Abstract
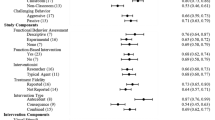
Challenging behavior is a significant barrier in accessing the general education curriculum for students with developmental disabilities. This necessitates the identification of evidence-based practices for addressing challenging behavior in inclusive settings. The purpose of our meta-analysis is to (a) quantify the magnitude of effect of interventions targeting the reduction of challenging behavior in students with developmental disabilities in inclusive educational settings and (b) determine if participant and intervention characteristics moderate intervention effects. A systematic search of academic databases was conducted to identify studies, which were evaluated for methodological rigor and analyzed for effects using Tau-U. Results indicate a strong overall effect of .94 (95% CI [.87, 1]) and moderating variables associated with behavior topography, interventionist, and intervention components were identified.

Adopted from The PRISMA Group (2009)
Similar content being viewed by others
References
References marked with an asterisk indicate studies included in the meta-analysis.
* Banda, D. R., & Sokolosky, S. (2012). Effectiveness of noncontingent attention to behaviors in the general education classroom. Child and Family Behavior Therapy, 34(2), 130–140. https://doi.org/10.1080/07317107.2012.684646
* Bennett, K., Reichow, B., & Wolery, M. (2011). Effects of structured teaching on the behavior of young children with disabilities. Focus on Autism and Other Developmental Disabilities, 26(3), 143–152. https://doi.org/10.1177/1088357611405040
* Blair, K.-S. C., Fox, L., & Lentini, R. (2010). Use of positive behavior support to address the challenging behavior of young children within a community early childhood program. Topics in Early Childhood Special Education, 30(2), 68–79. https://doi.org/10.1177/0271121410372676
* Blair, K.-S. C., Umbreit, J., Dunlap, G., & Jung, G. (2007). Promoting inclusion and peer participation through assessment-based intervention. Topics in Early Childhood Special Education, 27(3), 134–147. https://doi.org/10.1177/02711214070270030401
* Crozier, S., & Tincani, M. (2007). Effects of social stories on prosocial behavior of preschool children with autism spectrum disorders. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 37(9), 1803–1814. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-006-0315-7
* Haley, J. L., Heick, P. F., & Luiselli, J. K. (2010). Use of an antecedent intervention to decrease vocal stereotypy of a student with autism in the general education classroom. Child & Family Behavior Therapy, 32(4), 311–321. https://doi.org/10.1080/07317107.2010.515527
* Ozdemir, S. (2008). The effectiveness of social stories on decreasing disruptive behaviors of children with autism: Three case studies. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 38(9), 1689–1696. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-008-0551-0
Andzik, N. R., Cannella-Malone, H. I., & Sigafoos, J. (2016). Practitioner-implemented functional communication training: A review of the literature. Research and Practice for Persons with Severe Disabilities,41(2), 79–89. https://doi.org/10.1177/1540796916633874.
* Arceneaux, M. C., & Murdock, J. Y. (1997). Peer prompting reduces disruptive vocalizations of a student with developmental disabilities in a general eighth-grade classroom. Focus on Autism and Other Developmental Disabilities, 12(3), 182–186.
* Blair, K.-S. C., Liaupsin, C. J., Umbreit, J., & Kweon, G. (2006). Function-based intervention to support the inclusive placements of young children in Korea. Education and Training in Developmental Disabilities, 41(1), 48–57.
Borenstein, M., Hedges, L. V., Higgins, J. P. T., & Rothstein, H. R. (2011). Introduction to meta-analysis. Chichester: Wiley.
Boulet, S. L., Boyle, C. A., & Schieve, L. A. (2009). Health care use and health and functional impact of developmental disabilities among US children, 1997–2005. Archives of Pediatrics and Adolescent Medicine,163(1), 19–26. https://doi.org/10.1001/archpediatrics.2008.506.
