Abstract
Purpose
This review investigates the therapeutic benefits of interferons (IFNs) in vitreoretinal diseases, focusing on their regulatory roles in innate immunological reactions and angiogenesis. The study aims to categorize the clinical outcomes of IFN applications and proposes a molecular mechanism underlying their action.
Methods
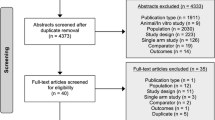
A systematic review was conducted using MEDLINE/PubMed, Web of Science, EMBASE, and Google Scholar databases to identify randomized clinical trials, case series, and case-control studies related to IFNs’ impact on vitreoretinal diseases (1990–2022). The data synthesis involved an in-depth analysis of the anti-inflammatory and anti-angiogenesis effects of IFNs across various studies.
Results
Our findings indicate that IFNs exhibit efficacy in treating inflammation-associated vitreoretinal disorders. However, a lack of sufficient evidence exists regarding the suitability of IFNs in angiogenesis-associated vitreoretinal diseases like choroidal neovascularization and diabetic retinopathies. The synthesis of data suggests that IFNs may not be optimal for managing advanced stages of angiogenesis-associated disorders.
Conclusion
While IFNs emerge as promising therapeutic candidates for inflammation-related vitreoretinal diseases, caution is warranted in their application for angiogenesis-associated disorders, especially in advanced stages. Further research is needed to elucidate the nuanced molecular pathways of IFN action, guiding their targeted use in specific vitreoretinal conditions.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
De Veer MJ, Holko M, Frevel M, Walker E, Der S, Paranjape JM et al (2001) Functional classification of interferon-stimulated genes identified using microarrays. J Leukoc Biol 69(6):912–920
Medrano RF, Hunger A, Mendonça SA, Barbuto JAM, Strauss BE (2017) Immunomodulatory and antitumor effects of type I interferons and their application in cancer therapy. Oncotarget 8(41):71249
Albini A, Marchisone C, Del Grosso F, Benelli R, Masiello L, Tacchetti C et al (2000) Inhibition of angiogenesis and vascular tumor growth by interferon-producing cells: a gene therapy approach. Am J Pathol 156(4):1381–1393
Sheppard P, Kindsvogel W, Xu W, Henderson K, Schlutsmeyer S, Whitmore TE et al (2003) IL-28, IL-29 and their class II cytokine receptor IL-28R. Nat Immunol 4(1):63–68
Kotenko SV, Gallagher G, Baurin VV, Lewis-Antes A, Shen M, Shah NK et al (2003) IFN-λs mediate antiviral protection through a distinct class II cytokine receptor complex. Nat Immunol 4(1):69–77
Wang H, Hu H, Zhang K (2017) Overview of interferon: characteristics, signaling and anti-cancer effect. Arch Biotechnol Biomed 1:1–16
Lee AJ, Ashkar AA (2018) The dual nature of type I and type II interferons. Frontiers in immunology, 2061
Lazear HM, Schoggins JW, Diamond MS (2019) Shared and distinct functions of type I and type III interferons. Immunity 50(4):907–923
Platanias LC (2005) Mechanisms of type-I-and type-II-interferon-mediated signalling. Nat Rev Immunol 5(5):375–386
Bekisz J, Baron S, Balinsky C, Morrow A, Zoon KC (2010) Antiproliferative properties of type I and type II interferon. Pharmaceuticals 3(4):994–1015
Yoshimura T, Sonoda K-H, Sugahara M, Mochizuki Y, Enaida H, Oshima Y et al (2009) Comprehensive analysis of inflammatory immune mediators in vitreoretinal diseases. PLoS ONE 4(12):e8158
Banerjee S, Savant V, Scott RA, Curnow SJ, Wallace GR, Murray PI (2007) Multiplex bead analysis of vitreous humor of patients with vitreoretinal disorders. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 48(5):2203–2207
