Abstract
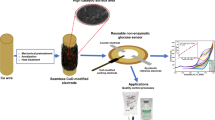
A carbon paste electrode, modified with chitosan-based magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer (CS-MIP), was utilized as a highly sensitive electrochemical sensor for the determination of lactic acid (LA) in spoilage milk samples. The electrochemical measurements were indirectly performed by cyclic voltammetry and differential pulse voltammetry in the presence of K3[Fe(CN)6] as a redox probe. A decrease in the faradic current of the redox probe was imputed to the gate effect mechanism, which was related to electrical effects causing to disrupt the electronic transport pathway. The linear response ranges were 0.01–10.0 µM and 10.0–500.0 µM, and the detection limit was 0.005 µM. The electrochemical sensor was used for the determination of lactic acid in real milk samples with satisfactory results.
Graphic abstract





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shumyantseva VV, Bulko TV, Sigolaeva LV, Kuzikov AV, Pogodin PV, Archakov AI (2018) Molecular imprinting coupled with electrochemical analysis for plasma samples classification in acute myocardial infarction diagnostic. Biosens Bioelectron 99:216–222
Yoshikawa M, Tharpa K, Dima S-O (2016) Molecularly imprinted membranes: past, present, and future. Chem Rev 116(19):11500–11528
Zamora-Gálvez A, Ait-Lahcen A, Mercante LA, Morales-Narváez E, Amine A, Merkoçi A (2016) Molecularly imprinted polymer-decorated magnetite nanoparticles for selective sulfonamide detection. Anal Chem 88(7):3578–3584
Gui R, Jin H, Guo H, Wang Z (2018) Recent advances and future prospects in molecularly imprinted polymers-based electrochemical biosensors. Biosens Bioelectron 100:56–70
Zhou T, Feng Y, Zhou L, Tao Y, Luo D, Jing T, Shen X, Zhou Y, Mei S (2016) Selective and sensitive detection of tetrabromobisphenol-A in water samples by molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensor. Sens Actuators B: Chem 236:153–162
Duan H, Li L, Wang X, Wang Y, Li J, Luo C (2015) A sensitive and selective chemiluminescence sensor for the determination of dopamine based on silanized magnetic graphene oxide-molecularly imprinted polymer. Spectrochim Acta Part A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 139:374–379
Duan H, Li X, Li L, Wang X, Feng J, Sun M, Luo C (2014) A novel chemiluminescence sensor for determination of vanillin with magnetite–graphene oxide molecularly imprinted polymers. Anal Methods 6(21):8706–8712
Han Q, Wang X, Yang Z, Zhu W, Zhou X, Jiang H (2014) Fe3O4@ rGO doped molecularly imprinted polymer membrane based on magnetic field directed self-assembly for the determination of amaranth. Talanta 123:101–108
Long F, Zhang Z, Yang Z, Zeng J, Jiang Y (2015) Imprinted electrochemical sensor based on magnetic multi-walled carbon nanotube for sensitive determination of kanamycin. J Electroanal Chem 755:7–14
Holm A, Kunz L, Riscoe AR, Kao K-C, Cargnello M, Frank CW (2019) General self-assembly method for deposition of graphene oxide into uniform close-packed monolayer films. Langmuir 35(13):4460–4470
Liu S, Zeng TH, Hofmann M, Burcombe E, Wei J, Jiang R, Kong J, Chen Y (2011) Antibacterial activity of graphite, graphite oxide, graphene oxide, and reduced graphene oxide: membrane and oxidative stress. ACS Nano 5(9):6971–6980
Yao H, Jin L, Sue H-J, Sumi Y, Nishimura R (2013) Facile decoration of Au nanoparticles on reduced graphene oxide surfaces via a one-step chemical functionalization approach. J Mater Chem A 1(36):10783–10789
Gan T, Lv Z, Sun J, Shi Z, Liu Y (2016) Preparation of graphene oxide-wrapped carbon sphere@ silver spheres for high performance chlorinated phenols sensor. J Hazard Mater 302:188–197
