Abstract
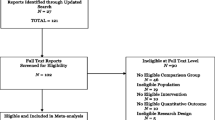
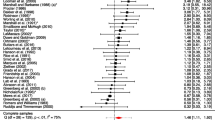
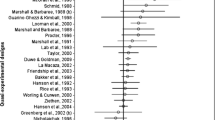
The current study investigated the effect on recidivism of treatment aimed at juveniles who have sexually offended. It also assessed the potential moderating effect of type of recidivism, and several treatment, participant and study characteristics. In total, 14 published and unpublished primary studies, making use of a comparison group and reporting on official recidivism rates, were included in a multilevel meta-analysis. This resulted in the use of 77 effect sizes, and 1726 participants. A three-level meta-analytic model was used to calculate the combined effect sizes (Cohens d) and to perform moderator analyses. Study quality was assessed with the EPHPP Quality Assessment Tool for Quantitative Studies. A moderate effect size was found (d = 0.37), indicating that the treatment groups achieved an estimated relative reduction in recidivism of 20.5% as compared to comparison groups. However, after controlling for publication bias, a significant treatment effect was no longer found. Type of recidivism did not moderate the effect of treatment, indicating that treatment groups were equally effective for all types of recidivism. Also, no moderating effects of participant or treatment characteristics were found. Regarding study characteristics, a shorter follow up time showed a trend for larger effect sizes, and the effect size calculation based on proportions yielded larger effect sizes than calculation via mean frequency of offending. Implications for future research and clinical practice are discussed.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
The asterisks indicate original research included in the analysis.
Adjorlolo, S., & Egbenya, D. L. (2016). Executive functioning profiles of adolescent and juvenile male sexual offenders: A systematic review. The Journal of Forensic Psychiatry and Psychology, 27, 349–375.
Armijo-Olivo, S., Stiles, C. R., Hagen, N. A., Biondo, P. D., & Cummings, G. G. (2012). Assessment of study quality for systematic reviews: A comparison of the Cochrane collaboration risk of bias tool and the effective public health practice project quality assessment tool. Journal of Evaluation in Clinical Practice, 18, 12–18.
Assink, M., & Wibbelink, C. M. (2016). Fitting three-level meta-analytic models in R: A step-by-step tutorial. The Quantitative Methods for Psychology, 12, 154–174.
Assink, M., Van Der Put, C. E., Hoeve, M., De Vries, S. L., Stams, G. J. J., & Oort, F. J. (2015). Risk factors for persistent delinquent behavior among juveniles: A meta-analytic review. Clinical Psychology Review, 42, 47–61.
Barbaree, H. E., & Marshall, W. L. (2006). The juvenile sex offender. New York: The Guilford Press.
*Barlow, K. N. (1998). Recidivism rates of level six residential programs for youthful male sexual offenders: 1995–1996. Unpublished Master’s thesis. Utah: Utah State University.
Beaudry-Cyr, M., Jennings, W. G., Zgoba, K. M., & Tewksbury, R. (2015). Examining the continuity of juvenile sex offending into adulthood and subsequent patterns of sex and general recidivism. International Journal of Offender Therapy and Comparative Criminology, 9, 1–18.
Becker, J. V., & Hunter, J. A. (1997). Understanding and treating child and adolescent sex offenders. In T. H. Ollendick & R. J. Prinz (Eds.), Advances in clinical Psychology (pp. 177–197). New York: Plenum.
Becker, J. V., & Johnson, B. R. (2001). Treating juvenile sex offenders. In J. Ashford & B. Sales (Eds.), Treating adult and juvenile sex offenders with special needs (pp. 273–289). Washington DC: American Psychological Association.
Beggs, S. M., & Grace, R. C. (2011). Treatment gain for sexual offenders against children predicts reduced recidivism: A comparative validity study. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 79, 182–192.
Bonta, J., & Andrews, D. A. (2007). Risk-need-Responsivity model for offender assessment and rehabilitation. Ottawa: Public Safety Canada.
*Borduin, C. M., Henggeler, S. W., Blaske, D. M., & Stein, R. J. (1990). Multisystemic treatment of adolescent sexual offenders. International Journal of Offender Therapy and Comparative Criminology, 996, 105–113.
*Borduin, C. M., Heiblum, N., & Schaeffer, C. M. (2009). A randomized clinical trial of Multisystemic therapy with juvenile sexual offenders: Effects on youth social ecology and criminal activity. Journal of Consulting Psychology, 77, 26–37.