Afarid M, Lashkarizadeh H, Ashraf MJ, Nowroozzadeh MH, Shafiee SM (2016) The efficacy of intravitreal interferon alpha-2b for the treatment of experimental endotoxin-induced uveitis. Indian J Ophthalmol 64(5):376
Afarid M, Meshksar A, Salehi A, Safarpour MM (2020) Evaluation of the effect of topical interferon α2b as a complementary treatment of macular edema of patients with diabetic retinopathy: a double-blind placebo-controlled randomized clinical trial study. Retina 40(5):936–942
Afarid M, Azimi A, Malekzadeh M (2019) Evaluation of serum interferons in patients with age-related macular degeneration. J Res Med Sci Official J Isfahan Univ Med Sci 24:24
Kötter I, Zierhut M, Eckstein A, Vonthein R, Ness T, Günaydin I et al (2003) Human recombinant interferon alfa-2a for the treatment of Behcet’s disease with sight threatening posterior or panuveitis. Br J Ophthalmol 87(4):423–431
Krause L, Turnbull JR, Torun N, Pleyer U, Zouboulis CC, Foerster MH (2004) Interferon alfa-2a in the treatment of ocular Adamantiades-Behçet’s disease. Adamantiades-Behçet’s Disease, 511–9
Sobacı G, Erdem Ü, Durukan AH, Erdurman C, Bayer A, Köksal S et al (2010) Safety and effectiveness of interferon alpha-2a in treatment of patients with Behçet’s uveitis refractory to conventional treatments. Ophthalmology 117(7):1430–1435
Park J-Y, Chung Y-R, Lee K, Song JH, Lee E-S (2015) Clinical experience of interferon alfa-2a treatment for refractory uveitis in Behcet’s disease. Yonsei Med J 56(4):1158–1162
Bielefeld P, Devilliers H, Deschasse C, Saadoun D, Sève P, Muselier A et al (2016) Potential of pegylated interferon alpha-2a in Behçet uveitis: a report of five cases. Ocul Immunol Inflamm 24(5):599–602
Lee JH, Lee CS, Lee SC (2018) Interferon alpha-2a treatment for refractory Behcet uveitis in Korean patients. BMC Ophthalmol 18(1):1–4
Eser-Ozturk H, Sullu Y (2019) The results of interferon-alpha treatment in Behçet uveitis. Ocular Immunol Inflamm
Celiker H, Kazokoglu H, Direskeneli H (2019) Long-term efficacy of pegylated interferon alpha-2b in Behçet’s uveitis: a small case series. Ocul Immunol Inflamm 27(1):15–22
Yalçindag N, Köse HC (2020) Comparison of the treatment results for Behçet uveitis in patients treated with infliximab and interferon. Ocul Immunol Inflamm 28(2):305–314
Atik BK, Altan Ç, Başarir B (2020) Therapeutic outcomes of interferon-alpha-2a treatment in Behçet uveitis Turkiye. Klinikleri J Ophthalmol 29(4):294–299
Qian Y, Qu Y, Gao F, Pei M, Liang A, Xiao J et al (2021) Comparison of the safety and efficacy of interferon alpha-2a and cyclosporine-a when combined with glucocorticoid in the treatment of refractory Behçet’s uveitis: a randomized controlled prospective study. Front Pharmacol 12:699903
Becker M, Heiligenhaus A, Hudde T, Storch-Hagenlocher B, Wildemann B, Barisani-Asenbauer T et al (2005) Interferon as a treatment for uveitis associated with multiple sclerosis. Br J Ophthalmol 89(10):1254–1257
Mackensen F, Jakob E, Springer C, Dobner BC, Wiehler U, Weimer P et al (2013) Interferon versus methotrexate in intermediate uveitis with macular edema: results of a randomized controlled clinical trial. Am j ophthalmol 156(3):478–486
Plskova J, Greiner K, Forrester JV (2007) Interferon-α as an effective treatment for noninfectious posterior uveitis and panuveitis. Am j ophthalmol 144(1):55–61
Yalcinbayir O, Yucel AA, Kaderli B, Gelisken O (2009) Subconjunctival interferon α-2a application in a case with serpiginous choroidopathy. Retinal Cases Brief Rep 3(2):214–217
