Abstract
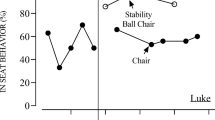
Children with ASD often display behavior problems that can lead to academic and social disruptions. This has led to the introduction of stability balls as an alternative seating method for children, both on the autism spectrum and with other needs. This study used a multiple baseline design and duration data to evaluate the effects of stability ball seating on attending and in-seat behavior for children with ASD who received ABA therapy in their homes. The intervention replaced their standard seating method with a stability ball. In the final phase participants chose their own seating method before beginning table work to assess preference. Following intervention the stability ball was found to increase both attending and in-seat durations for children with ASD.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Eisa, E., Buragadda, S., & Melam, G. (2013). Effect of therapy ball seating on learning and sitting discomforts among Saudi female students. BioMed Research International,2013, 1–4.
Bagatell, N., Mirigliani, G., Patterson, C., Reyes, Y., & Test, L. (2010). Effectiveness of therapy ball chairs on classroom participation in children with autism spectrum disorders. American Journal of Occupational Therapy,64, 895–903.
Fedewa, A., & Erwin, H. (2011). Stability balls and students with attention and hyperactivity concerns: Implications for on-task and in-seat behavior. American Journal of Occupational Therapy,65, 393–399.
Haskell, M. (2011). A well-rounded education: New seating helps fidgety first-graders stay on the ball at Orland school. Bangor Daily News [Bangor, ME] 4 Mar. 2011. Business Insights: Essentials. Web. 12 Nov. 2014.
Jakubek, M. D. (2007). Stability balls: Reviewing the literature regarding their use and effectiveness. Strength and Conditioning Journal,29, 58–63.
Schilling, D. L., & Schwartz, I. S. (2004). Alternative seating for young children with autism spectrum disorder: Effects on classroom behavior. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders,34, 423–432.
Schilling, D. L., Washington, K., Billingsley, F., & Deitz, J. (2003). Classroom seating for children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: Therapy balls versus chairs. The American Journal of Occupational Therapy,57, 534–541.
Wu, W., Wang, C., Chen, C., Lai, C., Yang, P., & Guo, L. (2012). Influence of therapy ball seats on attentional ability in children with attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Journal of Physical Therapy Science,24, 1177–1182.
Funding
There was no funding for this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
TK and RM designed the study and wrote the manuscript. TK conducted data collection and implemented intervention.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
All authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in this study involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed Consent
University IRB approval was obtained and informed consent was obtained from the parents of all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Krombach, T., Miltenberger, R. The Effects of Stability Ball Seating on the Behavior of Children with Autism During Instructional Activities. J Autism Dev Disord 50, 551–559 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-019-04283-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-019-04283-8