Carr, E. G., & Durand, V. M. (1985). Reducing behaviour problems through functional communication training. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis,18(2), 111–126.
Council for Exceptional Children. (2014). Council for exceptional children standards for evidence-based practices in special education. Exceptional Children,80(4), 504–511.
Dart, E. H., Radley, K. C., Mason, B. A., & Allen, J. P. (2018). Addressing escape-maintained behavior for students with developmental disabilities: A systematic review of school-based interventions. Psychology in the Schools,55(3), 295–304. https://doi.org/10.1002/pits.22108.
Davis, K., & Gavidia-Payne, S. (2009). The impact of child, family, and professional support characteristics on the quality of life in families of young children with disabilities. Journal of Intellectual and Developmental Disability,34(2), 153–162. https://doi.org/10.1080/13668250902874608.
Dunlap, G., & Carr, E. G. (2007). Positive behavior support and developmental disabilities: A summary and analysis of research. In S. L. Odom, et al. (Eds.), Handbook of developmental disabilities (pp. 469–482). New York: Guilford Press.
Dunlap, G., Iovannone, R., Wilson, K. J., Kincaid, D. K., & Strain, P. (2010). Prevent-teach-reinforce: A standardized model of school-based behavioral intervention. Journal of Positive Behavior Interventions,12(1), 9–22. https://doi.org/10.1177/1098300708330880.
Dunn, O. J. (1964). Multiple comparisons using rank sums. Technometrics,6(3), 241–252.
Emerson, E. (2003). Prevalence of psychiatric disorders in children and adolescents with and without intellectual disability. Journal of Intellectual Disability Research,47(1), 51–58.
Emerson, E., Kiernan, C., Alborz, A., Reeves, D., Mason, H., Swarbrick, R., … Hatton, C. (2001). The prevalence of challenging behaviors: A total population study. Research in Developmental Disabilities, 22(1), 77–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0891-4222(00)00061-5
Every Student Succeeds Act, Pub. L. No. 114-95, § 1177 Stat. (2015).
Frea, W., Arnold, C. L., & Vittimberga, G. L. (2001). A demonstration of the effects of augmentative communication on the extensive aggressive behaviour of a child with autism within an integrated pre school setting. Journal of Positive Behaviour Interventions,3(4), 194–198.
Gage, N. A., Cook, B. G., & Reichow, B. (2017). Publication bias in special education meta-analyses. Exceptional Children,83(4), 428–445. https://doi.org/10.1177/0014402917691016.
Gavaldá, J. M. S., & Qinyi, T. (2012). Improving the process of inclusive education in children with ASD in mainstream schools. Procedia—Social and Behavioral Sciences,46, 4072–4076. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2012.06.200.
Goh, A. E., & Bambara, L. M. (2012). Individualized positive behavior support in school settings: A meta-analysis. Remedial and Special Education,33(5), 271–286. https://doi.org/10.1177/0741932510383990.
Green, V. A., O’Reilly, M., Itchon, J., & Sigafoos, J. (2005). Persistence of early emerging aberrant behavior in children with developmental disabilities. Research in Developmental Disabilities,26(1), 47–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ridd.2004.07.003.
Hart, S. L., & Banda, D. R. (2010). Picture exchange communication system with individuals with developmental disabilities: A meta-analysis of single subject studies. Remedial and Special Education,31(6), 476–488. https://doi.org/10.1177/0741932509338354.
Higgins, J. P. T., & Thompson, S. G. (2002). Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Statistics in Medicine,21(11), 1539–1558. https://doi.org/10.1002/sim.1186.
Horner, R. H., Carr, E. G., Strain, P. S., Todd, A. W., & Reed, H. K. (2002). Problem behavior interventions for young children with autism: A research synthesis. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders,32(5), 423–446. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1020593922901.
Individuals with Disabilities Education Improvement Act, 20 U.S.C. § 1400 (2004).