Gan T, Wang Z, Shi Z, Zheng D, Sun J, Liu Y (2018) Graphene oxide reinforced core–shell structured Ag@ Cu2O with tunable hierarchical morphologies and their morphology–dependent electrocatalytic properties for bio-sensing applications. Biosens Bioelectron 112:23–30
Moro G, De Wael K, Moretto LM (2019) Challenges in the electrochemical (bio) sensing of nonelectroactive food and environmental contaminants. Curr Opin Electrochem 16:57–65
Karimian N, Vagin M, Zavar MHA, Chamsaz M, Turner AP, Tiwari A (2013) An ultrasensitive molecularly-imprinted human cardiac troponin sensor. Biosens Bioelectron 50:492–498
Sharma PS, Garcia-Cruz A, Cieplak M, Noworyta KR, Kutner W (2019) ‘Gate effect’ in molecularly imprinted polymers: the current state of understanding. Curr Opin Electrochem 16:50–56
Lach P, Cieplak M, Majewska M, Noworyta KR, Sharma PS, Kutner W (2019) “Gate effect” in p-synephrine electrochemical sensing with a molecularly imprinted polymer and redox probes. Anal Chem 91(12):7546–7553
Yoshimi Y, Sato K, Ohshima M, Piletska E (2013) Application of the ‘gate effect’ of a molecularly imprinted polymer grafted on an electrode for the real-time sensing of heparin in blood. Analyst 138(17):5121–5128
Gan T, Lv Z, Sun Y, Shi Z, Sun J, Zhao A (2016) Highly sensitive and molecular selective electrochemical sensing of 6-benzylaminopurine with multiwall carbon nanotube@ SnS 2-assisted signal amplification. J Appl Electrochem 46(3):389–401
Chen C, Bloomfield AJ, Sheehan SW (2017) Selective electrochemical oxidation of lactic acid using iridium-based catalysts. Ind Eng Chem Res 56(13):3560–3567
Tsai Y-C, Chen S-Y, Liaw H-W (2007) Immobilization of lactate dehydrogenase within multiwalled carbon nanotube-chitosan nanocomposite for application to lactate biosensors. Sens Actuators B 125(2):474–481
Bouteille R, Gaudet M, Lecanu B, This H (2013) Monitoring lactic acid production during milk fermentation by in situ quantitative proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. J Dairy Sci 96(4):2071–2080
Shapiro F, Silanikove N (2010) Rapid and accurate determination of D-and L-lactate, lactose and galactose by enzymatic reactions coupled to formation of a fluorochromophore: applications in food quality control. Food Chem 119(2):829–833
Alizadeh T, Nayeri S, Mirzaee S (2019) A high performance potentiometric sensor for lactic acid determination based on molecularly imprinted polymer/MWCNTs/PVC nanocomposite film covered carbon rod electrode. Talanta 192:103–111
Hashemzadeh S, Omidi Y, Rafii-Tabar H (2019) Amperometric lactate nanobiosensor based on reduced graphene oxide, carbon nanotube and gold nanoparticle nanocomposite. Microchim Acta 186(10):680
Ewaschuk JB, Zello GA, Naylor JM, Brocks DR (2002) Metabolic acidosis: separation methods and biological relevance of organic acids and lactic acid enantiomers. J Chromatogr B 781(1–2):39–56
Paik MJ, Cho EY, Kim H, Kim KR, Choi S, Ahn YH, Lee G (2008) Simultaneous clinical monitoring of lactic acid, pyruvic acid and ketone bodies in plasma as methoxime/tert-butyldimethylsilyl derivatives by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry in selected ion monitoring mode. Biomed Chromatogr 22(5):450–453
Figenschou DL, Marais JP (1991) Spectrophotometric method for the determination of microquantities of lactic acid in biological material. Anal Biochem 195(2):308–312
Zouaoui F, Bourouina-Bacha S, Bourouina M, Jaffrezic-Renault N, Zine N, Errachid A (2020) Electrochemical sensors based on molecularly imprinted chitosan: a review. TrAC Trends Anal Chem. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2020.115982
Yang Y, Yan W, Guo C, Zhang J, Yu L, Zhang G, Wang X, Fang G, Sun D (2020) Magnetic molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensors: a review. Anal Chim Acta 1106:1–21
