Abstract
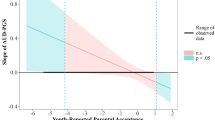
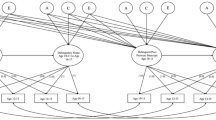
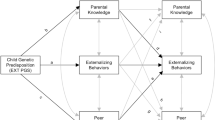
Alcohol use emerges during early adolescence and is strongly associated with individual and peer risky, delinquent, and rule breaking behaviors. Genetic predisposition for risky behavior contributes to individual rule breaking in adolescence and can also evoke peer rule breaking or lead youth to select into delinquent peer groups via gene-environment correlations (rGE), collectively increasing risk for alcohol use. Little research has examined whether genetic predisposition for risky behavior contributes to individual and peer rule breaking behavior in developmental pathways to alcohol use in early adolescence or in large diverse racial/ethnic populations. To address this, polygenic scores for risky behavior were considered predictors of individual rule breaking, peer rule breaking, and alcohol sips using data from the Adolescent Brain Cognitive Development (ABCD) study at age 11–12 and 12–13 in a cross-time cross-lagged model. This was examined separately in European American (EA; n = 5113; 47% female), African American (AA; n = 1159; 50% female), and Hispanic/Latinx (Latinx; n = 1624; 48% female) subgroups accounting for sociodemographic covariates and genetic ancestry principal components. Polygenic scores were positively associated with all constructs in EAs, with individual rule breaking at age 11–12 in AAs and Latinx, and with alcohol sips at age 11–12 in Latinx. Individual and peer rule breaking were associated with one another across time only in the EA subgroup. In all subgroups, peer rule breaking at 12–13 was associated with alcohol sips at 12–13. Results indicate that alcohol sips in early adolescence are associated with individual and peer rule breaking with rGE implicated in EAs.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data analyzed in the current study are available from the National Institutes of Mental Health Data Archive (https://nda.nih.gov/).
References
Achenbach, T. M., & Ruffle, T. M. (2000). The child Behavior Checklist and related forms for assessing behavioral/emotional problems and competencies. Pediatrics in Review, 21(8), 265–271. https://doi.org/10.1542/pir.21-8-265
Aiken, A., Clare, P. J., Boland, V. C., Degenhardt, L., Yuen, W. S., Hutchinson, D., Najman, J., McCambridge, J., Slade, T., McBride, N., De Torres, C., Wadolowski, M., Bruno, R., Kypri, K., Mattick, R. P., & Peacock, A. (2020). Parental supply of sips and whole drinks of alcohol to adolescents and associations with binge drinking and alcohol-related harms: A prospective cohort study. Drug and alcohol dependence, 215, 108204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2020.108204
Bingham, C. R., Fitzgerald, H. E., & Zucker, R. A. (1995). Peer Behavior Profile/Peer Activities Questionnaire Unpublished questionnaire. Department of Psychology, Michigan State University.
Campbell, M. C., & Tishkoff, S. A. (2008). African genetic diversity: Implications for human demographic history, modern human origins, and complex disease mapping. Annual review of genomics and human genetics, 9, 403–433. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.genom.9.081307.164258
Chartier, K., & Caetano, R. (2010). Ethnicity and health disparities in alcohol research. Alcohol Research and Health, 33(1–2), 152–160.
Derringer, J., Corley, R. P., Haberstick, B. C., Young, S. E., Demmitt, B. A., Howrigan, D. P., & McQueen, M. B. (2015). Genome-wide association study of behavioral disinhibition in a selected adolescent sample. Behavior genetics, 45(4), 375–381.
Dick, D. M. (2007). Identification of genes influencing a spectrum of externalizing psychopathology. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 16(6), 331–335. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-8721.2007.00530
Dodge, K. A., Malone, P. S., Lansford, J. E., Miller, S., Pettit, G. S., & Bates, J. E. (2009). A dynamic cascade model of the development of substance-use onset. Monographs of the Society for Research in Child Development, 74(3), vii–119. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1540-5834.2009.00528.x
Donovan, J. E., & Molina, B. S. (2008). Children’s introduction to alcohol use: Sips and tastes. Alcoholism Clinical and Experimental Research, 32(1), 108–119. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1530-0277.2007.00565.x
Elam, K. K., Chassin, L., Lemery-Chalfant, K., Pandika, D., Wang, F. L., Bountress, K., Dick, D., & Agrawal, A. (2017). Affiliation with substance-using peers: Examining gene-environment correlations among parent monitoring, polygenic risk, and children’s impulsivity. Developmental Psychobiology, 59(5), 561–573. https://doi.org/10.1002/dev.21529
Elam, K. K., Chassin, L., & Pandika, D. (2018). Polygenic risk, family cohesion, and adolescent aggression in mexican american and european american families: Developmental pathways to alcohol use. Development and Psychopathology, 30(5), 1715–1728. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0954579418000901
Elam, K. K., Ha, T., Neale, Z., Aliev, F., Dick, D., & Lemery-Chalfant, K. (2021). Polygenic effects on alcohol use in African Americans and European Americans: Age varying associations from adolescence to adulthood. Scientific Reports, 11, 22425.
