Abstract
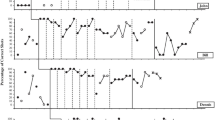
A multiple baseline design across three children with autism and within child across activity was used to assess the effects of interventions designed to teach children with autism to play two common athletic group games, handball and 4-square. Treatment consisted of two phases. In Phase I, athletic skills training, the children participated in sessions designed facilitate their acquisition of the athletic skills required by the targeted games. During Phase II, rules training, the children were instructed on the rules of the targeted games. Mastering the athletic skills and participating in rules training resulted in increased athletic group play and concomitant increases in speech. These gains were maintained at 8–16 weeks follow-up. However, generalization to participation in school recess activities did not occur.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Psychiatric Association. (2000). Pervasive developmental disorders. In Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (Fourth edition-text revision; DSM-IV-TR) (pp. 69–70). Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association.
Anderson, A., Moore, D. W., Godfrey, R., & Fletcher-Flinn, C. M. (2004). Social skills assessment of children with autism in free-play situations. Autism, 8, 369–385. doi:10.1177/1362361304045216.
Baker, M. J. (2000). Incorporating the thematic ritualistic behaviors of children with autism into games: Increasing play interaction with siblings. Journal of Positive Behavior Interventions, 2, 66–84. doi:10.1177/109830070000200201.
Baranek, G. T. (2002). Efficacy of sensory and motor interventions in children with autism. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 32, 397–422. doi:10.1023/A:1020541906063.
Blatchford, P., Baines, E., & Pellegrini, A. (2003). The social context of school playground games: Sex and ethnic differences, and changes over time after entry to junior school. British Journal of Developmental Psychology, 21, 481–505. doi:10.1348/026151003322535183.
Boutot, E. A., Guenther, T., & Crozier, S. (2005). Teaching play skills to young children with autism. Education and Training in Developmental Disabilities, 40, 285–292.
Charlop-Christy, M. H., Le, L., & Freeman, K. A. (2000). A comparison of video modeling with in vivo modeling for teaching children with autism. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 30, 537–552. doi:10.1023/A:1005635326276.
Coe, D., Matson, J., Fee, V., Manikam, R., & Linarello, C. (1990). Training nonverbal and verbal play skills to mentally retarded and autistic children. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 20, 177–187. doi:10.1007/BF02284717.
Cooper, J. O., Heron, T. E., & Heward, W. L. (2007). Applied behavior analysis (2nd ed.). New York: Pearson Publishers.
Creasey, G. L., Jarvis, P. A., & Berk, L. E. (1998). Play and social competence. In O. N. Saracho (Ed.), Multiple perspectives on play in early childhood education (pp. 116–145). Albany, NY: State University of New York Press.
D’Ateno, P., Mangiapanello, K., & Taylor, B. A. (2003). Using video modeling to teach complex play sequences to a preschooler with autism. Journal of Positive Behavior Interventions, 1, 5–11. doi:10.1177/10983007030050010801.
Hine, J. F., & Wolery, M. (2006). Using point-of-view video modeling to teach play to preschoolers with autism. Topics in Early Childhood Special Education, 26, 83–93. doi:10.1177/02711214060260020301.
Hume, K., & Odom, S. (2007). Effects of an individual work system on the independent functioning of students with autism. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 37, 1166–1180. doi:10.1007/s10803-006-0260-5.
Kasari, C., Paparella, T., Freeman, S., & Jahromi, L. B. (2008). Language outcome in autism: Randomized comparison of joint attention and play interventions. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 76, 125–137. doi:10.1037/0022-006X.76.1.125.
Lang, R., O’Reilly, M., Rispoli, M., Shogren, K., Machalicek, W., Sigafoos, J., et al. (2009). Review of interventions to increase functional and symbolic play in children with autism. Education and Training in Developmental Disabilities, 44, 481–492.
Libby, S., Powell, S., Messer, D., & Jordan, R. (1998). Spontaneous play in children with autism: A reappraisal. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 28, 487–497. doi:10.1023/A:1026095910558.
