Abstract
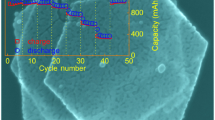
Novel goethite (α-FeOOH) corner-truncated tetragonal prisms (CTPs) with a length of about 1 μm and a width of about 200 nm have been synthesized by a hydrothermal method. The morphology, structure and electrochemical properties of CTPs are systematically studied. The obtained α-FeOOH CTPs exhibit high-quality single-crystalline nature. In addition, the single α-FeOOH corner-truncated tetragonal prism (CTP) is enclosed by six side facets, two {020} and four {110}. Depending on the reaction time, two different types of top-endings, one flat or two canted facets, are obtained. The formation of α-FeOOH is associated with the growth and subsequent phase transformation of β-FeOOH. The CTP contributes to structural stability and avoids the common pulverization process of electrodes. In addition, tiny crystallites are generated during the cycle, which increase the contact area between the electrode and electrolyte. Therefore, the α-FeOOH CTPs electrode displays excellent cycling performance with a reversible specific capacity of 870 mAh g−1 at 100 mA g−1 after 100 cycles.
Graphical abstract














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armand M, Tarascon JM (2008) Building better batteries. Nature 451:652–657
Wang ZY, Zhou L, Low XW (2012) Metal oxide hollow nanostructures for lithium-ion batteries. Adv Mater 24:1903–1911
Yu S, Lee SH, Lee DJ, Sung Y, Hyeon T (2016) Conversion reaction-based oxide nanomaterials for lithium ion battery anodes. Small 12:2146–2172
Navrotsky A, Mazeina L, Majzlan J (2008) Size-driven structural and thermodynamic complexity in iron oxides. Science 319:1635–1638
Zhang L, Wu HB, Lou XW (2014) Iron-oxide-based advanced anode materials for lithium-ion batteries. Adv Energy Mater 4:1300958
Zheng F, He M, Yang Y, Chen Q (2015) Nano electrochemical reactors of Fe2O3 nanoparticles embedded in shells of nitrogen-doped hollow carbon spheres as high-performance anodes for Lithium-ion batteries. Nanoscale 7:3410–3417
Imtiaz M, Chen Z, Zhu CL, Pan H, Zada I, Li Y, Bokhari SW, Luan RY, Nigar S, Zhu SM (2018) In situ growth of β-FeOOH on hierarchically porous carbon as anodes for high-performance lithium-ion batteries. Electrochim Acta 283:401–409
Bhuvaneswari S, Pratheeksha PM, Anandan S, Rangappa D, Gopalan R, Rao TN (2014) Efficient reduced graphene oxide grafted porous Fe3O4 composite as a high performance anode material for Li-ion batteries. Phys Chem Chem Phys 16:5284–5294
Qi H, Cao L, Li J, Huang J, Xu Z, Cheng Y, Kong X, Yanagisawa K (2016) High pseudocapacitance in FeOOH/rGO composites with superior performance for high rate anode in Li-ion battery. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8:35253–35263
Zhai Y, Xu L, Qian Y (2016) Ce-doped α-FeOOH nanorods as high-performance anode material for energy storage. J Power Sources 327:423–431
Yu LH, Xi SB, Wei C, Zhang WY, Du YH, Yan QY, Xu ZC (2015) Superior lithium storage properties of β-FeOOH. Adv Energy Mater 5:1401517
Yu LH, Wei C, Yan QY, Xu ZJ (2015) Controlled synthesis of high-performance β-FeOOH anodes for lithium-ion batteries and their size effects. Nano Energy 13:397–404
Wu R, Wang DP, Rui XH, Liu B, Zhou K, Law AWK, Yan QY, Wei J, Chen Z (2015) In-situ formation of hollow hybrids composed of cobalt sulfides embedded within porous carbon polyhedra/carbon nanotubes for high-performance lithium-ion batteries. Adv Mater 27:3038–3044
Wu R, Qian X, Zhou K, Wei J, Lou J, Ajayan PM (2014) Porous spinel ZnxCo3-xO4 hollow polyhedra templated for high-rate lithium-ion batteries. ACS Nano 8:6297–6303
Liu DQ, Wang X, Wang XB, Tian W, Bando Y, Golberg D (2013) Co3O4 nanocages with highly exposed {110} facets for high-performance lithium storage. Sci Rep 3:2543
Kakuta S, Numata T, Okayama T (2014) Shape effects of goethite particles on their photocatalytic activity in the decomposition of acetaldehyde. Catal Sci Technol 4:164–169
Frost R, Zhu H, Wu P, Bostrom T (2005) Synthesis of acicular goethite with surfactants. Mater Lett 59:2238–2241
Meng F, Morin S, Jin S (2011) Rational solution growth of α-FeOOH nanowires driven by screw dislocations and their conversion to α-Fe2O3 nanowires. J Am Chem Soc 133:8408–8411
Geng FX, Zhao ZG, Cong HT, Geng JX, Cheng HM (2006) An environment-friendly microemulsion approach to α-FeOOH nanorods at room temperature. Mater Res Bull 41:2238–2243
Zhu T, Chen JS, Lou XW (2011) Glucose-assisted one-pot synthesis of FeOOH nanorods and their transformation to Fe3O4@carbon nanorods for application in lithium ion batteries. J Phys Chem C 115:9814–9820
Varanda LC, Morales MP, Jafelicci JM, Serna CJ (2002) Monodispersed spindle-type goethite nanoparticles from FeIII solutions. J Mater Chem 12:3649–3653
Liang H, Chen W, Wang R, Qi Z, Mi J, Wang Z (2015) X-shaped hollow α-FeOOH penetration twins and their conversion to α-Fe2O3 nanocrystals bound by high-index facets with enhanced photocatalytic activity. Chem Eng J 274:224–230