Kirkpatrick J, Dick A, Forrester J (1993) Clinical experience with interferon alfa-2a for exudative age-related macular degeneration. British j Ophthal 77(12):766–770
Brasnu E, Wechsler B, Bron A, Charlotte F, Bliefeld P, Lehoang P et al (2005) Efficacy of interferon-α for the treatment of Kaposi’s sarcoma herpesvirus-associated uveitis. Am J Ophthalmol 140(4):746–748
Invernizzi A, Iannaccone F, Marchi S, Mastrofilippo V, Coassin M, Fontana L, et al (2018) Interferon alpha-2a for the treatment of post-infectious uveitis secondary to presumed intraocular tuberculosis. Ocular Immunol Inflamm
Deuter CM, Koetter I, Guenaydin I, Stuebiger N, Zierhut M (2006) Interferon alfa-2a: a new treatment option for long lasting refractory cystoid macular edema in uveitis?: A pilot study. Retina 26(7):786–791
Deuter CM, Kötter I, Günaydin I, Stübiger N, Doycheva DG, Zierhut M (2009) Efficacy and tolerability of interferon alpha treatment in patients with chronic cystoid macular oedema due to non-infectious uveitis. Br J Ophthalmol 93(7):906–913
Maleki A, Aghaei H, Lee S (2018) Topical interferon alpha 2b in the treatment of refractory pseudophakic cystoid macular edema. Am J Ophthalmol Case Rep 10:203–205
Deuter CM, Fausel J, Doycheva D, Zierhut M (2019) Long-term results of therapy with interferon alpha in chronic uveitic macular edema. Invest Ophthalmol Visual Sci 60(9):3515
Dimopoulos S, Deuter CM, Blumenstock G, Zierhut M, Dimopoulou A, Voykov B, et al (2019) Interferon alpha for refractory pseudophakic cystoid macular edema (irvine-gass syndrome). Ocular Immunol Inflamm
Aksu-Ceylan N, Cebeci Z, Altinkurt E, Kir N, Oray M, Tugal-Tutkun I (2021) Interferon Alpha-2a for the treatment of cystoid macular edema secondary to acute retinal necrosis. Ocular Immunol Inflamm, 1–10
Maleki A, Stephenson AP, Hajizadeh F (2020) Topical interferon alpha 2b in the treatment of refractory diabetic macular edema. J Ophthalmic Vis Res 15(4):453
Faghihi H, Inanloo B, Mirzaee A, Fadakar K, Mirshahi A, Ebrahimiadib N et al (2022) Evaluation of the additive effect of interferon α 2b with monthly intravitreal injection of bevacizumab in refractory diabetic macular edema. International Journal of Retina and Vitreous 8(1):1–9
Couret C, Servant M, Lebranchu P, Hamidou M, Weber M (2020) Efficacy and safety of interferon alpha 2a and pegylated interferon alpha 2a in inflammatory macular edema. Ocul Immunol Inflamm 28(2):329–336
Skowsky WR, Siddiqui T, Hodgetts D, Lambrou FH Jr, Stewart MW, Foster MT Jr (1996) A pilot study of chronic recombinant interferon-alfa 2a for diabetic proliferative retinopathy: metabolic effects and opthalmologic effects. J Diabetes Complications 10(2):94–99
Fardeau C, Simon A, Rodde B, Viscogliosi F, Labalette P, Looten V et al (2017) Interferon-alpha2a and systemic corticosteroid in monotherapy in chronic uveitis: results of the randomized controlled BIRDFERON study. Am J Ophthalmol 177:182–194
Leibovitch I, Loewenstein A, Alster Y, Rosenblatt I, Lazar M, Yassur Y et al (2004) Interferon alpha-2a for proliferative diabetic retinopathy after complete laser panretinal photocoagulation treatment slack incorporated thorofare. NJ 35:16–22
Loughnan MS, Heriot WJ, O'Day J (1992) Treatment of subfoveal choroidal neovascular membranes with systemic interferonl α 2a. Australian and New Zealand. J Ophthalmol 20(3):173-175
Thomas MA, Ibanez HE (1993) Interferon alfa-2a in the treatment of subfoveal choroidal neovascularization. Am J Ophthalmol 115(5):563–568