Brannon, J. M., & Troyer, R. (1991). Peer group counseling: A normalized residential alternative to the specialized treatment of adolescent sex offenders. International Journal of Offender Therapy and Comparative Criminology, 35, 225–234.
Butler, S., & Seto, M. C. (2002). Distinguishing two types of adolescent sex offenders. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 41, 83–90.
Caldwell, M. F. (2010). Study characteristics and recidivism base rates in juvenile sex offender recidivism. International Journal of Offender Therapy and Comparative Criminology, 54, 197–211.
Caldwell, M. F. (2016). Quantifying the decline in juvenile sexual recidivism rates. Psychology, Public Policy and Law, 22, 414–426.
Cale, J., Smallbone, S., Rayment-McHugh, S., & Dowling, C. (2016). Offense trajectories, the unfolding of sexual and non-sexual criminal activity, and sex offense characteristics of adolescent sex offenders. Sexual Abuse: A Journal of Research and Treatment, 28, 791–812.
Carpentier, J., & Proulx, J. (2011). Correlates of recidivism among adolescents who have sexually offended. Sexual Abuse: A Journal of Research and Treatment, 23, 434–455.
Carpentier, M. Y., Silovsky, J. F., & Chaffin, M. (2006). Randomized trial of treatment for children with sexual behavior problems: Ten years later. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 74, 482–488.
Cheung, M. W. L. (2014). Modeling dependent effect sizes with three-level meta-analyses: A structural equation modeling approach. Psychological Methods, 19, 211–229.
Christiansen, A. K., & Vincent, J. P. (2013). Characterization and prediction of sexual and nonsexual recidivism among adjudicated juvenile sex offenders. Behavioural Sciences and the Law, 31, 506–529.
Deeks, J. J., Dinnes, J., D’Amico, R., Sowden, A. J., Sakarovitch, C., Song, F., et al. (2003). Evaluating non-randomized intervention studies. Health Technology Assessment, 7, 3–173.
Dopp, A. R., Borduin, C. M., & Brown, C. E. (2015). Evidence-based treatments for juvenile sexual offenders: Review and recommendations. Journal of Aggression, Conflict and Peace Research, 7, 223–236.
Drew, C. H. (2013). Classification of juvenile sexual offenders by victim age based subgroups. Electronic Theses, Treatises and Dissertations. Paper 7359.
Duval, S., & Tweedie, R. (2000). Trim and fill: A simple funnel-plot–based method of testing and adjusting for publication bias in meta-analysis. Biometrics, 56, 455–463.
Fanniff, A. M., & Kimonis, E. R. (2014). Juveniles who have committed sexual offenses: A special group? Behavioural Sciences and the Law, 32, 240–257.
*Gillis, H. L., & Gass, M. A. (2010). Treating juveniles in a sex offender program using adventure-based programming: A matched group design. Journal of Child Sexual Abuse, 19, 20–34.
Glowacz, F., & Born, M. (2012). Do adolescent child abusers, peer abusers, and non-sex offenders have different personality profiles? European Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 22, 117–225.
Groth, N. A., Longo, R. E., & McFaddin, J. B. (1982). Undetected recidivism among rapists and child molesters. Crime and Delinquency, 128, 450–458.
*Guarino-Ghezzi, S., & Kimball, L. M. (1998). Juvenile sex offenders in treatment. Corrections Management Quarterly, 2, 45–54.
Hanson, R. K., & Morton-Bourgon, K. E. (2005). The characteristics of persistent sexual offenders: A meta-analysis of recidivism studies. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 73, 1154–1163.
Hanson, R. K., Bourgon, G., Helmus, L., & Hodgson, S. (2009). A meta-analysis of the effectiveness of treatment for sexual offenders: Risk, need, and Responsivity. Ottawa: Public Safety Canada.
Hart-Kerkhoffs, L. A., Doreleijers, T. A. H., Jansen, L. M. C., Van Wijk, A. P. H., & Bullens, R. A. R. (2009). Offense related characteristics and psychosexual development of juvenile sex offenders. Child and Adolescent Psychiatry and Mental Health, 3, 1–10.
Hendriks, J. (2006). Jeugdige zedendelinquenten. Een studie naar subtypen en recidive. [Juvenile sex offenders. A study on subtypes and recidivism]. Dissertation. Retrieved from http://dare.ubvu.vu.nl/handle/1871/15503.