Zhang CM, Zhu JX, Rui XH, Chen J, Sim DH, Shi WH, Hng HH, Lim TM, Yan QY (2012) Synthesis of hexagonal-symmetry α-iron oxyhydroxide crystals using reduced graphene oxide as a surfactant and their Li storage properties. CrystEngComm 14:147–153
Granados-Correa F, Corral-Capulin NG, Olguín MT, Acosta-León CE (2011) Comparison of the Cd(II) adsorption processes between boehmite (γ-AlOOH) and goethite (α-FeOOH). Chem Eng J 171:1027–1034
Mao XB, Yang HC, Zhou XM, Wang CX, Wnag YS, Yang YL, Wnag C, Liu G (2010) Straight and branched goethite topology by oriented attachment at high pH. Cryst Growth Des 10:504–509
Lin M, Tng L, Lim T, Choo M, Zhang J, Tan HR, Bai S (2014) Hydrothermal synthesis of octadecahedral hematite (α-Fe2O3) nanoparticles: an epitaxial growth from goethite (α-FeOOH). J Phys Chem C 118:10903–10910
Chun C, Penn RL, Arnold WA (2006) Kinetic and microscopic studies of reductive transformations of organic contaminants on goethite. Environ Sci Technol 40:3299–3304
Jolivet JP, Chanéac C, Tronc E (2004) Iron oxide chemistry: from molecular clusters to extended solid networks. Chem Commun 35:477–483
Almeida TP, Fay MW, Zhu Y, Brown PD (2010) A valve-assisted snapshot approach to understand the hydrothermal synthesis of α-Fe2O3 nanorods. CrystEngComm 12:1700–1704
Wei C, Nan Z (2011) Effects of experimental conditions on one-dimensional single-crystal nanostructure of β-FeOOH. Mater Chem Phys 127:220–226
Morterra C, Chiorlno A, Borello E (1984) An IR spectroscopic characterization of α-FeOOH (goethite). Mater Chem Phys 10:119–138
Liang J, Luo M, Yang C, Fang J, Li L (2011) Synthesis of spindle-shaped α-FeOOH and α-Fe2O3 nanocrystals. Cryst Res Technol 46:493–496
Frandsen C, Legg BA, Comolli LR, Zhang HZ, Gilbert B, Johnson E, Banfield JF (2014) Aggregation-induced growth and transformation of β-FeOOH nanorods to micron-sized α-Fe2O3 spindles. CrystEngComm 16:1451–1458
Burleson DJ, Penn RL (2006) Two-step growth of goethite from ferrihydrite. Langmuir 22:402–409
Guyodo Y, Mostrom A, Penn RL, Banerjee SK (2003) From nanodots to nanorods: oriented aggregation and magnetic evolution of nanocrystalline goethite. Geophys Res Lett 30:405–414
Banfield JF, Welch SA, Zhang HZ, Ebert TT, Penn RL (2000) Aggregation-based crystal growth and microstructure development in natural iron oxyhydroxide biomineralization products. Science 289:751–754
Burrows ND, Kesselman E, Sabyrov K, Stemig A, Talmon Y, Penn RL (2014) Crystalline nanoparticle aggregation in non-aqueous solvents. CrystEngComm 16:1472–1481
Raming TP, Winnubst AJA, van Kats CM, Philipse AP (2002) The synthesis and magnetic properties of nanosized hematite (α-Fe2O3) particles. J Colloid Interface Sci 249:346–350
Wiogo H, Lim M, Munroe P, Amal R (2011) Understanding the formation of iron oxide nanoparticles with acicular structure from iron(III) chloride and hydrazine monohydrate. Cryst Growth Des 11:1689–1696
Lou X, Wu X, Zhang Y (2009) Goethite nanorods as anode electrode materials for rechargeable Li-ion batteries. Electrochem Commun 11:1696–1699
Wang J, Polleux J, Lim J, Dunn B (2007) Pseudocapacitive contributions to electrochemical energy storage in TiO2 anatase nanoparticles. J Phys Chem C 111:14925–14931
Chao D, Zhu C, Yang PH, Xia XH, Liu JL, Wang J, Fan XF, Savilov SV, Lin J, Fan HJ, Shen ZX (2016) Array of nanosheets render ultrafast and high-capacity Na-ion storage by tunable pseudocapacitance. Nature Commun 7:12122
Shenouda AY, Liu HK (2008) Electrochemical behavior of tin borophosphate negative electrodes for energy storage systems. J Power Sources 185:1386–1391
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 10974105, 21701095), Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province, China (Grant No. ZR2017BEM007), Program of Science and Technology for Higher Education in Shandong Province, China (Grant No.:J17KA010), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (Grant No. 2017M622131), and High-end Foreign Experts Recruitment Programs (Grant Nos. GDW20163500110 and GDW20173500154). Y. Q. Wang would also like to thank the financial support from the Top-notch Innovative Talent Program of Qingdao City (Grant No. 13-CX-08), the Taishan Scholar Program of Shandong Province, and Qingdao International Center for Semiconductor Photoelectric Nanomaterials and Shandong Provincial University Key Laboratory of Optoelectrical Material Physics and Devices.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, H., Zou, J., Ding, Y. et al. Novel α-FeOOH corner-truncated tetragonal prisms: crystal structure, growth mechanism and lithium storage properties. J Appl Electrochem 49, 657–669 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-019-01315-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-019-01315-0