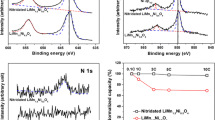
Abstract
A simple method was applied to control the morphology of LiMn2O4 and Li1.05Mn1.97Nb0.03O4 in the sintering process by premixing a suitable proportion of acetylene black in the raw material. Both specific discharge capacity and cycling stability of the samples were improved. The results demonstrated that the doped samples showed excellent electrochemical performance at both 25 °C and 55 °C.
Graphic Abstract













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Xu G, Liu Z, Zhang C et al (2015) Strategies for improving the cyclability and thermo-stability of LiMn2O4-based batteries at elevated temperatures. J Mater Chem A 3(8):4092–4123
Jang DH, Shin YJ et al (1996) Dissolution of spinel oxides and capacity losses in 4V Li/LixMn2O4 cells. J Elctrochem Soc 143(7):2204–2211
Hunter JC (1981) Preparation of a new crystal form of manganese dioxide: λ-MnO2. J Solid State Chem 39(2):142–147
Jang DH, Oh SM (1997) Electrolyte effects on spinel dissolution and cathodic capacity losses in 4 V Li/LixMn2O4 rechargeable cells. J Electrochem Soc 144(10):3342–3348
Wang L-F, Chin-Ching Ou et al (2003) Study of Mn dissolution from LiMn2O4 spinel electrodes using rotating ring-disk collection experiments. J Electrochem Soc 150(7):A905–A911
Bhandari A, Bhattacharya J (2017) Review—manganese dissolution from spinel cathode: few unanswered questions. J Electrochem Soc 164(2):A106–A127
Amarilla J, Petrov K et al (2009) Sucrose-aided combustion synthesis of nanosized LiMn1.99− yLiyM0.01O4 (M= Al3+, Ni2+, Cr3+, Co3+, y= 001 and 006) spinels: characterization and electrochemical behavior at 25 and at 55 °C in rechargeable lithium cells. J Power Sources 191(2):591–600
Xiong LL, Xu YL et al (2012) Synthesis and electrochemical characterization of multi-cations doped spinel LiMn2O4 used for lithium ion batteries. J Power Sources 199:214–219
Takahashi M, Yoshida T et al (2006) Effect of oxygen deficiency reduction in Mg-doped Mn-spinel on its cell storage performance at high temperature. Electrochim Acta 51(25):5508–5514
Hao Wu, Liu W et al (2015) Influence of co-substitution on structure and electrochemical performances of Li-rich spinel LiMn2O4. Integr Ferroelectr 164(1):23–32
Yao Fu, Jiang H et al (2015) Synergistic enhancement effect of Al doping and highly active facets of LiMn2O4 cathode materials for lithium-ion batteries. Ind Eng Chem Res 54(15):3800–3805
Lee YK, Park J et al (2016) Electronic and bonding properties of LiMn2O4 spinel with different surface orientations and doping elements and their effects on manganese dissolution. J Electrochem Soc 163(7):A1359–A1368
Akhoon SA, Rubab S et al (2017) Enhanced cycling properties and better rate capabilities of Al-doped LiMn2O4 nanorods and nanospheres. Mater Res Express 4(10):105016
Iqbal A, Iqbal Y et al (2017) Low content Ni and Cr Co-doped LiMn2O4 with enhanced capacity retention. Ionics 23(8):1995–2003
Yi TF, Xie Y et al (2012) High rate micron-sized niobium-doped LiMn1.5Ni0.5O4 as ultra high power positive-electrode material for lithium-ion batteries. J Power Sources 211:59–65
Xia Y, Zhang WK et al (2011) Synthesis and electrochemical properties of Nb-doped Li3V2(PO4)3/C cathode materials for lithium-ion batteries. Mater Sci Eng B 176(8):633–639
Li J, Tian Y et al (2012) Influence of Nb5+ doping on structure and electrochemical properties of spinel Li1.02Mn2O4. J Mater Sci Technol 28(9):817–822
Benedek R, Thackeray MM (2011) Simulation of the surface structure of lithium manganese oxide spinel. Phys Rev B 83:195439
Kaga K, Hiroaki M et al (2010) Effect of polyhedron primary particle of Mn-spinel on electrochemical and Mn dissolution properties at high temperature. In: The 51th battery symposium in Japan
Lee SXLT, Huasheng Hu et al (2013) Morphology-control preparation and electrochemical performance of Mn-spinel cathode materials. China Sci Bull 58:3350–3356 (in Chinese)
Kim JS, Kim KS et al (2012) A Truncated manganese spinel cathode for excellent power and lifetime in lithium-ion batteries. Nano Lett 12:6358–6365
Bao SJ, Li CM et al (2007) Morphology and electrochemistry of LiMn2O4 optimized by using different Mn-sources. J Power Sources 164(2):885–889
Jiang JB, Du K et al (2013) Syntheses of spherical LiMn2O4 with Mn3O4 and its electrochemistry performance. J Alloys Compds 577:138–142
Fey GTK, Cho YD et al (2004) A TEA-starch combustion method for the synthesis of fine-particulate LiMn2O4. Mater Chem Phys 87(2–3):275–284
Yu AS, Frech R (2002) Novel high rate lithium intercalation cathode materials. J Electrochem Soc 149(2):A99–A102
Zhang Na, Tang Z et al (2005) Research on performance of spinel LiMn1.98RE0.02O4 (RE=Ce, Nd). J Mater Eng 11:35–37
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the Science and Technology Program of State Grid Corporation of China (Program Title: Development of Manganese-based Lithium Ion Batteries with Low Cost and High Safety).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pan, K., Hu, C., Sun, Z. et al. Structural and electrochemical characterization of LiMn2O4 and Li1.05Mn1.97Nb0.03O4 with excellent high-temperature cycling stability synthesized by a simple route. J Appl Electrochem 50, 451–462 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-020-01403-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-020-01403-6