*Hendriks, J., & Bijleveld, C. (2005). Recidive van jeugdige zedendelinquenten: poliklinisch behandelden versus niet-behandelden. [Recidivism by juvenile sexual offenders: Outpatient treatment versus non treatment]. Tijdschrift voor Seksuologie, 29, 150–160.
Henggeler, S. W., Letourneau, E. J., Chapman, J. E., Borduin, C. M., Schewe, P. A., & McCart, M. R. (2009). Mediators of change for multisystemic therapy with juvenile sexual offenders. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 77, 451–462.
Hissel, S., Bijleveld, C., Hendriks, J., Jansen, B., & Collot d’Escury-Koenigs, A. (2006). Jeugdige zedendelinquenten: Specialisten, generalisten en first offenders [juvenile sex offenders: Specialists, generalists, and first offenders]. Tijdschrift voor Seksuologie, 30, 215–225.
*Holly, M. C. (2000). Long-term follow up of a community based treatment program for adolescent sex offenders. Unpublished master’s thesis. Thunder Bay: Lakehead University.
Houben, M., Van Den Noortgate, W., & Kuppens, P. (2015). The relation between short-term emotion dynamics and psychological well-being: A meta-analysis. Psychological Bulletin, 141, 901–930.
Hox, J. (2002). Multilevel analysis: Techniques and applications. Mahwah: Lawrence.
Jackson, N., & Waters, E. (2005). Criteria for the systematic review of health promotion and public health interventions. Health Promotion International, 20, 367–374.
*Johnson Erickson, C. (2008). The effectiveness of functional family therapy in the treatment of juvenile sexual offenders. Unpublished thesis. Bloomington: Indiana University.
Kahn, T. J., & Chambers, H. J. (1991). Assessing re-offense risk with juvenile sexual offenders. Child Welfare, 70, 333–345.
Kjellgren, C., Wassberg, A., Carlberg, M., Långström, N., & Svedin, C. G. (2006). Adolescent sexual offenders: A total survey of referrals to social services in Sweden and subgroup characteristics. Sexual Abuse: A Journal of Research and Treatment, 18, 357–372.
Knapp, G., & Hartung, J. (2003). Improved tests for a random effects meta-regression with a single covariate. Statistics in Medicine, 22, 2693–2710.
*Lab, S. P., Schields, G., & Schondel, C. (1993). Research note: An evaluation of juvenile sexual offender treatment. Crime and Delinquency, 39, 543–553.
Landis, J. R., & Koch, G. G. (1977). The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics, 33, 159–174.
Lawing, C., Frick, P. J., & Cruise, K. R. (2010). Differences in offending patterns between adolescent sex offenders high or low in callous-unemotional traits. Psychological Assessment, 22, 298–305.
Letourneau, E. J., & Armstrong, K. S. (2008). Recidivism rates for registered and nonregistered juvenile sexual offenders. Sexual Abuse, 20, 393–408.
Letourneau, E. J., Henggeler, S. W., Borduin, C. M., Schewe, P. A., McCart, M. R., Chapman, J. E., & Saldana, L. (2009). Mutisystemic therapy for juvenile sexual offenders: 1 year results from a randomized effectiveness trial. Journal of Family Psychology, 23, 89–201.
*Letourneau, E. J., Borduin, C. M., Henggeler, S. W., McCart, M. R., Schewe, P. A., & Armstrong, K. S. (2013). Two-year follow-up of a randomized effectiveness trail evaluating MST for juveniles who sexually offend. Journal of Family Psychology, 27, 978–985.
Lipsey, M. W., & Wilson, D. B. (2001). Practical meta-analysis. Thousand Oaks: Sage publications.
Lobanov-Rostovsky, C. (2015). Recidivism of juveniles who commit sexual offenses. SO+MAPI Research Brief. July 2015.
Loeber, R., Hoeve, M., Slot, N. W., & Van Der Laan, P. H. (2012). Persisters and desisters in crime from adolescence into adulthood. Surrey: Ashgate Publishing Limited.
Lord, A. (2016). Integrating risk, the good lives model and recovery for mentally disordered sexual offenders. Journal of Sexual Agression, 22, 107–122.
Lösel, F., & Schmucker, M. (2005). The effectiveness of treatment for sexual offenders: A comprehensive meta-analysis. Journal of Experimental Criminology, 1, 117–146.
