Abstract
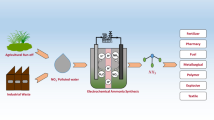
The electrochemical reduction of CO2 to formate was investigated in seawater as an alternative electrolyte to the bicarbonate buffer commonly used. Bismuth nanoparticles were prepared by pulsed laser ablation in liquids in ethanol, avoiding the use of toxic reagents or solvents. TEM analysis showed the nanoparticles were monodisperse and had an average number weighted diameter of 13 ± 5 nm. XRD showed that the nanoparticles were metallic which could suggest the presence of a carbon shell on the nanoparticles. However, this potential carbon shell does not appear to interfere with the electrocatalytic activity of the nanoparticles. A stepwise optimization of the catalyst weight fraction, Nafion® content, and loading showed that the best performances were achieved for 90% wt. bismuth nanoparticles on carbon, at a loading of 0.25 mg cm−2 and with 0.24% wt. Nafion®. The electrolysis in seawater showed similar or improved results both in terms of onset potential (− 1 V vs Ag/AgCl) selectivity (81 ± 4%) and activity (− 47 ± 11 mA cm−2) when compared to the reference bicarbonate buffer, demonstrating that seawater is an abundant, affordable alternative to the current buffer.
Graphical abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data are available upon request.
Code availability
NA.
References
Hori Y, Kikuchi K, Suzuki S (1985) Production of CO and CH4 in electrochemical reduction of CO2 at metal electrodes in aqueous hydrogencarbonate solution. Chem Lett 14(11):1695–1698
Olah GA, Prakash GKS, Goeppert A (2011) Anthropogenic chemical carbon cycle for a sustainable future. J Am Chem Soc 133(33):12881–12898
Nitopi S, Bertheussen E, Scott SB, Liu X, Engstfeld AK, Horch S, Seger B, Stephens IEL, Chan K, Hahn C, Nørskov JK, Jaramillo TF, Chorkendorff I (2019) Progress and perspectives of electrochemical CO2 reduction on copper in aqueous electrolyte. Chem Rev 119(12):7610–7672
Kuhl KP, Cave ER, Abram DN, Jaramillo TF (2012) New insights into the electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide on metallic copper surfaces. Energy Environ Sci 5(5):7050–7059
Wesselmark M, Lagergren C, Lindbergh G (2008) Methanol and formic acid oxidation in zinc electrowinning under process conditions. J Appl Electrochem 38(1):17–24
Westin EM, Schnitzer R, Ciccomascolo F, Maderthoner A, Grönlund K, Runnsjö G (2016) Austenitic stainless steel bismuth-free flux-cored wires for high-temperature applications. Weld World 60(6):1147–1158
Çögenli MS, Bayrakçeken Yurtcan A (2018) Graphene aerogel supported platinum nanoparticles for formic acid electro-oxidation. Mater Res Express 5(7):075513
Huttunen-Saarivirta E, Kuokkala VT, Kokkonen J, Paajanen H (2011) Corrosion effects of runway de-icing chemicals on aircraft alloys and coatings. Mater Chem Phys 126(1–2):138–151
Díaz-Sainz G, Alvarez-Guerra M, Solla-Gullón J, García-Cruz L, Montiel V, Irabien A (2019) CO2 electroreduction to formate: continuous single-pass operation in a filter-press reactor at high current densities using Bi gas diffusion electrodes. J CO2 Util 34(June):12–19
Díaz-Sainz G, Alvarez-Guerra M, Ávila-Bolívar B, Solla-Gullón J, Montiel V, Irabien A (2021) Improving trade-offs in the figures of merit of gas-phase single-pass continuous CO2 electrocatalytic reduction to formate. Chem Eng J 405:126965–126965
Gao T, Wen X, Xie T, Han N, Sun K, Han L, Wang H, Zhang Y, Kuang Y, Sun X (2019) Morphology effects of bismuth catalysts on electroreduction of carbon dioxide into formate. Electrochim Acta 305:388–393
Miola M, De Jong BCA, Pescarmona PP (2020) An efficient method to prepare supported bismuth nanoparticles as highly selective electrocatalyst for the conversion of CO2 into formate. Chem Commun 56(95):14992–14995
Wang Q, Zhu C, Wu C, Yu H (2019) Direct synthesis of bismuth nanosheets on a gas diffusion layer as a high-performance cathode for a coupled electrochemical system capable of electroreduction of CO2 to formate with simultaneous degradation of organic pollutants. Electrochim Acta 319:138–147
Bertin E, Garbarino S, Roy C, Kazemi S, Guay D (2017) Selective electroreduction of CO2 to formate on Bi and oxide-derived Bi films. J CO2 Util 19:276–283
Dadashi S, Poursalehi R, Delavari H (2018) Optical and structural properties of Bi-based nanoparticles prepared via pulsed Nd:YAG laser ablation in organic liquids. Appl Phys A 124(6):1–7
Marzun G, Levish A, Mackert V, Kallio T, Barcikowski S, Wagener P (2017) Laser synthesis, structure and chemical properties of colloidal nickel-molybdenum nanoparticles for the substitution of noble metals in heterogeneous catalysis. J Colloid Interface Sci 489:57–67
Streubel R, Bendt G, Gökce B (2016) Pilot-scale synthesis of metal nanoparticles by high-speed pulsed laser ablation in liquids. Nanotechnology 27(20):1–9
Reske R, Mistry H, Behafarid F, Roldan Cuenya B, Strasser P (2014) Particle size effects in the catalytic electroreduction of CO2 on Cu nanoparticles. J Am Chem Soc 136(19):6978–6986