Ingram, K., Lewis-Palmer, T., & Sugai, G. (2005). Function-based intervention planning: Comparing the effeciveness of FBA function-based and non-funcion-based intervenion plans. Journal of Positive Behavior Interventions,7(4), 224–236. https://doi.org/10.1177/10983007050070040401.
Kennedy, C. H., Cushing, L. S., & Itkonen, T. (1997). General education participation improves the social contacts and friendship networks of students with severe disabilities. Journal of Behavioral Education,7(2), 167–189. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1022888924438.
Knight, V., Sartini, E., & Spriggs, A. D. (2014). Evaluating visual activity schedules as evidence-based practice for individuals with autism spectrum disorders. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders,45(1), 157–178. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-014-2201-z.
Koegel, L. K., Vernon, T. W., Koegel, R. L., Koegel, B. L., & Paullin, A. W. (2012). Improving social engagement and initiations between children with autism spectrum disorder and their peers in inclusive settings. Journal of Positive Behavior Interventions,14(4), 220–227. https://doi.org/10.1177/1098300712437042.
Koyama, T., & Wang, H. T. (2011). Use of activity schedule to promote independent performance of individuals with autism and other intellectual disabilities: A review. Research in Developmental Disabilities,32(6), 2235–2242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ridd.2011.05.003.
Kratochwill, T. R., Hitchcock, J., Horner, R. H., Levin, J. R., Odom, S. L., Rindskopf, D. M., & Shadish, W. R. (2010). Single-case designs technical documentation. Single-Case Designs Technical Documentation.
Kratochwill, T. R., Hitchcock, J. H., Horner, R. H., Levin, J. R., Odom, S. L., Rindskopf, D. M., et al. (2013). Single-case intervention research design standards. Remedial and Special Education,34(1), 26–38. https://doi.org/10.1177/0741932512452794.
Kruskal, W. H., & Wallis, W. A. (1952). Use of ranks in one-criterion variance analysis. Journal of the American Statistical Association,47(260), 583–621. https://doi.org/10.1080/01621459.1952.10483441.
Kurth, J., & Mastergeorge, A. M. (2010). Individual Education Plan goals and services for adolescents with autism: Impact of age and educational setting. The Journal of Special Education,44(3), 146–160. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022466908329825.
Kurtz, P. F., Boelter, E. W., Jarmolowicz, D. P., Chin, M. D., & Hagopian, L. P. (2011). An analysis of functional communication training as an empirically supported treatment for problem behavior displayed by individuals with intellectual disabilities. Research in Developmental Disabilities,32(6), 2935–2942. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ridd.2011.05.009.
Lancioni, G. E., O’Reilly, M. F., Cuvo, A. J., Singh, N. N., Sigafoos, J., & Didden, R. (2007). PECS and VOCAs to enable students with developmental disabilities to make requests: An overview of the literature. Research in Developmental Disabilities,28(5), 468–488. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ridd.2006.06.003.
Lecavalier, L., Leone, S., & Wiltz, J. (2006). The impact of behaviour problems on caregiver stress in young people with autism spectrum disorders. Journal of Intellectual Disability Research,50(3), 172–183. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2788.2005.00732.x.
* Lee, S., & Odom, S. L. (1996). The relationship between stereotypic behavior and peer social interaction for children with severe disabilities. Research and Practice for Persons with Severe Disabilities, 21(2), 88–95. https://doi.org/10.1177/154079699602100204
Lequia, J., MacHalicek, W., & Rispoli, M. J. (2012). Effects of activity schedules on challenging behavior exhibited in children with autism spectrum disorders: A systematic review. Research in Autism Spectrum Disorders,6(1), 480–492. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rasd.2011.07.008.
Lloyd, B. P., & Kennedy, C. H. (2014). Assessment and treatment of challenging behaviour for individuals with intellectual disability: A research review. Journal of Applied Research in Intellectual Disabilities,27(3), 187–199. https://doi.org/10.1111/jar.12089.