MacDonald, R., Clark, M., Garrigan, E., & Vangala, M. (2005). Using video modeling to teach pretend play to children with autism. Journal of Behavioral Interventions, 20, 225–238. doi:10.1002/bin.197.
MacDonald, R., Sacramone, S., Mansfield, R., Wiltz, K., Aheam, W. H., & Taylor, B. (2009). Using video modeling to teach reciprocal pretend play to children with autism. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 42, 43–55. doi:10.1901/jaba.2009.42-43.
MacDuff, G. S., Krantz, P. J., & McClannahan, L. E. (2001). Prompts and prompt-fading strategies for people with autism. In C. Maurice, G. Green, & R. M. Foxx (Eds.), Making a difference: Behavioral intervention for autism (pp. 37–50). Austin, TX: PRO-ED.
Marquez Charter School. (2012). Playground rules. Retrieved from http://marquezcharter.org/parent-resources/basic-recess-rules/playground-rules/.
Mastrangelo, S. (2009). Play and the child with autism spectrum disorder: From possibilities to practice. International Journal of Play Therapy, 18, 13–30. doi:10.1037/a0013810.
Nuzzolo-Gomez, R., Leonard, M. A., Ortiz, E., Rivera, C. M., & Greer, R. (2002). Teaching children with autism to prefer books or toys over stereotypy or passivity. Journal of Positive Behavior Interventions, 4, 80–87. doi:10.1177/109830070200400203.
Obrusnikova, I., & Cavalier, A. R. (2011). Perceived barriers and facilitators of participation in after-school physical activity by children with autism spectrum disorders. Journal of Developmental and Physical Disabilities, 23, 195–211. doi:10.1007/s10882-010-9215-z.
Paterson, C. R., & Arco, L. (2007). Using video modeling for generalizing toy play in children with autism. Behavior Modification, 31, 660–681. doi:10.1177/0145445507301651.
Pellegrini, A. D., Blatchford, P., Kato, K., & Baines, E. (2004). A short-term longitudinal study of children’s playground games in primary school: Implications for adjustment to school and social adjustment in the USA and UK. Social Development, 31, 107–123. doi:10.1111/j.1467-9507.2004.00259.x.
Rogers, S. J. (2000). Interventions that facilitate socialization. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 30, 399–409. doi:10.1023/A:1005543321840.
Schleien, S. J., Heyne, L. A., & Berken, S. B. (1988). Integrated physical education to teach appropriate play skills to learners with autism: A pilot study. Adapted Physical Activity Quarterly, 5, 182–192.
Schleien, S. J., Rynders, J. E., Mustonen, T., & Fox, A. (1990). Effects of social play activities on the play behavior of children with autism. Journal of Leisure Research, 22, 317–328.
Simpson, R., & Otten, K. (2005). Structuring behavior management strategies and building social competence. In D. Zager (Ed.), ASD: Identification, education, and treatment (pp. 367–394). Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum.
Sparrow, S., Cicchetti, D., & Balla, D. (2005). Vineland-II: Vineland adaptive behavior scales: Survey forms manual (2nd ed.). Circle Pines, MN: American Guidance Services.
Stahmer, A. C. (1995). Teaching symbolic play skills to children with autism using pivotal response training. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 25, 123–141. doi:10.1007/BF02178500.
Stone, W. L., & Lemanek, K. L. (1990). Parental report of social behaviors in autistic preschoolers. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 20, 513–522. doi:10.1007/BF02216056.
Stone, W. L., Lemanek, K. L., Fishel, P. T., Fernandez, M. C., & Altemeier, W. A. (1990). Play and imitation skills in the diagnosis of autism in young children. Pediatrics, 86, 267–272.
Thorp, D. M., Stahmer, A. C., & Schreibman, L. (1995). Effects of sociodramatic play training on children with autism. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 25, 265–282. doi:10.1007/BF02179288.
Williams, E., Reddy, Vasudevi, & Costall, A. (2001). Taking a closer look at functional play in children with autism. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 31, 67–77. doi:10.1023/A:1005665714197.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miltenberger, C.A., Charlop, M.H. Increasing the Athletic Group Play of Children with Autism. J Autism Dev Disord 44, 41–54 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-013-1850-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-013-1850-7