Abstract
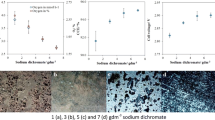
This study focuses on how different electrolyte parameters of the chlorate process affect the cathode potential for hydrogen evolution on iron in a wide current-density range. The varied parameters were pH, temperature, mass transport conditions and the ionic concentrations of chloride, chlorate, chromate and hypochlorite. At lower current densities, where cathodic protection of the electrode material is important, the pH buffering capacity of the electrolyte influenced the potential to a large extent. It could be concluded that none of the electrolyte parameters had any major effects (<50 mV) on the chlorate-cathode potential at industrially relevant current densities (around 3 kA m−2). Certainly, there is more voltage to gain from changing the cathode material than from modifying the electrolyte composition. This is exemplified by experiments on steel corroded from operation in a chlorate plant, which exhibits significantly higher activity for hydrogen evolution than polished steel or iron.









Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- c i :
-
Concentration of species i (mol m−3)
- D i :
-
Diffusion coefficient of species i (m2 s−1)
- E :
-
Cathode potential vs reference electrode (Ag/AgCl) (V)
- F :
-
Faraday constant (As mol−1)
- j k :
-
Current density for reaction k (A m−2)
- \( k^{\prime}_{2} \) :
-
Coefficient in the Tafel expression of Eq. 2, which is given in Eq. 15 (mol m−2 s−1)
- k 14 :
-
Coefficient in the Tafel expression of Eq. 14, which is given in equation 16 (m s−1)
- N i :
-
Molar flux of species i (mol m−2 s−1)
- R :
-
Universal gas constant (J mol−1 K−1)
- R i :
-
Homogeneous production rate of species i (mol m−3 s−1)
- T :
-
Temperature (K)
- u z :
-
Convective velocity perpendicular to the electrode surface, i.e. in the direction of the z-axis (m s−1)
- z :
-
Axial coordinate (m)
- α:
-
Transfer coefficient
- δ D :
-
Diffusion layer (m)
- δ R :
-
Reaction layer (m)
References
Cornell A, Lindbergh G, Simonsson D (1992) Electrochim Acta 37:1873
Tilak BV, Tari K, Hoover CL (1988) J Electrochem Soc 135:1386
Cornell A, Simonsson D (1993) J Electrochem Soc 140:3123
Lindbergh G, Simonsson D (1990) J Electrochem Soc 137:3094
Lindbergh G, Simonsson D (1991) Electrochim Acta 36:1985
Ahlberg Tidblad A, Lindbergh G (1991) Electrochim Acta 36:1605
Schumacher JW, Bradley R, Leder A, Takei N (1999) CEH product review, The chemical economics handbook-SRI international
Coleman JE (1981) In: Alkire R, Beck T (eds) Tutorial lectures in electrochemical engineering and technology, vol 77. American institute of chemical engineering symposium series no. 204, Institute of Chemical Engineers, New York, p 244
Andolfatto F, Joubert P, Duboeuf G (2004) FR 2852973
Guay D, Roue L, Schulz R, Bonneau M-E (2006) CA 2492128
Chow N, Socol J, Oehr K, Remple G (2006) WO 2006039804
Krstajic N, Jovic V, Martelli GN (2007) WO 2007063081
Jackson JR, Zhao M (2005) US 2005011753
Håkansson B, Fontes E, Herlitz F, Lindstrand V (2004) US 2004124094
Cornell A, Håkansson B, Lindbergh G (2003) Electrochim Acta 48:473
Nylén L, Cornell A (2006) J Electrochem Soc 153:D14
Coleman JE and Tilak BV (1995) In: McKetta JJ (ed) Encyclopedia of chemical processing and design. Marcel Dekker, Inc. N.Y., p 126
Tilak BV, Chen C-P (1999) In: Burney HS, Furuya N, Hine F, Ota KI (eds) Chlor-alkali and chlorate technology, PV 99–21. The electrochemical society proceedings series, Pennington, NJ, p 8
Ibl N, Vogt H (1981) In: Bockris JO′M, Conway BE, Yeager E, White RE (eds) Comprehensive treatise of electrochemistry, vol 2. Plenum Press, New York, p 167
Jaksic MM (1974) J Electrochem Soc 121:70
Hammar L, Wranglén G (1964) Electrochim Acta 9:1
Wulff J, Cornell A (2007) J Appl Electrochem 37:181
Hardee KL, Mitchell LK (1989) J Electrochem Soc 136:3314
Eberil VI, Fedotova NS, Novikov EA, Mazanko AF (2000) Elektrokhimiya 36:1463
Eberil VI, Fedotova NS, Novikov EA (1997) Elektrokhimiya 33:610
Elina LM, Gitneva VM, Bystrov VI, Shmygul NM (1974) Elektrokhimiya 10:68
Cornell A, Håkansson B, Lindbergh G (2003) J Electrochem Soc 150:D6
Jaksic MM, Nikolic BZ, Karanovic DM, Milovanovic CR (1969) J Electrochem Soc 116:394
YuV Dobrov, Elina LM (1967) Zashch Met 3:618
Nylén L, Behm M, Cornell A, Lindbergh G (2007) Electrochim Acta 52:4513
Albery J (1975) Electrode kinetics. Clarendon Press, Oxford, p 125
Hurlen T, Gunvaldsen S, Blaker F (1984) Electrochim Acta 29:1163
Ahlberg Tidblad A, Mårtensson J (1997) Electrochim Acta 42:389
Vračar LJ, Dražić DM (1992) J Electroanal Chem 339:269
Byrne P, Fontes E, Parhammar O, Lindbergh G (2001) J Electrochem Soc 148:D125
Koryta J, Dvorák J (1987) Principles of electrochemistry. Wiley, Great Britain, pp 264–276
Tamm J, Tamm L, Vares P (2000) Elektrokhimiya 36:1327
Jin S, Van Neste A, Ghali E, Boily S, Schultz R (1997) J Electrochem Soc 144:4272
Acknowledgements
This work was financed by the Swedish Energy Agency, Eka Chemicals AB and Permascand AB.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nylén, L., Cornell, A. Effects of electrolyte parameters on the iron/steel cathode potential in the chlorate process. J Appl Electrochem 39, 71–81 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-008-9642-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-008-9642-z