Abstract
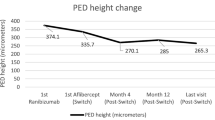
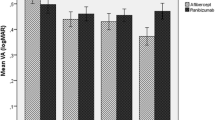
The purpose of the study was to assess the efficacy and safety of transition from ranibizumab to aflibercept intravitreal injections in treatment-resistant retinal pigment epithelial detachment (PED). The data of intravitreal ranibizumab treatment-resistant patients who have been switched to aflibercept treatment were reviewed retrospectively. After three monthly injections, bimonthly regimen was performed. The changes of PED height and radius, and the best-corrected visual acuity (BCVA) were analyzed retrospectively. Mean baseline PED height decreased from 297 ± 151 to 122 ± 42 µm at month 12 (P = 0.0007). Mean baseline PED radius decreased from 2371 ± 882 to 1859 ± 779 µm at month 12 (P = 0.0007). No complete PED resolution occurred in any of the patients at the end of the 12 months. Baseline BCVA improved from 0.63 ± 0.21 to 0.43 ± 0.17 logMar at month 12 (P = 0.0049). Mean BCVA gain was 1.4 decimal chart lines (7 letters) at month 12. Switching to aflibercept seems to have promising functional and anatomical outcomes with a reasonable complication rate in treatment-resistant PED.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zayit-Soudry S, Moroz I, Loewenstein A (2007) Retinal pigment epithelial detachment. Surv Ophthalmol 52(3):227–243
Roquet W, Roudot-Thoraval F, Coscas G, Soubrane G (2004) Clinical features of drusenoid pigment epithelial detachment in age related macular degeneration. Br J Ophthalmol 88(5):638–642
Iordanous Y, Powell AM, Mao A, Hooper PL, Eng KT, Schwartz C, Kertes PJ, Sheidow TG (2014) Intravitreal ranibizumab for the treatment of fibrovascular pigment epithelial detachment in age-related macular degeneration. Can J Ophthalmol 49(4):367–376. doi:10.1016/j.jcjo.2014.05.010
Murphy RP, Yeo JH, Green WR et al (1985) Dehiscences of the pigment epithelium. Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc 83:63–81
Mrejen S, Sarraf D, Mukkamala SK, Freund KB (2013) Multimodal imaging of pigment epithelial detachment: a guide to evaluation. Retina 33:1735–1762
Yannuzzi LA (1989) Retinal pigment epithelial detachment. J Fr Ophtalmol 12:761–774
Abdelfattah NS, Sadda SR (2015) Dry AMD progression in wet AMD: what we know and don’t know about geographic atrophy. Retina Specialist 6(June):18–21
Gelisken F, Inhoffen W, Partsch M et al (2001) Retinal pigment epithelial tear after photodynamic therapy for choroidal neovascularization. Am J Ophthalmol 131:518–520
Weinberger AW, Thiel M, Mohammadi B et al (2007) Retinal pigment epithelium tears after intravitreal bevacizumab in pigment epithelium detachment. Am J Ophthalmol 144(2):294–296
Lommatzsch A, Heimes B, Gutfleisch M et al (2009) Serous pigment epithelial detachment in age-related macular degeneration: comparison of different treatments. Eye 23(12):2163–2168
Brown DM, Kaiser PK, Michels M, ANCHOR Study Group et al (2006) Ranibizumab versus verteporfin for neovascular age-related macular degeneration. N Engl J Med 355:1432–1444
Rosenfeld PJ, Brown DM, Heier JS, MARINA Study Group et al (2006) Ranibizumab for neovascular age-related macular degeneration. N Engl J Med 355:1419–1431
Fung AE, Lalwani GA, Rosenfeld PJ et al (2007) An optical coherence tomography-guided, variable dosing regimen with intravitreal ranibizumab (Lucentis) for neovascular age-related macular degeneration. Am J Ophthalmol 143:566–583
Broadhead GK, Hong T, Zhu M, Li H, Schlub TE, Wijeyakumar W, Chang AA (2015) Response of pigment epithelial detachments to intravitreal aflibercept among patients with treatment-resistant neovascular age-related macular degeneration. Retina 35(5):975–981. doi:10.1097/IAE.0000000000000409