Gillies M, Sarks J, Beaumont P, Hunyor A, McKay D, Kearns M et al (1993) Treatment of choroidal neovascularisation in age-related macular degeneration with interferon alfa-2a and alfa-2b. Br J Ophthalmol 77(12):759–765
Poliner LS, Tornambe PE, Michelson PE, Heitzmann JG (1993) Interferon alpha-2a for subfoveal neovascularization in age-related macular degeneration. Ophthalmology 100(9):1417–1424
Chan CK, Kempin SJ, Noble SK, Palmer GA (1994) The treatment of choroidal neovascular membranes by alpha interferon: an efficacy and toxicity study. Ophthalmology 101(2):289–300
Engler C, Sander B, Villumsen J, Lund-Andersen H (1994) Interferon alfa-2a modifies the course of subfoveal and juxtafoveal choroidal neovascularisation. Br J Ophthalmol 78(10):749–753
Engler CB, Sander B, Koefoed P, Larsen M, Vinding T, Lund-Andersen H (1993) Interferon alpha-2a treatment of patients with subfoveal neovascular macular degeneration: a pilot investigation. Acta Ophthalmol 71(1):27–31
Thoelen A, Menozzi M, Huber C, Messmer E (1995) Treatment of choroidal neovascularization in age-related macular degeneration with interferon alpha-2a: a short term, nonrandomized pilot study. Ger J Ophthalmol 4(3):137–143
Guyer DR, Adamis AP, Yannuzzi LA, Gragoudas ES, Coscas GJ, Brancato R et al (1997) Interferon alfa-2a is ineffective for patients with choroidal neovascularization secondary to age-related macular degeneration: results of a prospective randomized placebo-controlled clinical trial. Arch Ophthalmol 115(7):865–872
Cirino AC, JEEVAN R MATHURA J, Jampol LM (2006) Resolution of activity (choroiditis and choroidal neovascularization) of chronic recurrent punctate inner choroidopathy after treatment with interferon B-1A. Retina26(9):1091–1092
Sobacı G, Bayraktar Z, Bayer A (2005) ORIGINAL ARTICLE, interferon alpha-2A treatment for serpiginous choroiditis. Ocul Immunol Inflamm 13(1):59–66
Lewis ML, Davis J, Chuang E (1993) Interferon alfa-2a in the treatment of exudative age-related macular degeneration. Graefe’s arch clin exp ophthalmol 231(11):615–618
Jaakkola A, Anttila PM, Immonen I (1994) Interferon alpha-2a in the treatment of exudative senile macular degeneration. Acta Ophthalmol 72(5):545–549
Lee RW, Nicholson LB, Sen H, Chan C-C, Wei L, Nussenblatt RB, et al.(2014) editors. Autoimmune and autoinflammatory mechanisms in uveitis. Seminars in immunopathology; Springer
Bodaghi B, Cassoux N, Wechsler B, Hannouche D, Fardeau C, Papo T et al (2001) Chronic severe uveitis: etiology and visual outcome in 927 patients from a single center. Medicine 80(4):263–270
Barisani-Asenbauer T, Maca SM, Mejdoubi L, Emminger W, Machold K, Auer H (2012) Uveitis-a rare disease often associated with systemic diseases and infections-a systematic review of 2619 patients. Orphanet J Rare Dis 7(1):1–7
Schrijver B, Kolijn PM, Ten Berge JC, Nagtzaam NM, van Rijswijk AL, Swagemakers SM et al (2022) Vitreous proteomics, a gateway to improved understanding and stratification of diverse uveitis aetiologies. Acta Ophthalmol 100:403
Tugal-Tutkun I (2009) Behçet’s uveitis. Middle East Afr J Ophthalmol 16(4):219
Tugal-Tutkun I, Onal S, Altan-Yaycioglu R, Altunbas HH, Urgancioglu M (2004) Uveitis in Behçet disease: an analysis of 880 patients. Am J Ophthalmol 138(3):373–380
Mackensen F, Max R, Becker MD (2009) Interferons and their potential in the treatment of ocular inflammation. Clin Ophthalmol, 559–66
Deuter C, Stübiger N, Zierhut M (2012) Interferon-α therapy in noninfectious uveitis. New Treat Noninfectious Uveitis 51:90–97
