Abstract
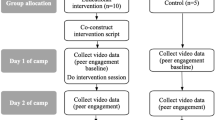
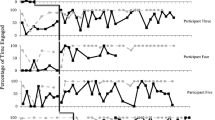
Children with autism spectrum disorder demonstrate challenges in socialization that can interfere with their participation in common childhood activities and can persist or worsen if not addressed. The purpose of this study was to assess whether individualized education program (IEP) social goals could be targeted by a supervised paraprofessional during a short-term inclusive summer camp program. Data were collected using a concurrent multiple baseline design across four children. Results showed that following a 2-week summer camp program all participants made social improvements, reaching their year-long IEP goals, that maintained at follow-up in natural environments. Further, the paraprofessionals reached fidelity of implementation. Findings are discussed in terms of the value and feasibility of providing social interventions in inclusive summer camps.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Psychiatric Association. (2013). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (5th edn.). Arlington: American Psychiatric Publishing.
Barlow, D. H., Nock, M. K., & Hersen, M. (2009). Single case experimental designs: Strategies for studying behavior change. Upper Saddle River: Pearson Education.
Bauminger, N., & Kasari, C. (2000). Loneliness and friendship in high-functioning children with autism. Child Development, 71, 447–456.
Brookman, L., Boettcher, M., Klein, E., Openden, D., Koegel, R. L., & Koegel, L. K. (2003). Facilitating social interactions in a community summer camp setting for children with autism. Journal of Positive Behavior Interventions, 5, 249–252.
Brown, T. S., & Stanton-Chapman, T. L. (2017). Experiences of paraprofessionals in US preschool special education and general education classrooms. Journal of Research in Special Educational Needs, 17(1), 18–30.
Camargo, S. P. H., Rispoli, M., Ganz, J., Hong, E. R., Davis, H., & Mason, R. (2014). A review of the quality of behaviorally-based intervention research to improve social interaction skills of children with ASD in inclusive settings. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 44, 2096–2116.
Carter, A. S., Davis, N. O., Klin, A., & Volkmar, F. R. (2005). Social development in autism. In F. R. Volkmar, R. Paul, A. Klin & D. Cohen (Eds.), Handbook of autism and pervasive developmental disorders: Diagnosis, development, neurobiology, and behavior (pp. 312–334). Hoboken: Wiley.
Chamberlain, B., Kasari, C., & Rotheram-Fuller, E. (2006). Involvement or isolation? The social networks of children with autism in regular classrooms. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 37, 230–242.
Croen, L. A., Grether, J. K., Hoogstrate, J., & Selvin, S. (2002). The changing prevalence of autism in California. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 32, 207–215.
Feldman, E. K., & Matos, R. (2012). Training paraprofessionals to facilitate social interactions between children with autism and their typically developing peers. Journal of Positive Behavior Interventions, 15, 169–179.
Holwerda, A., Van der Klink, J. J., Groothoff, J. W., & Brouwer, S. (2012). Predictors for work participation in individuals with an autism spectrum disorder: A systematic review. Journal of Occupational Rehabilitation, 22, 333–352.
Jackson, S. L., Hart, L., Brown, J. T., & Volkmar, F. R. (2018). Brief report: Self reported academic, social, and mental health experiences of post-secondary students with autism spectrum disorder. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 48, 643–650.
Katsiyannis, A. (1991). Extended school year policies: An established necessity. Remedial and Special Education, 12(1), 24–28.
Koegel, L. K., Koegel, R. L., Ashbaugh, K., & Bradshaw, J. (2014). The importance of early identification and intervention for children with or at risk for autism spectrum disorders. International Journal of Speech-Language Pathology, 16(1), 50–56.
Koegel, L. K., Koegel, R. L., Frea, W., & Green-Hopkins, I. (2003). Priming as a method of coordinating educational services for students with autism. Language, Speech, and Hearing Services in Schools, 34, 228–235.
Koegel, R. L., Fredeen, R., Kim, S., Danial, J., Rubinstein, D., & Koegel, L. (2012). Using perseverative interests to improve interactions between adolescents with autism and their typical peers in school settings. Journal of Positive Behavior Interventions, 14, 133–141.
