Abstract
Purpose
The purpose of the study was to measure the effect of rim-off deep lateral decompression for Graves orbitopathy on the lateral rectus muscle path and oculomotor balance.
Methods
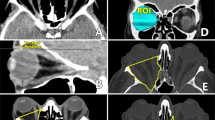
Retrospective analysis of the medical records and pre- and postoperative computed tomography scans of 34 orbits of 23 patients who underwent deep lateral decompression alone. The oculomotor balance of these 23 patients was measured with the alternate cover test and prisms before and after surgery. Bezier functions were used to measure the postoperative path of the lateral rectus in all decompressed orbits.
Results
Deep lateral decompression induced a curvilinear deformation of the lateral rectus.
There was no significant correlation between the position of the point of maximum muscle displacement and the size of the residual lateral wall. The changes in the lateral rectus path had no adverse effects on the oculomotor balance of the patients.
Conclusions
The location of the curvilinear deformation of the lateral rectus does not depend on the residual segment of the lateral wall. The changes of the lateral rectus path have no deleterious effect on the oculomotor balance.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cruz AAV, Equiterio BSN, Cunha BSA, Caetano FB, Souza RL (2021) Deep lateral orbital decompression for Graves orbitopathy: a systematic review. Int Ophthalmol 41:1929–1947. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10792-021-01722-3
DeParis SW, Tian J, Rajaii F (2019) Practice patterns in orbital decompression surgery among American society of ophthalmic plastic and reconstructive surgery members. Ophthalmol Ther 8:541–548. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40123-019-00206-z
Goldberg RA, Kim AJ, Kerivan KM (1998) The lacrimal keyhole, orbital door jamb, and basin of the inferior orbital fissure. Three areas of deep bone in the lateral orbit. Arch Ophthalmol 116:1618–1624. https://doi.org/10.1001/archopht.116.12.1618
Chang EL, Piva AP (2008) Temporal fossa orbital decompression for treatment of disfiguring thyroid-related orbitopathy. Ophthalmology 115:1613–1619. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ophtha.2008.02.024
Hurwitz JJ, Birt D (1985) An individualized approach to orbital decompression in Graves’ orbitopathy. Arch Ophthalmol 103:660–665. https://doi.org/10.1001/archopht.1985.01050050052016
Gupta A, Nobori A, Wang Y, Rootman D, Goldberg R (2017) Lateral rectus muscle expands more than medial rectus following maximal deep balanced orbital decompression. Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg 34:140–142. https://doi.org/10.1097/IOP.0000000000000894
Kakizaki H, Takahashi Y, Ichinose A, Iwaki M, Selva D, Leibovitch I (2011) The importance of rim removal in deep lateral orbital wall decompression. Clin ophthalmol 5:865–869. https://doi.org/10.2147/OPTH.S20855
Leone CR, Piest KL, Newman RJ (1989) Medial and lateral wall decompression for thyroid ophthalmopathy. Am J Ophthalmol 108:160–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/0002-9394(89)90011-1
Cubuk MO, Konuk O, Unal M (2018) Orbital decompression surgery for the treatment of Graves’ ophthalmopathy comparison of different techniques and long-term results. Int J Ophthalmol 11:1363–1370. https://doi.org/10.18240/ijo.2018.08.18
Fayers T, Barker LE, Verity DH, Rose GE (2013) Oscillopsia after lateral wall orbital decompression. Ophthalmology 120:1920–1923. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ophtha.2013.01.063
Hernandez-Garcia E, San-Roman JJ, Gonzalez R, Nogueira A, Genol I, Stoica B, Toledano N, Plaza G (2017) Balanced (endoscopic medial and transcutaneous lateral) orbital decompression in Graves’ orbitopathy. Acta Otolaryngol 137:1183–1187. https://doi.org/10.1080/00016489.2017.1354394
Mehta P, Durrani OM (2011) Outcome of deep lateral wall rim-sparing orbital decompression in thyroid-associated orbitopathy: a new technique and results of a case series. Orbit 30:265–268. https://doi.org/10.3109/01676830.2011.603456
Ueland HO, Haugen OH, Rodahl E (2016) Temporal hollowing and other adverse effects after lateral orbital wall decompression. Acta Ophthalmol 94:793–797. https://doi.org/10.1111/aos.13135
Bailey KL, Tower RN, Dailey RA (2005) Customized, single-incision, three-wall orbital decompression. Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg 21:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.iop.0000150410.30992.c3
Choe CH, Cho RI, Elner VM (2011) Comparison of lateral and medial orbital decompression for the treatment of compressive optic neuropathy in thyroid eye disease. Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg 27:4–11. https://doi.org/10.1097/IOP.0b013e3181df6a87
Oeverhaus M, Copei A, Mattheis S, Ringelstein A, Tiemessen M, Esser J, Eckstein A, Stähr K (2019) Influence of orbital morphology on proptosis reduction and ocular motility after decompression surgery in patients with Graves’ orbitopathy. PLoS ONE 14:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0218701