Lussier, P., Van Den Berg, C., Bijleveld, C., & Hendriks, J. (2012). A developmental taxonomy of juvenile sex offenders for theory, research and prevention. Criminal Justice and Behaviour, 39, 1559–1581.
Man-Son-Hing, M., Laupacis, A., O’Rourke, K., Molnar, F. J., Mahon, J., Chan, K. B. Y., & Wells, G. (2002). Determination of the clinical importance of study results: A review. Journal of General Internal Medicine, 17, 469–476.
Margari, F., Lecce, P. A., Craig, F., Lafortezza, E., Lisi, A., Pinto, F., Stallone, F., Pierri, G., Pisani, R., Zagaria, G., Margari, L., & Grattagliano, I. (2015). Juvenile sex offenders: Personality profile, coping styles and parental care. Psychiatry Research, 229, 82–88.
Moffit, T. E. (1993). Adolescence-limited and life-course persistent antisocial behaviour, a developmental taxonomy. Psychological Review, 100, 674–701.
Nakagawa, S., & Santos, E. S. A. (2012). Methodological issues and advances in biological meta-analysis. Evolutionary Ecology, 26, 1253–1274.
Pedersen, L., Rasmussen, K., & Elsass, P. (2010). Risk assessment: The value of structured professional judgments. International Journal of Forensic Mental Health, 9, 74–81.
Peters, J. L., Sutton, A. J., Jones, D. R., Abrams, K. R., & Rushton, L. (2007). Performance of the trim and fill method in the presence of publication bias and between-study heterogeneity. Statistics in Medicine, 26, 4544–4562.
Purcel, M. (2010). A personality based classification of male adolescent sex offenders using the MACI (Thesis). Retrieved from https://researchspace.auckland.ac.nz/bitstream/handle/2292/6538/01front.pdf?sequence=2.
Reitzel, L. R., & Carbonell, J. L. (2006). The effectiveness of sexual offender treatment for juveniles as measured by recidivism: A meta-analysis. Sexual Abuse, 18, 401–421.
Rosenthal, R. (1979). The file drawer problem and tolerance for null results. Psychological Bulletin, 86, 638–641.
Ryan, G., Leversee, T., & Lane, S. (2010). Juvenile sexual offending, causes, consequences and correction. Hoboken: John Wiley and Sons.
Schmucker, M., & Lösel, F. (2015). The effects of sexual offender treatment on recidivism: An international meta-analysis of sound quality evaluations. Journal of Experimental Criminology, 11, 597–630.
*Schram, D. D., Darling Milloy, C., & Rowe, W. E. (1991). Juvenile sex offenders: a follow up study of reoffensive behavior. Unpublished research report. Washington: Washington State institute for public policy.
Seabloom, W., Seabloom, M. E., Seabloom, E., Barron, R., & Hendrickson, S. (2003). A 14 to 24 year longitudinal study of a comprehensive sexual health model treatment program for adolescent sex offenders. International Journal of Offender Therapy and Comparative Criminology, 47, 468–481.
Seto, M. C., & Lalumière, M. L. (2010). What is so special about male adolescent sexual offending? A review and test of explanations through meta-analysis. Psychological Bulletin, 136, 526–575.
Shrout, P. E. (1989). Measurement reliability and agreement in psychiatry. Statistical Methods in Medical Research, 7, 301–317.
Spruit, A., Assink, M., Van Vugt, E. S., Van Der Put, C. E., & Stams, G. J. J. M. (2016). The effects of physical activity interventions on psychosocial outcomes in adolescents: A meta-analytic review. Clinical Psychology Review, 45, 56–71.
Swenson, C. C., Henggeler, S. W., Taylor, I. S., & Addison, O. W. (2005). Multisystemic Therapy and Neighborhood Partnerships. New York: The Guildford Press.
Tabachnik, B. G., & Fidell, L. S. (2013). Using multivariate statistics (6th ed.). Boston: Allynand Bacon.
Ter Beek, E., Van Der Rijken, R. A. E., Kuiper, C. H. Z., Hendriks, J., & Stams, G. J. J. M. (2016). The allocation of sexually transgressive juveniles to intensive specialized treatment. International Journal of Offender Therapy and Comparative Criminology. Advance online publication.
