Abstract
Purpose
To compare the biometric measurements obtained from the Verion Image-Guided System to those obtained by auto-refracto-keratometer in normal eyes.
Methods
This is a prospective, observational, comparative study conducted at the Asociación para Evitar la Ceguera en México I.A.P., Mexico. Three sets of keratometry measurements were obtained using the image-guided system to assess the coefficient of variation, the within-subject standard deviation and intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC). A paired Student t test was used to assess statistical significance between the Verion and the auto-refracto-keratometer. A Pearson’s correlation coefficient (r) was obtained for all measurements, and the level of agreement was verified using Bland–Altman plots.
Results
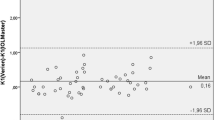
The right eyes of 73 patients were evaluated by each platform. The Verion coefficient of variation was 0.3% for the flat and steep keratometry, with the ICC being greater than 0.9 for all parameters measured. Paired t test showed statistically significant differences between groups (P = 0.0001). A good correlation was evidenced for keratometry values between platforms (r = 0.903, P = 0.0001 for K1, and r = 0.890, P = 0.0001). Bland–Altman plots showed a wide data spread for all variables.
Conclusion
The image-guided system provided highly repeatable corneal power and keratometry measurements. However, significant differences were evidenced between the two platforms, and although values were highly correlated, they showed a wide data spread for all analysed variables; therefore, their interchangeable use for biometry assessment is not advisable.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hayashi K, Hayashi H, Nakao F, Hayashi F (2000) Influence of astigmatism on multifocal and monofocal intraocular lenses. Am J Ophthalmol 130(4):477–482
Yuan X, Song H, Peng G, Hua X, Tang X (2014) Clinical study prevalence of corneal astigmatism in patients before cataract surgery in Northern China. J Ophthalmol 2014:536412
Reitblat OR, Levy A, Kleinmann G, Abulafia A, Assia EI (2016) Effect of posterior corneal astigmatism on power calculation and alignment of toric intraocular lenses: comparison of methodologies. J Cataract Refract Surg 42(2):217–225
Ventura BV, Al-Mohtaseb Z, Wang L, Koch DD, Weikert MP (2015) Repeatability and comparability of corneal power and corneal astigmatism obtained from a point-source color light-emitting diode topographer, a Placido-based corneal topographer, and a low-coherence reflectometer. J Cataract Refract Surg 41(10):2242–2250
Zheng T, Chen Z, Lu Y (2016) Influence factors of estimation errors for total corneal astigmatism using keratometric astigmatism in patients before cataract surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg 42(1):84–94
Goebels S, Pattmöller M, Eppig T, Cayless A, Seitz B, Langenbucher A (2015) Comparison of 3 biometry devices in cataract patients. J Cataract Refract Surg 41(11):2387–2393
Li J, Chen H, Savini G et al (2016) Measurement agreement between a new biometer based on partial coherence interferometry and a validated biometer based on optical low-coherence reflectometry. J Cataract Refract Surg 42(1):68–75
Huang J, Savini G, Wu F et al (2015) Repeatability and reproducibility of ocular biometry using a new noncontact optical low-coherence interferometer. J Cataract Refract Surg 41(10):2233–2241
Elhofi AH, Helaly HA (2015) Comparison between digital and manual marking for toric intraocular lenses. Medicine 94(38):e1618-4
Potvin R, Davison J (2015) Refractive cylinder outcomes after calculating toric intraocular lens cylinder power using total corneal refractive power. Clin Ophthalmol 19(9):1511–1517
Nemeth G, Szalai E, Hassan Z, Lipecz A, Berta A, Modis L Jr (2015) Repeatability data and agreement of keratometry with the VERION system compared to the IOLMaster. J Cataract Refract Surg 31(5):333–337
Mueller A, Thomas BC, Auffarth GU, Holzer MP (2016) Comparison of a new image-guided system versus partial coherence interferometry, Scheimpflug imaging, and optical low-coherence reflectometry devices: keratometry and repeatability. J Cataract Refract Surg 42(5):672–678
Santodomingo-Rubido J, Mallen EAH, Gilmartin B, Wolffsohn JS (2002) A new non-contact optical device for ocular biometry. Br J Ophthalmol 86(4):458–462
Vitale S, Ellwein L, Cotch MF, Ferris FL, Sperduto R (2008) Prevalence of refractive error in the United States. Arch Ophthalmol 126(8):1111–1116
Srivannaboon S, Chirapapaisan C, Chonpimai P, Koodkaew S (2015) Comparison of corneal astigmatism measurements of 2 optical biometer models for toric intraocular lens selection. J Cataract Refract Surg 41(2):364–371
Asena L, Güngör SG, Akman A. (2016) Comparison of keratometric measurements obtained by the Verion Image Guided System with optical biometry and auto-keratorefractometer. Int Ophthalmol 1–9. [Epub ahead of print]
Verion Reference Unit. Alcon Laboratories. Fort Worth, Texas. http://crstoday.com/pdfs/0614_supp2.pd
Lauschke JL, Lawless M, Sutton G, Roberts TV, Hodge C (2016) Assessment of corneal curvature using verion optical imaging system: a comparative study. Clin Exp Ophthalmol 44(5):369–376
Srivannaboon S, Soeharnila Chirapapaisan C, Chonpimai P (2012) Comparison of corneal astigmatism and axis location in cataract patients measured by total corneal power, automated keratometry, and simulated keratometry. J Cataract Refract Surg 38:2088–2093
Acknowledgement
The Asociación Para Evitar la Ceguera en México I.A.P. provided financial support in the form of biometry assessment grant for enrolled subjects (Grant Number SA-16-00). The sponsor had no role in the design or conduct of this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors certify that they have no affiliations with or involvement in any organization or entity with any financial interest (such as honoraria; educational grants; participation in speakers’ bureaus; membership, employment, consultancies, stock ownership or other equity interest; and expert testimony or patent-licensing arrangements), or non-financial interest (such as personal or professional relationships, affiliations, knowledge or beliefs) in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Velasco-Barona, C., Cervantes-Coste, G., Mendoza-Schuster, E. et al. Comparison of biometric measurements obtained by the Verion Image-Guided System versus the auto-refracto-keratometer. Int Ophthalmol 38, 951–957 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10792-017-0541-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10792-017-0541-3