Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate sequential changes in the inner retinal surface using en face spectral domain optical coherence tomography (SD-OCT) following internal limiting membrane (ILM) peeling for idiopathic full thickness macular holes.
Methods
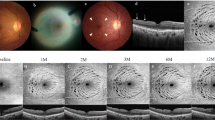
Retrospective, interventional study on 45 eyes of 42 patients with type 1 macular hole closure after a single procedure and a minimum post-operative follow up of 6 months. Best corrected visual acuity (BCVA), fundus photographs, B scan and en face SD-OCT scans were analysed pre-operatively, at 2, 6, 12 months post-operatively and then yearly. The presence or absence of concentric macular dark spots (CMDS) on the ILM slab of en face SD-OCT, their distribution pattern and course in terms of number and size of the dark spots was qualitatively assessed at each follow up.
Results
CMDS was identified in a total of 26 eyes (57.78%). Of these, it was detected in 21 eyes at 2 months and the remaining by 6 months. At the time of first detection, the distribution was classified as type 1 in 9 eyes (35%), type 2 in 7 eyes (27%) and type 3 in 10 eyes (38%). There was apparent increase in the number and size of the CMDS in 16 eyes (62%) no later than 12 months follow up, while 10 eyes (38%) remained stable. There was no decrease or resolution noted in any patient. The mean post-operative follow up was 19.4 months (range 6–69 months).
Conclusion
Inner retinal defects in the form of CMDS can be picked up on en face SD-OCT between 2–6 months post-operatively. They remain stable or become more prominent upto 12 months follow up, but do not regress once present. En face SD-OCT is recommended in all cases where ILM is peeled to assess CMDS.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tadayoni R, Paques M, Massin P, Mouki-Benani S, Mikol J, Gaudric A (2001) Dissociated optic nerve fiber layer appearance of the fundus after idiopathic epiretinal membrane removal. Ophthalmology 108:2279–2283
Mitamura Y, Ohtsuka K (2005) Relationship of dissociated optic nerve fiber layer appearance to internal limiting membrane peeling. Ophthalmology 112:1766–1770
Ito Y, Terasaki H, Takahashi A, Yamakoshi T, Kondo M, Nakamura M (2005) Dissociated optic nerve fiber layer appearance after internal limiting membrane peeling for idiopathic macular holes. Ophthalmology 112:1415–1420
Mitamura Y, Suzuki T, Kinoshita T, Miyano N, Tashimo A, Ohtsuka K (2004) Optical coherence tomographic findings of dissociated optic nerve fiber layer appearance. Am J Ophthalmol 137:1155–1156
Spaide RF (2012) “Dissociated optic nerve fiber layer appearance” after internal limiting membrane removal is inner retinal dimpling. Retina 32:1719–1726
Nukada K, Hangai M, Ooto S, Yoshikawa M, Yoshimura N (2013) Tomographic features of macula after successful macular hole surgery. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 54:2417–2428
Forte R, Cennamo G, Pascotto F, de Crecchio G (2008) En face optical coherence tomography of the posterior pole in high myopia. Am J Ophthalmol 145:281–288
Kishimoto H, Kusuhara S, Matsumiya W, Nagai T, Negi A (2011) Retinal surface imaging provided by cirrus high-definition optical coherence tomography prominently visualizes a dissociated optic nerve fiber layer appearance after macular hole surgery. Int Ophthalmol 31:385–392
Alkabes M, Salinas C, Vitale L, Burés-Jelstrup A, Nucci P, Mateo C (2011) En face optical coherence tomography of inner retinal defects after internal limiting membrane peeling for idiopathic macular hole. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 52:8349–8355
Liu J, Chen Y, Wang S, Zhang X, Zhao P (2018) Evaluating inner retinal dimples after inner limiting membrane removal using multimodal imaging of optical coherence tomography. BMC Ophthalmol 18:155
Holladay JT, Prager TC (1991) Mean visual acuity. Am J Ophthalmol 111:372–374
Gass JD (1995) Reappraisal of biomicroscopic classification of stages of development of a macular hole. Am J Ophthalmol 119:752–759
Navajas EV, Schuck N, Govetto A, Akil H, Docherty G, Heisler M et al (2020) En face optical coherence tomography and optical coherence tomography angiography of inner retinal dimples after internal limiting membrane peeling for full-thickness macular holes. Retina 40:557–566
Kim KY, Yu SY, Kim M, Kim ES, Kwak HW (2013) Morphological change of inner retinal layer on spectral-domain optical coherence tomography following macular hole surgery. Ophthalmologica 230:18–26
Terasaki H, Miyake Y, Nomura R, Piao CH, Hori K, Niwa T et al (2001) Focal macular ERGs in eyes after removal of macular ILM during macular hole surgery. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 42:229–234
Distler C, Dreher Z (1996) Glia cells of the monkey retina—II Müller cells. Vis Res 36:2381–2394
Amouyal F, Shah SU, Pan CK, Schwartz SD, Hubschman JP (2014) Morphologic features and evolution of inner retinal dimples on optical coherence tomography after internal limiting membrane peeling. Retina 34:2096–2102
Pichi F, Lembo A, Morara M, Veronese C, Alkabes M, Nucci P, Ciardella AP (2014) Early and late inner retinal changes after inner limiting membrane peeling. Int Ophthalmol 34:437–446
Sakimoto S, Ikuno Y, Fujimoto S, Sakaguchi H, Nishida K (2014) Characteristics of the retinal surface after internal limiting membrane peeling in highly myopic eyes. Am J Ophthalmol 158:762-768.e1
Park SH, Kim YJ, Lee SJ (2016) Incidence of and risk factors for dissociated optic nerve fiber layer after epiretinal membrane surgery. Retina 36:1469–1473
Funding
No funding was received for this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of ICARE eye hospital and postgraduate institute, NOIDA, U.P., India and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Goel, N., Shukla, G. Long-term follow up of en face optical coherence tomography of the inner retinal surface following internal limiting membrane peeling for idiopathic macular holes. Int Ophthalmol 41, 1003–1010 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10792-020-01657-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10792-020-01657-1