Koegel, R. L., & Koegel, L. K. (2006). Pivotal response treatments for autism: Communication, social & academic development. Baltimore: Paul H. Brookes Publishing.
Kurth, J., & Mastergeorge, A. M. (2010). Individual education plan goals and services for adolescents with autism: Impact of age and educational setting. The Journal of Special Education, 44, 146–160. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022466908329825.
Mayes, S. D., Calhoun, S. L., Murray, M. J., & Zahid, J. (2011). Variables associated with anxiety and depression in children with autism. Journal of Developmental and Physical Disabilities, 23, 325–337.
McConnell, S. R. (2002). Interventions to facilitate social interaction for young children with autism: Review of available research and recommendations for educational intervention and future research. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 32, 351–372.
Reed, D. K., Aloe, A. M., Reeger, A. J., & Folsom, J. S. (2019). Defining summer gain among elementary students with or at risk for reading disabilities. Exceptional Children. https://doi.org/10.1177/0014402918819426.
Rogers, S. J. (2000). Interventions that facilitate socialization in children with autism. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 30, 399–409.
Ruble, L. A., McGrew, J., Dalrymple, N., & Jung, L. A. (2010). Examining the quality of IEPs for young children with autism. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 40(12), 1459–1470.
Rudy, L. J. (2018). Extended school year for kids with autism. Very Well Health. https://www.verywellhealth.com/what-is-extended-school-year-esy-for-kids-with-autism-260451.
Schenkelberg, M. A., Rosenkranz, R. R., Milliken, G. A., Menear, K., & Dzewaltowski, D. A. (2017). Implications of social groups on sedentary behavior of children with autism: A pilot study. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 47, 1223–1230.
Simacek, J., Reichle, J., Byiers, B. J., Parker-McGowan, Q., Dimian, A. F., & Elmquist, M. (2018). Promoting conditional use of communication skills for learners with complex communication needs: A tutorial. American Journal of Speech Language Pathology, 27, 519–535.
Sutton, B. M., Webster, A. A., & Westerveld, M. F. (2018). A systematic review of school-based interventions targeting social communication behaviors for students with autism. Autism. https://doi.org/10.1177/1362361317753564.
Watkins, L., Kuhn, M., Ledbetter-Cho, K., Gevarter, C., & O’Reilly, M. (2017). Evidence-based social communication interventions for children with autism spectrum disorder. The Indian Journal of Pediatrics, 84(1), 68–75.
Watkins, L., O’Reilly, M., Kuhn, M., Gevarter, C., Lancioni, G. E., Sigafoos, J., & Lang, R. (2014). A review of peer-mediated social interaction interventions for students with autism in inclusive settings. Journal of Autism Developmental Disorders, 45, 1070–1083. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-014-2264.
White, S. W., Keonig, K., & Scahill, L. (2007). Social skills development in children with autism spectrum disorders: A review of the intervention research. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 37, 1858–1868.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Sunny Kim, Maya Fehler, and Madison Werchowsky for their assistance with data collection and analysis. This manuscript was partially funded by National Institute of Mental Health Grant #MH28210 National Institute of Deafness and Other Communication Disorders #DC010924 the Kind World Foundation, the Bialis Family Foundation, and the Eli and Edythe L. Broad Foundation. Lynn and Robert Koegel are partners in the private firm Koegel Autism Consultants, LLC.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LKK and RLK conceived the study, its design, data analysis, and coordinated and drafted the manuscript. LBG and LKK supervised the intervention and coordinated the study. LBG and FAC developed the scoring systems, collected and scored the data. LBG analyzed IEPs and LKK and LBG developed the individualized interventions. LBG and FAC assisted with the literature review. All authors assisted with interpretation of the data, the manuscript draft, and read and approved the final version.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koegel, L.K., Glugatch, L.B., Koegel, R.L. et al. Targeting IEP Social Goals for Children with Autism in an Inclusive Summer Camp. J Autism Dev Disord 49, 2426–2436 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-019-03992-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-019-03992-4