Terrin, N., Schmid, C. H., Lau, J., & Olkin, I. (2003). Adjusting for publication bias in the presence of heterogeneity. Statistics in Medicine, 22, 2113–2126.
Thomas, B. H., Ciliska, D., Dobbins, M., & Micucci, S. (2004). A process for systematically reviewing the literature: Providing the research evidence for public health nursing interventions. Worldviews on Evidence-Based Nursing, 1, 176–184.
Van Den Noortgate, W., & Onghena, P. (2003). Multilevel meta-analysis: A comparison with traditional meta-analytical procedures. Educational and Psychological Measurement, 6, 765–790.
Van den Noortgate, W., López-López, J. A., Marín-Martínez, F., & Sánchez-Meca, J. (2013). Three-level meta-analysis of dependent effect sizes. Behavior Research Methods, 45, 576–594.
Van Outsem, R. E. (2009). Exploring psychological characteristics of sexually abusive juveniles. Unpublished Thesis. Amsterdam: Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam.
Van Wijk, A. P., Vreugdenhil, C., Van Horn, J., Vermeiren, R., & Doreleijers, T. A. H. (2007). Incarcerated Dutch juvenile sex offenders compared with non-sex offenders. Journal of Child Sexual Abuse, 16, 1–21.
Veneziano, C., & Veneziano, L. (2002). Adolescent sex offenders: A review of the literature. Trauma, Violence and Abuse, 3, 247–260.
Viechtbauer, W. (2010). Conducting meta-analyses in R with the metafor package. Journal of Statistical Software, 36, 1–48.
*Waite, D., Keller, A., McGarvey, E. L., Wieckowski, E., Pinkerton, R., & Brown, G. L. (2005). Juvenile sex offender re-arrest rates for sexual, violent nonsexual and property crimes: A 10-year follow-up study. Sexual Abuse: A Journal of Research and Treatment, 17, 313–331.
Walker, D. F., McGovern, S. K., Poey, E. L., & Otis, K. E. (2004). Treatment effectiveness for male adolescent sexual offenders: A meta-analysis and review. Journal of Child Sexual Abuse, 13, 281–293.
Weinrott, M. R., Riggan, M., & Frothingham, S. (1997). Reducing deviant arousal in juvenile sex offenders using vicarious sensitization. Journal of Interpersonal Violence, 12, 704–728.
Weisburd, D., Lum, C., & Petrosino, A. (2001). Does research design affect study outcomes in criminal justice? The Annals of the American Academy of Political and Social Science, 578, 50–70.
Weisz, J. R., Kuppens, S., Eckshtain, D., Ugueto, A. M., Hawley, K. M., & Jensen-Doss, A. (2013). Performance of evidence-based youth psychotherapies compared with usual clinical care. JAMA Psychiatry, 70, 750–761.
Wibbelink, C. J. M., & Assink, M. (2015). Manual for conducting a three-level meta-analysis in R. Amsterdam: Universiteit van Amsterdam.
Wilson, D. B. (2013). Practical meta-analysis effect size calculator. Retrieved from: http://www.campbellcollaboration.org/escalc/html/EffectSizeCalculator-Home.php.
Wittebrood, K. (2006). Slachtoffers van criminaliteit: Feiten en achtergronden. (Victims of crime: facts and backgrounds). Den Haag: Sociaal Cultureel Planbureau.
*Worling, J. R., & Curwen, T. (2000). Adolescent sexual offender recidivism: Success of specialized treatment and implications of risk prediction. Child Abuse and Neglect, 24, 965–982.
Worling, J. W., & Långström, N. (2003). Assessment of criminal recidivism risk with adolescents who have offended sexually: A review. Trauma, Violence & Abuse, 4, 341–362.
*Worling, J. R., Littlejohn, M. A., & Bookalam, M. A. (2010). 20-year prospective follow-up study of specialized treatment for adolescents who offend sexually. Behavioural Sciences and the Law, 28, 46–57.
Yun, I., & Lee, J. (2013). IQ and delinquency: The differential detection hypothesis revisited. Youth Violence and Juvenile Justice, 11, 196–211.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Human Studies
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
ter Beek, E., Spruit, A., Kuiper, C.H.Z. et al. Treatment Effect on Recidivism for Juveniles Who Have Sexually Offended: a Multilevel Meta-Analysis. J Abnorm Child Psychol 46, 543–556 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10802-017-0308-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10802-017-0308-3