Gan T, Li J, Zhao A, Xu J, Zheng D, Wang H, Liu Y (2018) Detection of theophylline using molecularly imprinted mesoporous silica spheres. Food Chem 268:1–8
Wei P, Zhu Z, Song R, Li Z, Chen C (2019) An ion-imprinted sensor based on chitosan-graphene oxide composite polymer modified glassy carbon electrode for environmental sensing application. Electrochim Acta 317:93–101
Zhang Z, Kong J (2011) Novel magnetic Fe3O4@ C nanoparticles as adsorbents for removal of organic dyes from aqueous solution. J Hazard Mater 193:325–329
Zaaba N, Foo K, Hashim U, Tan S, Liu W-W, Voon C (2017) Synthesis of graphene oxide using modified hummers method: solvent influence. Proc Eng 184:469–477
Kong D, Wang N, Qiao N, Wang Q, Wang Z, Zhou Z, Ren Z (2017) Facile preparation of ion-imprinted chitosan microspheres enwrapping Fe3O4 and graphene oxide by inverse suspension cross-linking for highly selective removal of copper (II). ACS Sustain Chem Eng 5(8):7401–7409
Wang Y, Yao L, Liu X, Cheng J, Liu W, Liu T, Sun M, Zhao L, Ding F, Lu Z (2019) CuCo2O4/N-Doped CNTs loaded with molecularly imprinted polymer for electrochemical sensor: preparation, characterization and detection of metronidazole. Biosens Bioelectron 142:111483
Anirudhan TS, Alexander S (2015) Design and fabrication of molecularly imprinted polymer-based potentiometric sensor from the surface modified multiwalled carbon nanotube for the determination of lindane (γ-hexachlorocyclohexane), an organochlorine pesticide. Biosens Bioelectron 64:586–593
Deng P, Xu Z, Li J, Kuang Y (2013) Acetylene black paste electrode modified with a molecularly imprinted chitosan film for the detection of bisphenol A. Microchim Acta 180(9–10):861–869
Takahashi S, Kurosawa S, Anzai J (2008) Electrochemical determination of L-lactate using phenylboronic acid monolayer‐modified electrodes. Electroanalysis 20(7):816–818
Xu L, Li J, Zhang J, Sun J, Gan T, Liu Y (2020) A disposable molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensor for the ultra-trace detection of the organophosphorus insecticide phosalone employing monodisperse Pt-doped UiO-66 for signal amplification. Analyst 145(9):3245–3256
Wang Z, Li H, Chen J, Xue Z, Wu B, Lu X (2011) Acetylsalicylic acid electrochemical sensor based on PATP–AuNPs modified molecularly imprinted polymer film. Talanta 85(3):1672–1679
Hernández-Ibáñez N, García-Cruz L, Montiel V, Foster CW, Banks CE, Iniesta J (2016) Electrochemical lactate biosensor based upon chitosan/carbon nanotubes modified screen-printed graphite electrodes for the determination of lactate in embryonic cell cultures. Biosens Bioelectron 77:1168–1174
Hashemzadeh S, Omidi Y, Rafii-Tabar H (2019) Amperometric lactate nanobiosensor based on reduced graphene oxide, carbon nanotube and gold nanoparticle nanocomposite. Microchim Acta 186(10):1–8
Goran JM, Lyon JL, Stevenson KJ (2011) Amperometric detection of l-lactate using nitrogen-doped carbon nanotubes modified with lactate oxidase. Anal Chem 83(21):8123–8129
Lei Y, Luo N, Yan X, Zhao Y, Zhang G, Zhang Y (2012) A highly sensitive electrochemical biosensor based on zinc oxide nanotetrapods for L-lactic acid detection. Nanoscale 4(11):3438–3443
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to express their gratitude to Shiraz University Research Council for the financial support of this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicts of interest to declare.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mahmoudi, Z., Tashkhourian, J. & Hemmateenejad, B. Voltammetric determination of lactic acid in milk samples using carbon paste electrode modified with chitosan-based magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer. J Appl Electrochem 52, 35–44 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-021-01619-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-021-01619-0