Plskova J, Greiner K, Muckersie E, Duncan L, Forrester JV (2006) Interferon-α: a key factor in autoimmune disease? Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 47(9):3946–3950
Sleijfer S, Bannink M, Van Gool AR, Kruit WH, Stoter G (2005) Side effects of interferon-α therapy. Pharm World Sci 27(6):423–431
Dusheiko G (1997) Side effects of α interferon in chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology 26(S3):112S-S121
Rentiya ZS, Wells M, Bae J, Chen K-J, Chao A-N, Turgeon N et al (2019) Interferon-α-induced retinopathy in chronic hepatitis C treatment: summary, considerations, and recommendations. Graefe’s Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 257(3):447–452
Foster GR (2010) Pegylated interferons for the treatment of chronic hepatitis C. Drugs 70(2):147–165
Bodaghi B, Gendron G, Wechsler B, Terrada C, Cassoux N, Lemaitre C et al (2007) Efficacy of interferon alpha in the treatment of refractory and sight threatening uveitis: a retrospective monocentric study of 45 patients. Br J Ophthalmol 91(3):335–339
Hasanreisoglu M, Cubuk MO, Ozdek S, Gurelik G, Aktas Z, Hasanreisoglu B (2017) Interferon alpha-2a therapy in patients with refractory Behçet uveitis. Ocul Immunol Inflamm 25(1):71–75
Deuter CM, Xenitidis T, Schoenfisch B, Doycheva D, Zierhut M, Koetter I (2011) Interim analysis of the clinical trial INCYTOB (interferon alpha-2a versus cyclosporin a for the treatment of severe ocular Behçet’s disease). Investig Ophthalmol Visual Sci 52(14):4254
De Simone L, Invernizzi A, Aldigeri R, Mastrofilippo V, Marvisi C, Gozzi F et al (2022) Effectiveness of infliximab and interferon alpha-2a for the treatment of Behçet’s uveitis: customizing therapy according to the clinical features. Ocul Immunol Inflamm 30(2):506–514
Vann RR, Karp CL (1999) Perilesional and topical interferon alfa-2b for conjunctival and corneal neoplasia. Ophthalmology 106(1):91–97
Nemet AY, Sharma V, Benger R (2006) Interferon α 2b treatment for residual ocular surface squamous neoplasia unresponsive to excision, cryotherapy and mitomycin-C. Clin Exp Ophthalmol 34(4):375–377
Mastropasqua R, D’Aloisio R, Di Nicola M, Di Martino G, Lamolinara A, Di Antonio L et al (2018) Relationship between aqueous humor cytokine level changes and retinal vascular changes after intravitreal aflibercept for diabetic macular edema. Sci Rep 8(1):1–9
Minaker SA, Mason RH, Lahaie Luna G, Farahvash A, Garg A, Bhambra N et al (2022) Changes in aqueous and vitreous inflammatory cytokine levels in diabetic macular oedema: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Acta Ophthalmol 100(1):e53–e70
de Smet MD, Okada AA (2010) Cystoid macular edema in uveitis. Macular Edema 47:136–147
Young S, Larkin G, Branley M, Lightman S (2001) Safety and efficacy of intravitreal triamcinolone for cystoid macular oedema in uveitis. Clin Exp Ophthalmol 29(1):2–6
Butler NJ, Suhler EB, Rosenbaum JT (2012) Interferon alpha 2b in the treatment of uveitic cystoid macular edema. Ocul Immunol Inflamm 20(2):86–90
De Simone L, Sangiovanni A, Aldigeri R, Mastrofilippo V, Bolletta E, Invernizzi A et al (2020) Interferon alpha-2a treatment for post-uveitic refractory macular edema. Ocul Immunol Inflamm 28(2):322–328
Stiefel HC, Kopplin LJ, Albini T, Chang M, Vegunta S, Suhler EB (2021) Treatment of refractory cystoid macular edema with pegylated interferon alfa-2a: a retrospective chart review. Ocul Immunol Inflamm 29(3):566–571
Kawali A, Sanjay S, Mohan A, Mahendradas P, Shroff S, Shetty R (2022) Intensive topical interferon therapy in uveitic macular edema. Indian J Ophthalmol 70(8):2986–2989