Elam, K. K., Lemery-Chalfant, K., & Chassin, L. (2022a). A gene-environment cascade theoretical framework of developmental psychopathology. Journal of Psychopathology and Clinical Science. https://doi.org/10.1037/abn0000546. Advance online publication.
Elam, K. K., Bountress, K. E., Ha, T., Shaw, D. S., Wilson, M. N., Aliev, F., Dick, D. M., & Lemery-Chalfant, K. (2022b). Developmental genetic effects on externalizing behavior and alcohol use: Examination across two longitudinal samples. Development and Psychopathology, 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0954579422000980. Advance online publication.
Elam, K. K., Clifford, S., & Ruof, A. (2022c). Genotype-environment correlation by intervention effects underlying middle childhood peer rejection and associations with adolescent marijuana use. Development and Psychopathology, 34, 171–182. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0954579420001066
Garavan, H., Bartsch, H., Conway, K., Decastro, A., Goldstein, R. Z., Heeringa, S., Jernigan, T., Potter, A., Thompson, W., & Zahs, D. (2018). Recruiting the ABCD sample: Design considerations and procedures. Developmental Cognitive Neuroscience, 32, 16–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dcn.2018.04.004
Ge, T., Chen, C. Y., Ni, Y., Feng, Y. A., & Smoller, J. W. (2019). Polygenic prediction via bayesian regression and continuous shrinkage priors. Nature communications, 10(1), 1776. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-09718-5
Gelernter, J., Kranzler, H. R., Sherva, R., Almasy, L., Koesterer, R., Smith, A. H., Anton, R., Preuss, U. W., Ridinger, M., Rujescu, D., Wodarz, N., Zill, P., Zhao, H., & Farrer, L. A. (2014). Genome-wide association study of alcohol dependence: Significant findings in african- and European-Americans including novel risk loci. Molecular Psychiatry, 19(1), 41–49. https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2013.145
Hoeben, E. M., Meldrum, R. C., Walker, D. A., & Young, J. T. (2016). The role of peer delinquency and unstructured socializing in explaining delinquency and substance use: A state-of-the-art review. Journal of Criminal Justice, 47, 108–122.
Jackson, K. M., Colby, S. M., Barnett, N. P., & Abar, C. C. (2015). Prevalence and correlates of sipping alcohol in a prospective middle school sample. Psychology of Addictive Behaviors, 29(3), 766–778. https://doi.org/10.1037/adb0000072
Linnér, K. R., Biroli, P., Kong, E., Meddens, S. F. W., Wedow, R., Fontana, M. A., Lebreton, M., Tino, S. P., Abdellaoui, A., Hammerschlag, A. R., Nivard, M. G., Okbay, A., Rietveld, C. A., Timshel, P. N., Trzaskowski, M., de Vlaming, R., Zünd, C. L., Bao, Y., Buzdugan, L., & Beauchamp, J. P. (2019). Genome-wide association analyses of risk tolerance and risky behaviors in over 1 million individuals identify hundreds of loci and shared genetic influences. Nature Genetics, 51(2), 245–257. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41588-018-0309-3
Kelly, A. B., Chan, G. C., Toumbourou, J. W., O’Flaherty, M., Homel, R., Patton, G. C., & Williams, J. (2012). Very young adolescents and alcohol: Evidence of a unique susceptibility to peer alcohol use. Addictive Behaviors, 37(4), 414–419. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addbeh.2011.11.038
Ksinan, A. J., Smith, R. L., Barr, P. B., & Vazsonyi, A. T. (2022). The associations of polygenic scores for risky behaviors and parenting behaviors with adolescent externalizing problems. Behavior Genetics, 52(1), 26–37.