Abdelfattah NS, Zhang H, Boyer DS, Sadda SR. (2016) Progression of macular atrophy in patients with neovascular age-related macular degeneration undergoing antivascular endothelial growth factor therapy. Retina 2016 Apr 28. [Epub ahead of print]
Schmidt-Erfurth U, Kaiser PK, Korobelnik JF et al (2014) Intravitreal aflibercept injection for neovascular age-related macular degeneration: ninety-six-week results of the VIEW studies. Ophthalmology 121(1):193–201. doi:10.1016/j.ophtha.2013.08.011
Carmeliet P, Moons L, Luttun A et al (2001) Synergism between vascular endothelial growth factor and placental growth factor contributes to angiogenesis and plasma extravasation in pathological conditions. Nat Med 7(5):575–583
Autiero M, Luttun A, Tjwa M, Carmeliet P (2003) Placental growth factor and its receptor, vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1: novel targets for stimulation of ischemic tissue revascularization and inhibition of angiogenic and inflammatory disorders. J Thromb Haemost 1(7):1356–1370
Kumar N, Marsiglia M, Mrejen S et al (2013) Visual and anatomical outcomes of intravitreal aflibercept in eyes with persistent subfoveal fluid despite previous treatments with ranibizumab in patients with neovascular age-related macular degeneration. Retina 33:1605–1612
Patel KH, Chow CC, Rathod R et al (2013) Rapid response of retinal pigment epithelial detachments to intravitreal aflibercept in neovascular age-related macular degeneration refractory to bevacizumab and ranibizumab. Eye 27:663–667
Punjabi OS, Huang J, Rodriguez L et al (2013) Imaging characteristics of neovascular pigment epithelial detachments and their response to anti-vascular endothelial growth factor therapy. Br J Ophthalmol 97:1024–1031
Goldstein M, Heilweil G, Barak A, Loewenstein A (2005) Retinal pigment epithelial tear following photodynamic therapy for choroidal neovascularization secondary to AMD. Eye 19(12):1315–1324
Pece A, Introini U, Bottoni F et al (2001) Acute retinal pigment epithelial tear after photodynamic therapy. Retina 21:661–665
Wykoff CC, Croft DE, Brown DM, Wang R, Payne JF, Clark L, Abdelfattah NS, Sadda SR (2015) TREX-AMD study group prospective trial of treat-and-extend versus monthly dosing for neovascular age-related macular degeneration: TREX-AMD 1-year results. Ophthalmology 122(12):2514–2522. doi:10.1016/j.ophtha.2015.08.009
Major JC Jr, Wykoff CC, Croft DE, Wang R, Mariani AF, Lehmann AE, Brown DM (2015) Aflibercept for pigment epithelial detachment for previously treated neovascular age-related macular degeneration. Can J Ophthalmol. 50(5):373–377. doi:10.1016/j.jcjo.2014.12.012
He L, Silva RA, Moshfeghi DM, Blumenkranz MS, Leng T (2016) Aflibercept for the treatment of retinal pigment epithelial detachments. Retina. 36(3):492–498. doi:10.1097/IAE.0000000000000749
Kanesa-Thasan A, Grewal DS, Gill MK, Lyon AT, Mirza R (2015) Quantification of change in pigment epithelial detachment volume and morphology after transition to intravitreal aflibercept in eyes with recalcitrant neovascular AMD: 18-month results. Ophthalmic Surg Lasers Imaging Retina 46(6):638–641. doi:10.3928/23258160-20150610-07
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kocak, I. Intravitreal aflibercept in treatment-resistant pigment epithelial detachment. Int Ophthalmol 37, 531–537 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10792-016-0294-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10792-016-0294-4