Pleyer U, Neri P, Deuter C (2021) New pharmacotherapy options for noninfectious posterior uveitis. Int Ophthalmol 41:2265–2281
Liu CY, Francis JH, Abramson DH (2018) Ocular side effects of systemically administered chemotherapy. UpToDate Waltham, MA: UpToDate
Zhang H, Houadj L, Wu KY, Tran SD (2024) Diagnosing and managing uveitis associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors: a review. Diagnostics 14(3):336
Modugno RL, Testi I, Pavesio C (2021) Intraocular therapy in noninfectious uveitis. J Ophthalmic Inflamm Infection 11:1–8
Fu L, Li Y, Yao S, Guo Q, You Y, Zhu X et al (2021) Autosomal recessive rod-cone dystrophy associated with compound heterozygous variants in ARL3 gene. Front cell dev biol 9:635424
Hood DC, Cideciyan AV, Roman AJ, Jacobson SG (1995) Enhanced S cone syndrome: evidence for an abnormally large number of S cones. Vision Res 35(10):1473–1481
Fishman GA, Peachey NS (1989) Rod-cone dystrophy associated with a rod system electroretinogram obtained under photopic conditions. Ophthalmology 96(6):913–918
Semeraro F, Morescalchi F, Russo A, Gambicorti E, Pilotto A, Parmeggiani F et al (2019) Central serous chorioretinopathy: pathogenesis and management. Clinical Ophthalmol (Auckland, NZ) 13:2341
Kawali A, Snehith R, Singh V, Sanjay S, Mahendradas P, Shetty R (2021) Topical interferon–a novel treatment for pseudophakic macular edema. Indian J Ophthalmol 69(9):2355
Aghaei H, Es’haghi A (2022) Improvement of pseudophakic cystoid macular edema with subconjunctival injections of interferon α2b: a case report. Am J Ophthalmol Case Rep 26:101504
Cellini M, Balducci N, Strobbe E, Campos EC (2013) Subtenon injection of natural leukocyte interferon α-2a in diabetic macular edema: a case report. BMC Ophthalmol 13(1):1–4
Qian Z, Fardeau C, Cardoso JN, Jellab B, Fan X, LeHoang P (2015) Effect of interferon α2a in cystoid macular edema due to intraocular infection. Eur J Ophthalmol 25(5):431–436
Oray M, Onal S, Uludag G, Akbay AK, Tugal-Tutkun I (2017) Interferon alpha for the treatment of cystoid macular edema associated with presumed ocular tuberculosis. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther 33(4):304–312
Deuter CM, Gelisken F, Stübiger N, Zierhut M, Doycheva D (2011) Successful treatment of chronic pseudophakic macular edema (Irvine-Gass syndrome) with interferon alpha: a report of three cases. Ocul Immunol Inflamm 19(3):216–218
Kawali A, Srinivasan S, Mahendradas P, Shetty R (2022) Topical interferon in recurrent inflammatory macular edema following a cat bite. European J Ophthalmol 32(6):NP32–NP5
Barth T, Zeman F, Helbig H, Gamulescu M-A (2019) Intravitreal anti-VEGF treatment for choroidal neovascularization secondary to traumatic choroidal rupture. BMC Ophthalmol 19(1):1–6
Raig ET, Jones NB, Varker KA, Benniger K, Go MR, Biber JL et al (2008) VEGF secretion is inhibited by interferon-alpha in several melanoma cell lines. J Interferon Cytokine Res 28(9):553–562
Ross C, Engler CB, Sander B, Bendtzen K (2002) IFN-α antibodies in patients with age-related macular degeneration treated with recombinant human IFN-α 2a. J Interferon Cytokine Res 22(4):421–426
Lückoff A, Caramoy A, Scholz R, Prinz M, Kalinke U, Langmann T (2016) Interferon-beta signaling in retinal mononuclear phagocytes attenuates pathological neovascularization. EMBO Mol Med 8(6):670–678
Thomas CN, Sim DA, Lee WH, Alfahad N, Dick AD, Denniston AK et al (2022) Emerging therapies and their delivery for treating age-related macular degeneration. Br J Pharmacol 179(9):1908–1937