Kuo, S. I., Salvatore, J. E., Barr, P. B., Aliev, F., Anokhin, A., Bucholz, K. K., Chan, G., Edenberg, H. J., Hesselbrock, V., Kamarajan, C., Kramer, J. R., Lai, D., Mallard, T. T., Nurnberger, J. I. Jr., Pandey, G., Plawecki, M. H., Sanchez-Roige, S., Waldman, I., Palmer, A. A., Consortium, E., & Dick, D. M. (2021). Mapping pathways by which genetic risk influences adolescent externalizing behavior: The interplay between externalizing polygenic risk scores, parental knowledge, and peer substance use. Behavior Genetics, 51(5), 543–558. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10519-021-10067-7
Martin, A. R., Gignoux, C. R., Walters, R. K., Wojcik, G. L., Neale, B. M., Gravel, S., Daly, M. J., Bustamante, C. D., & Kenny, E. E. (2017). Human demographic history impacts genetic risk prediction across diverse populations. American Journal of Human Genetics, 100(4), 635–649. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajhg.2017.03.004
Martin, A. R., Kanai, M., Kamatani, Y., Okada, Y., Neale, B. M., & Daly, M. J. (2019). Clinical use of current polygenic risk scores may exacerbate health disparities. Nature Genetics, 51(4), 584–591. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41588-019-0379-x
Miles, D. R., van den Bree, M. B., Gupman, A. E., Newlin, D. B., Glantz, M. D., & Pickens, R. W. (2001). A twin study on sensation seeking, risk taking behavior and marijuana use. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 62(1), 57–68.
Mulia, N., Ye, Y., Greenfield, T. K., & Zemore, S. E. (2009). Disparities in alcohol-related problems among white, black, and hispanic Americans. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research, 33(4), 654–662. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1530-0277.2008.00880.x
Mundt, M. P. (2011). The impact of peer social networks on adolescent alcohol use initiation. Academic Pediatrics, 11(5), 414–421. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acap.2011.05.005
Murphy, M. A., Dufour, S. C., & Gray, J. C. (2021). The association between child alcohol sipping and alcohol expectancies in the ABCD study. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 221, 108624. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2021.108624
Peterson, R. E., Edwards, A. C., Bacanu, S. A., Dick, D. M., Kendler, K. S., & Webb, B. T. (2017). The utility of empirically assigning ancestry groups in cross-population genetic studies of addiction. The American Journal on Addictions, 26(5), 494–501.
Plomin, R., DeFries, J. C., & Loehlin, J. C. (1977). Genotype-environment interaction and correlation in the analysis of human behavior. Psychological Bulletin, 84, 309–322. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-2909.84.2.309
Popejoy, A. B., & Fullerton, S. M. (2016). Genomics is failing on diversity. In Nature (Vol. 538, Issue 7624) (pp. 161–164). Nature Publishing Group. https://doi.org/10.1038/538161a
Rabinowitz, J. A., Jin, J., Kahn, G., Kuo, S. I. C., Campos, A., Renteria, M., & Cohen, D. (2021). Genetic propensity for risky behavior and depression and risk of lifetime suicide attempt among urban African Americans in adolescence and young adulthood. American Journal of Medical Genetics Part B: Neuropsychiatric Genetics, 186(8), 456–468.
Reiter, A. M., Suzuki, S., O’Doherty, J. P., Li, S. C., & Eppinger, B. (2019). Risk contagion by peers affects learning and decision-making in adolescents. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 148(9), 1494.
Sacks, J. J., Gonzales, K. R., Bouchery, E. E., & Tomedi, L. E. (2015). &Brewer, R. D. 2010 national and state costs of excessive alcohol consumption. American Journal of Preventive Medicine, 49, e73–e79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amepre.2015.05.031
Salvatore, J. E., Cho, S. B., & Dick, D. M. (2017). Genes, environments, and sex differences in alcohol research. Journal of Studies on Alcohol and Drugs, 78(4), 494–501.
Savi-Çakar, F., Tagay, Ö., & Ebru Ikiz, F. (2015). Risky behaviors of adolescents: Definitions and prevntion. In A. M. Columbus (Ed.), Advances in psychology research (106 vol., pp. 137–167). Nova Science.
Scarr, S., & McCartney, K. (1983). How people make their own environments: A theory of genotype environment effects. Child Development, 54, 424–435. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-8624.1983.tb03884.x
Scott, M. S. (2017). Commentary: Perspectives on alcohol-related gene and environment interplay in diverse populations. American Journal on Addictions, 26(5), 526–531. https://doi.org/10.1111/ajad.12584
Sobell, L. C., & Sobell, M. B. (1992). Timeline follow-back: A technique for assessing self-reported alcohol consumption. In R. Z. Litten, & J. P. Allen (Eds.), Measuring Alcohol Consumption: Psychosocial and Biological Methods (pp. 41–72). Humana Press.