Lohrmann, S., & Bambara, L. M. (2006). Elementary education teachers’ beliefs about essential supports needed o successfully include students with developmental disabilities who engage in challenging behaviors. Research & Practice for Persons with Severe Disabilities,31(2), 157–173.
Maggin, D. M., Chafouleas, S. M., Goddard, K. M., & Johnson, A. H. (2011). A systematic evaluation of token economies as a classroom management tool for students with challenging behavior. Journal of School Psychology,49(5), 529–554. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsp.2011.05.001.
* Mancil, G. R., Haydon, T., & Whitby, P. (2009). Differentiated effects of paper and computer-assisted social stories on inappropriate behavior in children with autism. Focus on Autism and Other Developmental Disabilities, 24(4), 205-215. https://doi.org/10.1177/1088357609347324
Martinez, J. R., Werch, B. L., & Conroy, M. A. (2016). School-based interventions targeting challenging behaviors exhibited by young children with autism spectrum disorder: A systematic literature review. Education and Training in Autism and Developmental Disabilities,51(3), 265–280.
Matson, J. L., Belva, B., Hattier, M. A., & Matson, M. L. (2011). Pica in persons with developmental disabilities: Characteristics, diagnosis, and assessment. Research in Autism Spectrum Disorders,5(4), 1459–1464. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rasd.2011.02.006.
Matson, J. L., Gardner, W. I., Coe, D. A., & Sovner, R. (1991). A scale for evaluating emotional disorders in severely and profoundly mentally retarded persons: Development of the diagnostic assessment for the severely handicapped (DASH) scale. British Journal of Psychiatry,159, 404–409.
Matson, J. L., & Neal, D. (2009). Psychotropic medication use for challenging behaviors in persons with intellectual disabilities: An overview. Research in Developmental Disabilities,30(3), 572–586. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ridd.2008.08.007.
Matson, J. L., & Nebel-Schwalm, M. (2007). Assessing challenging behaviors in children with autism spectrum disorders: A review. Research in Developmental Disabilities,28(6), 567–579. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ridd.2006.08.001.
Mazaleski, J. L., Iwata, B. A., Vollmer, T. R., Zarcone, J. R., & Smith, R. G. (1993). Analysis of the reinforcement and extinction components in DRO contingencies with self-injury. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis,26(2), 143–156.
McCahill, J., Healy, O., Lydon, S., & Ramey, D. (2014). Training educational staff in functional behavioral assessment: A systematic review. Journal of Developmental and Physical Disabilities,26, 479–505. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10882-014-9378-0.
* McCurdy, E. E., & Cole, C. L. (2014). Use of a peer support intervention for promoting academic engagement of students with autism in general education settings. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 44(4), 883–893. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-013-1941-5
McDonald, T. A., & Machalicek, W. (2013). Systematic review of intervention research with adolescents with autism spectrum disorders. Research in Autism Spectrum Disorders,7(11), 1439–1460. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rasd.2013.07.015.
McLeskey, J., Landers, E., Williamson, P., & Hoppey, D. (2012). Are we moving toward educating students with disabilities in less restrictive settings? Journal of Special Education,46(3), 131–140. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022466910376670.
Morningstar, M. E., Kurth, J. A., & Johnson, P. E. (2017). Examining national trends in educational placements for students with significant disabilities. Remedial and Special Education,38(1), 3–12. https://doi.org/10.1177/0741932516678327.
Myrbakk, E., & von Tetzchner, S. (2008). Psychiatric disorders and behavior problems in people with intellectual disability. Research in Developmental Disabilities,29(4), 316–332. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ridd.2007.06.002.
Newcomb, E. T., & Hagopian, L. P. (2018). Treatment of severe problem behaviour in children with autism spectrum disorder and intellectual disabilities. International Review of Psychiatry,30(1), 96–109. https://doi.org/10.1080/09540261.2018.1435513.
