Abstract
Purpose
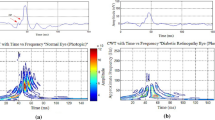
To evaluate the effects of retinitis pigmentosa (RP) on time, frequency, and time–frequency components of Xenon flash ERG signals using Fourier and wavelet transforms.
Methods
Xenon flash ERG was done in 18 eyes of nine RP patients and 20 normal eyes. After examining latency and amplitude, Fourier and wavelet transforms were performed using MATLAB software. Then, we extracted the mode frequency from the Fourier transform and main frequencies and their occurrence time from the wavelet transform. Finally, mean differences were analyzed using statistical tests.
Results
The results indicated increased latency and reduced ERG wave amplitude, no significant inter-group difference in the average mode frequency, and significant reduction in main signal frequencies and their increased occurrence times. Also one or two of the three main frequencies had disappeared in more advanced cases.
Conclusion
Retinitis pigmentosa can induce changes in ERG time and time–frequency components. Impacted areas can be identified more accurately by wavelet transform and converting scales to frequencies.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Birch DG (2006) Retinitis pigmentosa. In: Heckenlively JR, Arden GB (eds) Principles and practice of clinical electrophysiology of vision. MIT Press, Cambridge, pp 781–794
Hamel C (2006) Retinitis pigmentosa. Orphanet J Rare Dis 1:40
Camacho ET, Wirkus S (2013) Tracing the progression of retinitis pigmentosa via photoreceptor interactions. J Theor Biol 317:105–118
Ropstad EO, Narfstrom K (2007) The obvious and the more hidden components of elecroretinogram. EJCAP 17:290–296
Berson EL (1993) Retinitis pigmentosa. The Friedenwald Lecture. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 34:1659–1676
Karimi HH, Jafarzadehpur E, Blouri B, Hashemi H, Sadeghi AZ, Mirzajani A (2012) Frequency domain electroretinography in retinitis pigmentosa versus normal eyes. J Ophthalmic Vis Res 7:34–38
Cideciyan AV, Jacobson SG (1993) Negative electroretinograms in retinitis pigmentosa. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 34:3253–3263
Seiple WH, Holopigian K, Greenstein VC, Hood DC (1993) Sites of cone system sensitivity loss in retinitis pigmentosa. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 34:2638–2645
Alexander KR, Barnes CS, Fishman GA (2003) ON-pathway dysfunction and timing properties of the flicker ERG in carriers of X-linked retinitis pigmentosa. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 44:4017–4025
Falsini B, Iarossi G, Fadda A, Porrello G, Valentini P, Piccardi M, Scullica L (1999) The fundamental and second harmonic of the photopic flicker electroretinogram: temporal frequency-dependent abnormalities in retinitis pigmentosa. Clin Neurophysiol 110:1554–1562
Nair SS, Joseph KP (2014) Wavelet based electroretinographic signal analysis for diagnosis. Biomed Signal Process Control 9:37–44
Barraco R, Adorno DP, Brai M, Tranchina L (2014) A comparison among different techniques for human ERG signals processing and classification. Phys Med 30:86–95
Gauvin M, Lina JM, Lachapelle P (2014) Advance in ERG analysis: from peak time and amplitude to frequency, power, and energy. Biomed Res Int 2014:246096. http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/246096
Gauvin M, Chakor H, Koenekoop RK, Little JM, Lina JM, Lachapelle P (2016) Witnessing the first sign of retinitis pigmentosa onset in the allegedly normal eye of a case of unilateral RP: a 30-year follow-up. Doc Ophthalmol 132:213–229
Hashemi H, Fotouhi A, Mohammad K (2003) The Tehran Eye Study: research design and eye examination protocol. BMC Ophthalmol 3:8
McCulloch DL, Marmor MF, Brigell MG, Hamilton R, Holder GE, Tzekov R, Bach M (2015) ISCEV standard for full-field clinical electroretinography (2015 update). Doc Ophthalmol 130:1–12
Barraco R, Adorno DP, Brai M (2011) ERG signal analysis using wavelet transform. Theory Biosci 130:155–163
Drissi H, Regragui F, Antoine J-P, Bennouna M (2000) Wavelet transform analysis of visual evoked potentials: some preliminary results. ITBM-RBM 21:84–91
Janaky M, Palffy A, Horvath G, Gb Tuboly, Benedek G (2008) Pattern-reversal electroretinograms and visual evoked potentials in retinitis pigmentosa. Doc Ophthalmol 117:27–36
Parisi V, Ziccardi L, Stifano G, Montrone L, Gallinaro G, Falsini B (2010) Impact of regional retinal responses on cortical visually evoked responses: multifocal ERGs and VEPs in the retinitis pigmentosa model. Clin Neurophysiol 121:380–385
Cuenca N, Fernandez-Sanchez L, Campello L, Maneu V, De la Villa P, Lax P, Pinilla I (2014) Cellular responses following retinal injuries and therapeutic approaches for neurodegenerative diseases. Prog Retin Eye Res 43:17–75
Hood DC, Birch DG (1996) Abnormalities of the retinal cone system in retinitis pigmentosa. Vis Res 36:1699–1709
Berson EL (1992) Electrical phenomena in the retina. In: Hart WM (ed) Adler’s physiology of the eye, 9th edn. Mosby, US, pp 641–708
Scholl HP, Kremers J (2000) Large phase differences between L-cone– and M-cone–driven electroretinograms in retinitis pigmentosa. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 41:3225–3233
Fariss RN, Li ZY, Milam AH (2000) Abnormalities in rod photoreceptors, amacrine cells, and horizontal cells in human retinas with retinitis pigmentosa. Am J Ophthalmol 129:215–223
Wen Y, Klein M, Hood DC, Birch DG (2012) Relationships among multifocal electroretinogram amplitude, visual field sensitivity, and SD-OCT receptor layer thicknesses in patients with retinitis pigmentosa. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 53:833–840
Birch DG, Sandberg MA (1987) Dependence of cone b-wave implicit time on rod amplitude in retinitis peigmentosa. Vis Res 27:1105–1112
Hamasaki DI, Liu M, Qiu H, Fujiwara E, Lam BL (2002) The a-wave latency in control subjects and patients with retinal diseases. Jpn J Ophthalmol 46:433–442
Wen Y, Locke KG, Hood DC, Birch DG (2011) Rod photoreceptor temporal properties in retinitis pigmentosa. Exp Eye Res 92:202–208
Janaky M, Palffy A, Deak A, Szilagyi M, Benedek G (2007) Multifocal ERG reveals several patterns of cone degeneration in retinitis pigmentosa with concentric narrowing of the visual field. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 48:383–389
Acknowledgements
This report concerns a postgraduate research project for a master’s degree in medical physics at Tarbiat Modares University by the first author under the supervision of the second and third authors at Noor Ophthalmology Research Center. The authors wish to express their appreciation for the sincere assistance of ophthalmologists, optometrists, and the staff at the Electrophysiology Unit of Noor Eye Hospital, particularly Mrs. Shariati.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors certify that they have no affiliations with or involvement in any organization or entity with any financial interest or non-financial interest in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript.
Ethical approval
The study protocol adhered to the tenets of the Helsinki declaration and was approved by the Ethics Committee of Tarbiat Modares University.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ebdali, S., Hashemi, B., Hashemi, H. et al. Time and frequency components of ERG responses in retinitis pigmentosa. Int Ophthalmol 38, 2435–2444 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10792-017-0748-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10792-017-0748-3