Kas R, Yang K, Bohra D, Kortlever R, Burdyny T, Smith WA (2020) Electrochemical CO2 reduction on nanostructured metal electrodes: fact or defect? Chem Sci 11(7):1738–1749
de Salles M, Pupo M, Kortlever R (2019) Electrolyte effects on the electrochemical reduction of CO2. ChemPhysChem 20(22):2926–2935
Varela AS (2020) The importance of pH in controlling the selectivity of the electrochemical CO2 reduction. Curr Opin Green Sustain Chem 26:100371
König M, Vaes J, Klemm E, Pant D (2019) Solvents and supporting electrolytes in the electrocatalytic reduction of CO2. iScience 19:135–160
Gattrell M, Gupta N, Co A (2006) A review of the aqueous electrochemical reduction of CO2 to hydrocarbons at copper. J Electroanal Chem 594(1):1–19
Kopljar D, Inan A, Vindayer P, Wagner N, Klemm E (2014) Electrochemical reduction of CO2 to formate at high current density using gas diffusion electrodes. J Appl Electrochem 44(10):1107–1116
Nakata K, Ozaki T, Terashima C, Fujishima A, Einaga Y (2014) High-yield electrochemical production of formaldehyde from CO2 and seawater. Angewandte Chemie Int Ed 53(3):871–874
Lee CY, Wallace GG (2018) CO2 electrolysis in seawater: calcification effect and a hybrid self-powered concept. J Mater Chem A 6(46):23301–23307
Flores-Castañeda M, Camps E, Camacho-López M, Muhl S, García E, Figueroa M (2015) Bismuth nanoparticles synthesized by laser ablation in lubricant oils for tribological tests. J Alloys Compd 643:S67
Escobar-Alarcón L, Granados EV, Solís-Casados D, Olea-Mejía O, Espinosa-Pesqueira M, Haro-Poniatowski E (2016) Preparation of bismuth-based nanosheets by ultrasound-assisted liquid laser ablation. Appl Phys A 122:433
Philips MF, Gruter G-JM, Koper MTM, Schouten KJP (2020) Optimizing the electrochemical reduction of CO2 to formate: a state-of-the-art analysis. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 8(41):15430–15444
Marzun G, Bönnemann H, Lehmann C, Spliethoff B, Weidenthaler C, Barcikowski S (2017) Role of dissolved and molecular oxygen on Cu and PtCu alloy particle structure during laser ablation synthesis in liquids. ChemPhysChem 18(9):1175–1184
Waag F, Li Y, Ziefuß AR, Bertin E, Kamp M, Duppel V, Marzun G, Kienle L, Barcikowski S, Gökce B (2019) Kinetically-controlled laser-synthesis of colloidal high-entropy alloy nanoparticles. RSC Adv 9(32):18547–18558
Chlistunoff J, Sansinena JM (2016) Nafion induced surface confinement of oxygen in carbon-supported oxygen reduction catalysts. J Phys Chem C 120(49):28038–28048
Dubau L, Castanheira L, Berthomé G, Maillard F (2013) An identical-location transmission electron microscopy study on the degradation of Pt/C nanoparticles under oxidizing, reducing and neutral atmosphere. Electrochim Acta 110:273–281
Koh JH, Won DH, Eom T, Kim N-K, Jung KD, Kim H, Hwang YJ, Min BK (2017) Facile CO2 electro-reduction to formate via oxygen bidentate intermediate stabilized by high-index planes of Bi dendrite catalyst. ACS Catal 7(8):5071–5077
Yang K, Kas R, Smith WA, Burdyny T (2021) Role of the carbon-based gas diffusion layer on flooding in a gas diffusion electrode cell for electrochemical CO2 reduction. ACS Energy Lett 6(1):33–40
Chang J, Duan F, Su C, Li Y, Cao H (2020) Removal of chloride ions using a bismuth electrode in capacitive deionization (CDI). Environ Sci 6(2):373–382
Piao G, Yoon SH, Han DS, Park H (2020) Ion-enhanced conversion of CO2 into formate on porous dendritic bismuth electrodes with high efficiency and durability. Chemsuschem 13(4):698–706
Yoon SH, Piao G, Park H, Elbashir NO, Han DS (2020) Theoretical insight into effect of cation–anion pairs on CO2 reduction on bismuth electrocatalysts. Appl Surf Sci 532:147459
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC) via the Discovery Grant program. The financial support of the start-up fund of St Francis Xavier University is gratefully acknowledged. Two of the authors, Aaron Mason and William (Joey) Murphy, would like to acknowledge the financial support of the Canada Summer jobs program. Another author, Kyla MacDonald, is also grateful for the financial support received through NSERC Undergraduate Research Award and the John P. Cunningham Award. The assistance and support of Arkadiy Reunov and Yulia Reunova with the SEM measurements of the ablation craters of the bismuth target after ablation was also highly appreciated.
Funding
This work was supported by the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC) via the Discovery Grant program and the start-up fund of St Francis Xavier University. Students were funded through NSERC Undergraduate Research Award and the Canada Summer jobs program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Mason, A., MacDonald, K., Murphy, W. et al. Electroreduction of CO2 on bismuth nanoparticles in seawater. J Appl Electrochem 53, 217–226 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-022-01774-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-022-01774-y