Su, J., Kuo, S. I., Bucholz, K. K., Edenberg, H. J., Kramer, J. R., Schuckit, M., & Dick, D. M. (2018). Understanding mechanisms of genetic risk for adolescent internalizing and externalizing problems: The mediating role of parenting and personality. Twin Research and Human Genetics: The Official Journal of the International Society for Twin Studies, 21(4), 310–321. https://doi.org/10.1017/thg.2018.36
Su, J., Kuo, S. I., Aliev, F., Chan, G., Edenberg, H. J., Kamarajan, C., McCutcheon, V. V., Meyers, J. L., Schuckit, M., Tischfield, J., & Dick, D. M. (2021). The associations between polygenic risk, sensation seeking, social support, and alcohol use in adulthood. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 130(5), 525–536.
Vrieze, S. I., McGue, M., Miller, M. B., Hicks, B. M., & Iacono, W. G. (2013). Three mutually informative ways to understand the genetic relationships among behavioral disinhibition, alcohol use, drug use, nicotine use/dependence, and their co-occurrence: Twin biometry, GCTA, and genome-wide scoring. Behavior Genetics, 43(2), 97–107.
Wang, X. T., Zheng, R., Xuan, Y. H., Chen, J., & Li, S. (2016). Not all risks are created equal: A twin study and meta-analyses of risk taking across seven domains. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 145(11), 1548.
Williams, D. R., Mohammed, S. A., Leavell, J., & Collins, C. (2010). Race, socioeconomic status, and health: Complexities, ongoing challenges, and research opportunities. In Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences (Vol. 1186) (pp. 69–101). Blackwell Publishing Inc. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1749-6632.2009.05339.x
Young, S. E., Friedman, N. P., Miyake, A., Willcutt, E. G., Corley, R. P., Haberstick, B. C., & Hewitt, J. K. (2009). Behavioral disinhibition: Liability for externalizing spectrum disorders and its genetic and environmental relation to response inhibition across adolescence. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 118(1), 117.
Acknowledgements
Data used in the preparation of this article were obtained from the Adolescent Brain Cognitive DevelopmentSM (ABCD) Study (https://abcdstudy.org), held in the NIMH Data Archive (NDA). This is a multisite, longitudinal study designed to recruit more than 10,000 children age 9–10 and follow them over 10 years into early adulthood. The ABCD Study® is supported by the National Institutes of Health and additional federal partners under award numbers U01DA041048, U01DA050989, U01DA051016, U01DA041022, U01DA051018, U01DA051037, U01DA050987, U01DA041174, U01DA041106, U01DA041117, U01DA041028, U01DA041134, U01DA050988, U01DA051039, U01DA041156, U01DA041025, U01DA041120, U01DA051038, U01DA041148, U01DA041093, U01DA041089, U24DA041123, U24DA041147. A full list of supporters is available at https://abcdstudy.org/federal-partners.html. A listing of participating sites and a complete listing of the study investigators can be found at https://abcdstudy.org/consortium_members/. ABCD consortium investigators designed and implemented the study and/or provided data but did not necessarily participate in the analysis or writing of this report. This manuscript reflects the views of the authors and may not reflect the opinions or views of the NIH or ABCD consortium investigators. The ABCD data repository grows and changes over time. The ABCD data used in this report came from ABCD Data Release 4.0 (https://doi.org/10.15154/1523041).
Funding
This research was supported by grants from the National Institute on Drug Abuse and National Institutes of Health: Office of the Director, and Office of Behavioral and Social Sciences Research (K01DA042828 to KE).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
KE conceived the current study and participated in its design, coordination, data analysis and drafting the manuscript; JS participated in study design and drafting the manuscript; FA participated in data analysis and drafting the manuscript; DS, AT, and JK participated in drafting the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors report no conflicts of interest. Dr. Kit Elam is an Editorial Board member of Research on Child and Adolescent Psychopathology.
Ethical Approval
The Indiana University Institutional Review Board approved the current study. The study was performed in accordance with the ethical standards as laid down in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed Consent
As part of the ABCD study, parents provided consent for their participation and written informed consent for youth participants and youths provided assent.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Elam, K.K., Su, J., Aliev, F. et al. Polygenic Effects on Individual Rule Breaking, Peer Rule Breaking, and Alcohol Sips Across Early Adolescence in the ABCD Study. Res Child Adolesc Psychopathol 51, 1425–1438 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10802-023-01090-9
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10802-023-01090-9