Abstract
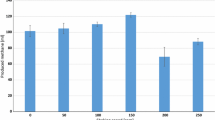
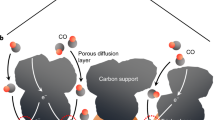
This paper reports an experimental investigation into the effects of five process variables on the performance of a bench-scale continuous electrochemical reactor used in the reduction of CO2 to potassium formate, and interprets the data in terms of reactor engineering for a (speculative) industrial process for electro-reduction of CO2. The process variables: temperature, catholyte species, catholyte conductivity, cathode specific surface area and cathode thickness were studied, along with CO2 pressure and current density, in a set of factorial and parametric experiments aimed to unravel their main effects and interactions. These variables showed complex interdependent effects on the reactor performance, as measured by the current efficiency and specific energy for generation of formate (HCO −2 ). The “best” result has a formate current efficiency of 86% at a superficial current density of 1.3 kA m−2, with a product solution of 0.08 m KHCO2 and specific electrochemical energy of 260 kWh per kmole formate. The combined results indicate good prospects for process optimization that could lead to development of an industrial scale reactor.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- C :
-
catholyte composition
- CE:
-
current efficiency (dimensionless)
- E :
-
cathode potential (VSHE)
- E cell :
-
full-cell operating voltage (absolute value) (V)
- E o :
-
Standard equilibrium electrode potential (VSHE)
- GDE:
-
gas diffusion electrode
- i :
-
geometric (superficial) current density (kA m−2)
- i max :
-
maximum geometric (superficial) current density (kA m−2)
- Me:
-
cathode material
- P :
-
CO2 pressure (Bar(abs) or kPa(abs))
- P cathode :
-
cathode side pressure (kPa (abs))
- T :
-
temperature (K)
- t :
-
operating time (h)
- X 1, X 2, X 3 :
-
factorial variables defined in Tables 6, 9, 10, 13, 14, 16 and 17
- y :
-
volume fraction (i.e. mole fraction) in gas phase (dimensionless)
- τ:
-
thickness of 3D cathode (m)
References
W. M. Ayers, in J. Paul and C.M. Pradier (Eds), Carbon Dioxide Chemistry: Environmental Issues (The Royal Society of Chemistry, 1994), 365 pp.
Williams R., Crandall R.S., Bloom A. (1978) Appl. Phys. Lett. 33(5):381
Rice C., Ha S., Masel R.I. (2002) J. Power Sources 111:83
Kirk-Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology (John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 2005)
Udupa K.S., Subramanian G.S., Udupa H.V.K. (1971) Electrochim. Acta. 16:1593
Ryu J., Andersen T.N., Eyring H. (1972) J. Phys. Chem. 76:3278
Ito K., Murata T., Ikeda S. (1975) Bull. Nagoya Inst. Techn. 27:209
Russell P., Kovac N., Srinivasan S., Steinberg M. (1977) J. Electrochem. Soc. 124(9):1329
Hori Y., Suzuki S. (1982) Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 55(3):660
Kapusta S., Hackerman N. (1983) J. Electrochem. Soc. 130:607
Mahmood M.N., Masheder D., Harty C.J. (1987) J. Appl. Electrochem. 17:1159
Todoroki M., Hara K., Kudo A., Sakata T. (1995) J.Electroanal. Chem. 394:199
Mizuno T., Ohta K., Sasaki A. (1995) Energy Sources, 17:503
Koleli F., Balun D. (2004) Appl. Catal. A General 274:237
Akahori Y., Iwanaga N., Kato Y., Hamamoto O., Ishii M. (2004) Electrochemistry (Tokyo, Japan), 72(4): 266
Li H., Oloman C. (2005) J. Appl. Electrochem. 35:955
F. Walsh, A First Course in Electrochemical Engineering (The Electrochemical Consultancy Romsey, 1993)
Sanchez-Sanchez X.M., Montiel V., Tryk D.A., Aldaz A., Fujishima A. (2001) Pure Appl. Chem. 73(12):1917
Murata A., Hori Y. (1991) Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn., 64:123
Hori Y., Murata A., Takahashi R., Suzuki S. (1988) J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1:17
Hara K., Kudo A., Sakata T. (1995) J. Electrochem. Soc. 142(4):L57
Vassiliev Y., Bagotzky V., Osetrova N., Khazova O., Mayorova N. (1985) J.Electroanal. Chem. 189:271
Oloman C. (1979) J. Electrochem. Soc. 126:1885
N. Gupta, M. Gattrell, B. MacDougall, J. App. Electrochem. (2005) (Online issue)
Cotton F., Wilkinson G. (1972) Advanced Inorganic Chemistry. Interscience, New York
Wong C.S., Tishchenko P.Y., Johnson W.K. (2005) J. Chem. Eng. Data 50:817
Harned H., Davies R. (1943) J. Am. Chem. Soc. 65:2030
Lide D.R. (2004) C.R.C. Handbook of Chemistry and Physics. CRC Press, New York
W. F. Linke (ed.), Solubilities: Inorganic and Metal-Organic Compounds (D.Van Nostrand Princeton, 1958)
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC) and supported by the University of British Columbia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, H., Oloman, C. Development of a continuous reactor for the electro-reduction of carbon dioxide to formate – Part 1: Process variables. J Appl Electrochem 36, 1105–1115 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-006-9194-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-006-9194-z