Ninci, J., Rispoli, M., Burke, M. D., & Neely, L. C. (2017). Embedding interests of individuals with autism spectrum disorder: A quality review. Review Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders,5, 15–28. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40489-017-0120-6.
Parker, R. I., & Vannest, K. (2009). An improved effect-size for single-case research: Nonoverlap of all pairs. Behavior Therapy,40(4), 357–367. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.beth.2008.10.006.
Parker, R. I., Vannest, K. J., Davis, J. L., & Sauber, S. B. (2011). Combining nonoverlap and trend for single-case research: Tau-U. Behavior Therapy,42(2), 284–299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.beth.2010.08.006.
Polanin, J. R., Tanner-Smith, E. E., & Hennessy, E. A. (2016). Estimating the difference between published and unpublished effect sizes: A meta-review. Review of Educational Research,86(1), 207–236. https://doi.org/10.3102/0034654315582067.
Reeves, L. M., Umbreit, J., Ferro, J. B., & Liaupsin, C. J. (2017). The role of the replacement beahvior in function-based intervention. Education and Training in Autism and Developmental Disabilities,52(3), 305–316.
Reitman, D., Murphy, M. A., Hupp, S. D. A., & O’Callaghan, P. M. (2004). Behavior change and perceptions of change: Evaluating the effectiveness of a token economy. Child & Family Behavior Therapy,26(2), 17–36. https://doi.org/10.1300/j019v26n02.
Roberts, C., Mazzucchelli, T., Taylor, K., & Reid, R. (2003). Early intervention for behaviour problems in young children with developmental disabilities. International Journal of Disability, Development and Education,50(3), 275–291. https://doi.org/10.1080/1034912032000120453.
Rohatgi, A. (2017). WebPlotDigitizer (Version 3). [Computer software]. Retrieved from https://automeris.io/WebPlotDigitizer
Ryndak, D. L., Taub, D., Jorgensen, C. M., Gonsier-Gerdin, J., Arndt, K., Sauer, J., … Allcock, H. (2014). Policy and the impact on placement, involvement, and progress in general education: Critical issues that require rectification. Research and Practice for Persons with Severe Disabilities, 39(1), 65–74. https://doi.org/10.1177/1540796914533942
Scruggs, T. E., Mastropieri, M. A., & Casto, G. (1987). The quantitative synthesis of single-subject research: Methodology and validation. RASE: Remedial & Special Education,8(2), 24–33.
Sigafoos, J. (2000). Communication development and aberrant behavior in children with developmental disabilities. Education and Training in Autism and Developmental Disabilities,35(2), 168–176.
Simonoff, E., Pickles, A., Charman, T., Chandler, S., Loucas, T., & Baird, G. (2008). Psychiatric disorders in children with autism spectrum disorders: Prevalence, comorbidity, and associated factors in a population-derived sample. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry,47(8), 921–929. https://doi.org/10.1097/chi.0b013e318179964f.
* Taylor, B. A., Hoch, H., & Weissman, M. (2005). The analysis and treatment of vocal stereotypy in a child with autism. Behavioral Interventions, 20(4), 239–253. https://doi.org/10.1002/bin.200.
Tiger, J. H., Fisher, W. W., & Bouxsein, K. J. (2009). Therapist- and self-monitored DRO contingencies as a treatment for the self-injurious skin picking of a young man with Asperger syndrome. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis,42(2), 315–319. https://doi.org/10.1901/jaba.2009.42-315.
Tiger, J. H., Hanley, G. P., & Bruzek, J. (2008). Functional communication training: a review and practical guide. Behavior Analysis in Practice,1(1), 16–23.
Tillery, A. D., Varjas, K., Meyers, J., & Collins, A. S. (2010). General education teachers’ perceptions of behavior management and intervention strategies. Journal of Positive Behavior Interventions,12(2), 86–102. https://doi.org/10.1177/1098300708330879.