Paridaens DA, Verhoeff K, Bouwens D, Van Den Bosch WA (2000) Transconjunctival orbital decompression in Graves’ ophthalmopathy: lateral wall approach ab interno. Br J Ophthalm 84:775–781. https://doi.org/10.1136/bjo.84.7.775
Porrua-Tubio L, Sales-Sanz A, de-Arriba-Palomero P, Felix-Espinar B, de-Arriba-Palomero F, Alonso-Rormento N, Albandea-Jiménez A, Rodríguez-del-Valle JM, Sales-Sanz M, (2020) Oscillopsia after isolated lateral wall decompression versus balanced or 3-wall decompression. Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg 37:1–4. https://doi.org/10.1097/IOP.0000000000001716
Sagiv O, Satchi K, Kinori M, Fabian ID, Rosen N, Simon GJB, McNab A (2016) Comparison of lateral orbital decompression with and without rim repositioning in thyroid eye disease. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 254:791–796. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-015-3237-2
Stahr K, Eckstein A, Holtmann L, Schlüter A, Dendy M, Lang S, Mattheis S (2019) A comparative analysis of piezosurgery and oscillating saw for balanced orbital decompression. Orbit 38:433–439. https://doi.org/10.1080/01676830.2018.1552709
Sweeney AR, Shaftel SS, Jacobs SM, Jian-Amadi A (2017) Lateral wall orbital decompression: comparison of outcomes in rim sparing and temporary rim removal techniques. J Craniofac Surg 28:379–382. https://doi.org/10.1080/01676830.2018.1552709
Cho RI, Choe CH, Elner VM (2010) Ultrasonic bone removal versus high-speed burring for lateral orbital decompression: comparison of surgical outcomes for the treatment of thyroid eye disease. Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg 26:83–87. https://doi.org/10.1097/IOP.0b013e3181b8e614
Fichter N, Guthoff RF (2015) Results after en bloc lateral wall decompression surgery with orbital fat resection in 111 patients with Graves’ orbitopathy. Int J Endocrinol 2015:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/860849
Fichter N, Guthoff RF, Schittkowski MP (2012) Orbital decompression in thyroid eye disease. ISRN Ophthalmol 2012:1–12. https://doi.org/10.5402/2012/739236
Fichter N, Krentz H, Guthoff RF (2013) Functional and esthetic outcome after bony lateral wall decompression with orbital rim removal and additional fat resection in Graves’ orbitopathy with regard to the configuration of the lateral canthal region. Orbit 32:239–246. https://doi.org/10.3109/01676830.2013.788662
Fichter N, Schittkowski MP, Vick HP, Guthoff RF (2004) Lateral orbital decompression for Graves’ orbitopathy. Indication, surgical technique, and treatment success. Ophthalmologe 101:339–349. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00347-004-1008-2
Kikkawa DO, Pornpanich K, Cruz RCJ, Levi L, Granet DB (2002) Graded orbital decompression based on severity of proptosis. Ophthalmology 109:1219–1224. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0161-6420(02)01068-0
Goldberg RA, Perry JD, Hortaleza V, Tong JT (2000) Strabismus after balanced medial plus lateral wall versus lateral wall only orbital decompression for dysthyroid orbitopathy. Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg 16:271–277. https://doi.org/10.1097/00002341-200007000-00004
Ben Simon GJ, Syed HM, Lee S, Wang DY, Schwarcz RM, McCann JD, Goldberg RA (2006) Strabismus after deep lateral wall orbital decompression in thyroid-related orbitopathy patients using automated hess screen. Ophthalmology 113:1050–1055. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ophtha.2006.02.015
Guo J, Li X, Ma R, Qian J (2021) Correlation between uniocular and duction changes following different decompression surgeries in thyroid eye disease. BMC Ophthalmol 21:134–142. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12886-021-01892-9
Demer JL, Miller JM, Poukens V, Vinters HV, Glasgow BJ (1995) Evidence for fibromuscular pulleys of the recti extraocular muscles. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 36:1125–1136
Funding
The research was supported by the National Research Council, Brasília (CNPq-PQ 2020).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the conception, design, data collection, and analysis of the study. In addition, all authors revided the final manuscript and are in accordance with its publication.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There are no competing interests to declare.
Ethics approval
This research was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Hospital das Clínicas, School of Medicine of Ribeirão Preto, University of São Paulo, and followed the Declaration of Helsinki, 2013.
Consent to participate
All patients enrolled signed a specific consent form.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Caetano, F.B., Garcia, D.M., Abbud, C.M.M. et al. The effect of rim-off deep lateral orbital decompression on the lateral rectus shape and oculomotor balance. Int Ophthalmol 43, 4315–4321 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10792-023-02843-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10792-023-02843-7