Behnke V, Langmann T (2020) IFN-β signaling dampens microglia reactivity but does not prevent from light-induced retinal degeneration. Biochemistry and Biophysics Reports 24:100866
Duh EJ, Sun JK, Stitt AW (2017) Diabetic retinopathy: current understanding, mechanisms, and treatment strategies. JCI insight, 2(14)
Daniel AL, Houlihan JL, Blum JS, Walsh JP (2009) Type B insulin resistance developing during interferon-α therapy. Endocr Pract 15(2):153–157
Dan-Brezis I, Zahavi A, Axer-Siegel R, Nisgav Y, Dahbash M, Weinberger D et al (2020) Inflammation, angiogenesis and coagulation interplay in a variety of retinal diseases. Acta Ophthalmol 98(5):e559–e562
Afarid M, Torabi-Nami M, Nemati A, Khosravi A, Malekzadeh M (2015) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor in patients with advanced age-related macular degeneration. Int J Ophthalmol 8(5):991
Afarid M, Namvar E, Sanie-Jahromi F (2020) Diabetic retinopathy and BDNF: a review on its molecular basis and clinical applications. J Ophthalmol, 2020
Schoenberger SD, Kim SJ (2013) Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for retinal disease. Int J Inflamm, 2013
Paulus YM, Sodhi A (2016) Anti-angiogenic therapy for retinal disease. Springer, Pharmacologic Therapy of Ocular Disease, pp 271–307
Rezzola S, Loda A, Corsini M, Semeraro F, Annese T, Presta M et al (2020) Angiogenesis-inflammation cross talk in diabetic retinopathy: novel insights from the chick embryo chorioallantoic membrane/human vitreous platform. Front Immunol 11:581288
Chen L, Deng H, Cui H, Fang J, Zuo Z, Deng J et al (2018) Inflammatory responses and inflammation-associated diseases in organs. Oncotarget 9(6):7204
Ashley NT, Weil ZM, Nelson RJ (2012) Inflammation: mechanisms, costs, and natural variation. Annu Rev Ecol Evol Syst 43(385):2012
Ribatti D, Crivellato E (2012) Sprouting angiogenesis, a reappraisal. Dev Biol 372(2):157–165
Jain RK (2003) Molecular regulation of vessel maturation. Nat Med 9(6):685–693
Udan RS, Culver JC, Dickinson ME (2013) Understanding vascular development. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Dev Biol 2(3):327–346
Wallsh JO, Gallemore RP (2021) Anti-VEGF-resistant retinal diseases: A review of the latest treatment options. Cells 10(5):1049
Yang S, Zhao J, Sun X (2016) Resistance to anti-VEGF therapy in neovascular age-related macular degeneration: a comprehensive review. Drug Des Dev Ther 10:1857
Yang P, Huang G, Du L, Ye Z, Hu K, Wang C et al (2019) Long-term efficacy and safety of interferon alpha-2a in the treatment of Chinese patients with Behçet’s uveitis not responding to conventional therapy. Ocul Immunol Inflamm 27(1):7–14
Egwuagu CE, Alhakeem SA, Mbanefo EC (2021) Uveitis: molecular pathogenesis and emerging therapies. Front Immunol 1293:623725
Cunha-Vaz J, Travassos A (1984) Breakdown of the blood-retinal barriers and cystoid macular edema. Surv Ophthalmol 28:485–492
Bolívar S, Anfossi R, Humeres C, Vivar R, Boza P, Muñoz C et al (2018) IFN-β plays both pro-and anti-inflammatory roles in the rat cardiac fibroblast through differential STAT protein activation. Front Pharmacol 9:1368
Indraccolo S (2010) Interferon-α as angiogenesis inhibitor: learning from tumor models. Autoimmunity 43(3):244–247
Karar J, Maity A (2011) PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in angiogenesis. Front Mol Neurosci 4:51
Ucuzian AA, Gassman AA, East AT, Greisler HP (2010) Molecular mediators of angiogenesis. J Burn Care Res 31(1):158–175