Trussell, R. P., Chen, H. J., Lewis, T. J., & Luna, N. E. (2018). Reducing escape-maintained behavior through the application of classroom-wide practices and individually designed interventions. Education and Treatment of Children,41(4), 507–531.
* Umbreit, J. (1995). Functional analysis of disruptive behavior in an inclusive classroom. Journal of Early Intervention, 20(1), 18–29.
U.S. Department of Education, National Center for Education Statistics. (2017). The Digest of Education Statistics, 2016 (NCES 2017–094). Retrieved from https://nces.ed.gov/fastfacts/display.asp?id=59
U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. (2015). Estimated prevalence of autism and oher developmental disabilities following questionnaire changes in the 2014 National Health Interview Survey. National Health Statistics Reports. https://doi.org/10.1021/jo901424v.
Wacker, D. P., Steege, M. W., Northup, J., Sasso, G., Berg, W., Reimers, T., … Donn, L. (1990). A component analysis of functional communication training across three different topographies of severe behavior problems. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 23(4), 417–429.
Walker, V. L., Chung, Y. C., & Bonnet, L. K. (2018). Function-based intervention in inclusive school settings: A meta-analysis. Journal of Positive Behavior Interventions,20(4), 203–216. https://doi.org/10.1177/1098300717718350.
Warren, J. S., Bohanon-Edmonson, H. M., Turnbull, A. P., Sailor, W., Wickham, D., Griggs, P., et al. (2006). School-wide positive behavior support: Addressing behavior problems that impede student learning. Educational Psychology Review,18(2), 187–198. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10648-006-9008-1.
Waters, M. B., Lerman, D. C., & Hovanetz, A. N. (2009). Separate and combined effects of visual schedules and extinction plus differential reinforcement on problem behavior occasioned by transitions. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis,42(2), 309–313. https://doi.org/10.1901/jaba.2009.42-309.
Watkins, L., Ledbetter-cho, K., O’Reilly, M., Barnard-Brak, L., & Garcia-Grau, P. (2019). Interventions for students with autism in inclusive setings: A best-evidence synthesis and meta-analysis. Psychological Bulletin,145(5), 490–507.
Wilcoxon, F. (1945). Individual comparisons by ranking methods. Biometrics Bulletin,1(6), 80–83. https://doi.org/10.1093/jee/39.2.269.
Wong, C., Odom, S. L., Hume, K. A., Cox, A. W., Fettig, A., Kucharczyk, S., … Schultz, T. R. (2015). Evidence-based practices for children, youth, and young adults with autism spectrum disorder: A comprehensive review. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 45(7), 1951–1966. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-014-2351-z
Yell, M. L. (2019). The law and special education (5th ed.). New York: Pearson.
Zablotsky, B., Black, L. I., & Blumberg, S. J. (2017). Estimated prevalence of children with diagnosed developmental disabilities in the United States 2014–2016. NCHS Data Brief,291, 1–8.
* Zimmerman, K. N., Ledford, J. R., & Barton, E. E. (2017). Using visual activity schedules for young children with challenging behavior. Journal of Early Intervention, 39(4), 339–358. https://doi.org/10.1177/1053815117725693
Funding
No funding was received for this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CL conceived of and designed the study. RAM participated in the design of the study. CL and RAM acquired the data. DW assisted in acquiring the descriptive, qualitative, and quantitative data. MD assisted in acquiring the descriptive data. JLD performed the statistical analyses. CL drafted the manuscript. RAM, JLD, SYK, and EG assisted in revising the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they no conflicts of interest.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in this study did not involve human participants.
Informed Consent
No informed consent was necessary for the completion of this study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lory, C., Mason, R.A., Davis, J.L. et al. A Meta-analysis of Challenging Behavior Interventions for Students with Developmental Disabilities in Inclusive School Settings. J Autism Dev Disord 50, 1221–1237 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-019-04329-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-019-04329-x