Abstract
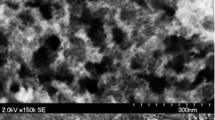
Microbial fuel cells (MFCs) are a potential method for enhanced water and waste treatment, which offer the additional benefit of energy generation. Manganese oxide was prepared by a simple chemical oxidation using potassium permanganate. Carbon-supported manganese oxide nanoparticles were successfully characterised as cathode materials for MFCs. The manganese oxide particles when used in a two-chamber MFC, using inoculum from an anaerobically digested sewage sludge, were found to exhibit similar oxygen reduction performance to that in separate electrochemical tests. MFC tests were conducted in a simple two chamber cell using aqueous air-saturated catholytes separated from the anode chamber by a Nafion membrane. MFC peak power densities were ca. 161 mW m−2 for MnO x /C compared to 193 mW m−2 for a benchmark Pt/C, in neutral solution at room temperature. The catalyst materials demonstrated good stability in the 7.0–10.0 pH range. Theoretical (IR free) peak power densities were 937 mW m−2 for MnO x /C compared with 1037 mW m−2 for Pt/C in the same experimental conditions: showing the MFCs performances can easily be improved by using more favourable conditions (more conductive electrolyte, improved cathode catalyst etc.). Our studies indicated that the use of our low cost MnO x /C catalysts is of potential interest for the future application of MFC systems.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Logan B (2005) Water Environ Res 77:211
Logan B (2004) Environ Sci Technol A38:160A
Rabaey K, Clauwaert P, Aelterman P, Verstraete W (2005) Environ Sci Technol 39:8077
Tender LM, Reimers CE, Stecher HA, Holmes DE, Bond DR, Lowy DA, Pilobello K, Fertig SJ, Lovley DR (2002) Nat Biotechnol 20:821
Kim HJ, Park HS, Hyun MS, Chang IS, Kim M, Kim BH (2002) Enz Microbial Technol 30:145
Jang JK, Pham TH, Chang LS, Kang KH, Moon H, Cho KS, Kim BH (2003) Process Biochem 39:1007
Delong EF, Chandler P (2002) Nat Biotechnol 20:788
Liu H, Ramnarayanan R, Logan B (2004) Environ Sci Technol 38:2281
Logan B (2005) Water Sci Technol 52:31
Debabov VG (2008) Microbiology 77:123–131
Rinaldi A, Mecheri B, Garavaglia V et al (2008) Energy Environ Sci 1:417–429
Cheng S, Liu H, Logan B (2006) Environ Sci Technol 40:2426
Davis F, Higson SPJ (2007) Biosens Bioelectron 22:1224–1235
Logan B, Regan JM (2006) Trends Microbiol 14:512–518
Gil GC, Chang IS, Kim BH, Kim M, Jang JK, Park HS, Kim HJ (2003) Biosens Bioelectron 18:327
Jang JK, Pham TH, Chang IS, Kang KH, Moon H, Cho KS, Kim BH (2004) Process Biochem 39:1007
Pham TH, Jang JK, Chang IS, Kim BH (2004) J Microbiol Biotechnol 14:324
Kinoshita K (1992) Electrochemical oxygen technology, Wiley, New York
Hao Yu E, Cheng S, Scott K, Logan B (2007) J Power Sources 171:275
Clauwaert P, Van der Ha D, Boon N, Verbeken K, Verhaege M, Rabaey K, Verstraete W (2007) Environ Sci Technol 41:7564
Zhang L, Liu C, Zhuang L, Li W, Zhou S, Zhang J (2009) Biosens Bioelectron 24:2825–2829
Lefebvre O, Al-Mamun A, Ooi WK, Tang Z, Chua DHC, Ng HY (2008) Water Sci Technol 57(12):2031–2037
Nguyen Cong H, Chartier P, Brenet J (1977) J Appl Electrochem 7:383–395
Heller-Ling N, Poillerat G, Koenig JF, Gautier JL, Chartier P (1994) Electrochim Acta 39:1669
Klápště B, Vondrák J, Velická J (2002) Electrochim Acta 47:2365
Mao L, Zhang D, Sotomura T, Nakatsu K, Koshiba N, Ohsaka T (2003) Electrochim Acta 48:1015
Chatenet M, Geniès-Bultel L, Aurousseau M, Durand R, Andolfatto F (2002) J Appl Electrochem 32:1131
Chatenet M, Aurousseau M, Durand R, Andolfatto F (2003) J Electrochem Soc 150:D47
Brock SL, Duan N, Tian ZR, Giraldo O, Zhou H, Suib SL (1998) Chem Mater 10:2619
Roche I, Scott K (2009) J Appl Electrochem 39:197–204
Roche I, Chainet E, Chatenet M, Vondrák J (2007) J Phys Chem C 111:1434–1443
Vondrák J, Klápště B, Velická J, Sedlaříková M, Novák V, Reiter J (2005) J New Mater Electrochem Syst 8:1
Bezdička P, Grygar T, Klápště B, Vondrák J (1999) J Electrochim Acta 45:913
Roche I (2007) PhD INPG
Acknowledgements
This research is support of the European Union for Transfer of Knowledge award on biological fuel cells (contract MTKD-CT-2004-517215).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roche, I., Katuri, K. & Scott, K. A microbial fuel cell using manganese oxide oxygen reduction catalysts. J Appl Electrochem 40, 13–21 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-009-9957-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-009-9957-4