Zhang L, Yang N, Park J-W, Katsaros D, Fracchioli S, Cao G et al (2003) Tumor-derived vascular endothelial growth factor up-regulates angiopoietin-2 in host endothelium and destabilizes host vasculature, supporting angiogenesis in ovarian cancer. Can Res 63(12):3403–3412
Hammes H-P, Lin J, Wagner P, Feng Y, Vom Hagen F, Krzizok T et al (2004) Angiopoietin-2 causes pericyte dropout in the normal retina: evidence for involvement in diabetic retinopathy. Diabetes 53(4):1104–1110
Lobov IB, Brooks PC, Lang RA (2002) Angiopoietin-2 displays VEGF-dependent modulation of capillary structure and endothelial cell survival in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci 99(17):11205–11210
Hakanpaa L, Sipila T, Leppanen V-M, Gautam P, Nurmi H, Jacquemet G et al (2015) Endothelial destabilization by angiopoietin-2 via integrin β1 activation. Nat Commun 6(1):1–12
Lee PY, Li Y, Kumagai Y, Xu Y, Weinstein JS, Kellner ES et al (2009) Type I interferon modulates monocyte recruitment and maturation in chronic inflammation. Am J Pathol 175(5):2023–2033
Hubbard NE, Lim D, Mukutmoni M, Cai A, Erickson KL (2005) Expression and regulation of murine macrophage angiopoietin-2. Cell Immunol 234(2):102–109
Buie JJ, Renaud LL, Muise-Helmericks R, Oates JC (2017) IFN-α negatively regulates the expression of endothelial nitric oxide synthase and nitric oxide production: implications for systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol 199(6):1979–1988
Wada H, Nagano H, Yamamoto H, Arai I, Ota H, Nakamura M et al (2007) Combination therapy of interferon-α and 5-fluorouracil inhibits tumor angiogenesis in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells by regulating vascular endothelial growth factor and angiopoietins. Oncol Rep 18(4):801–809
Vazquez A (2011) The universe of normal and cancer cell line responses to anticancer treatment: lessons for cancer therapy. Nature Precedings, 1-1
Hamamcioglu K, Reder A (2007) Interferon-β regulates cytokines and BDNF: greater effect in relapsing than in progressive multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler J 13(4):459–470
Afarid M, Bahari H, Sanie-Jahromi F (2023) In vitro evaluation of apoptosis, inflammation, angiogenesis, and neuroprotection gene expression in retinal pigmented epithelial cell treated with interferon α−2b. J Interf Cytokine Res 43:299
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the directors of Shiraz University of Medical Sciences for supporting this research. The authors would like to thank Ms. A. Keivanshekouh at the Research Consultation Center (RCC) of Shiraz University of Medical Sciences for her invaluable assistance in improving the use of English in the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by Shiraz University of Medical Science (Grant# 22323).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
F.SJ. and M.A. designed the project. F.SJ., A.A., and A.M. were involved in obtaining the data. All authors were involved in writing the manuscript and revising the final version.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors report no commercial or proprietary interest in any product or concept discussed in this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Afarid, M., Azimi, A., Meshksar, A. et al. Interferons in vitreoretinal diseases; a review on their clinical application, and mechanism of action. Int Ophthalmol 44, 223 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10792-024-03144-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10792-024-03144-3