart, M. E., & Austin, E. J. (2009). The structure of the Autism-Spectrum Quotient (AQ): Evidence from a student sample in Scotland. Personality and Individual Differences, 47(3), 224–228.
Wakabayashi, A., Baron-Cohen, S., & Wheelwright, S. (2006). Are autistic traits an independent personality dimension? A study of the Autism-Spectrum Quotient (AQ) and the NEO-PI-R. Personality and Individual Differences, 41(5), 873–883.
Wheelwright, S., Baron-Cohen, S., Goldenfeld, N., Delaney, J., Fine, D., Smith, R., et al. (2006). Predicting autism spectrum quotient (AQ) from the systemizing quotient-revised (SQ-R) and empathy quotient (EQ). Brain Research, 1079(1), 47–56.
Woodbury-Smith, M. R., Robinson, J., Wheelwright, S., & Baron-Cohen, S. (2005). Screening adults for Asperger syndrome using the AQ: A preliminary study of its diagnostic validity in clinical practice. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 35(3), 331–335.
Funding
The authors did not receive any specific funding for this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Leth-Steensen and Gallitto provided half ot the data, ran the analyses, and were mainly responsible for writing up the manuscript. Mintah and Parlow provided the other half of the data in addition to helpful consultation and insight during the witing stage.
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Leth-Steensen, C., Gallitto, E., Mintah, K. et al. Testing the Latent Structure of the Autism Spectrum Quotient in a Sub-clinical Sample of University Students Using Factor Mixture Modelling. J Autism Dev Disord 51, 3722–3732 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-020-04823-7
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-020-04823-7