Abstract
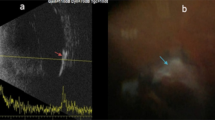
The aim of this study was to evaluate and compare 10-MHz and 20-MHz ultrasonography in the assessment of patients with optic nerve head drusen (ONHD). The design of the study was prospective, comparative and cross-sectional. Ultrasonographic examination with a 10 and 20 MHz probe was performed in 45 eyes with suspected ONHD. The 20 MHz probe showed drusen in 43 eyes (95.5 %), while the 10 MHz probe revealed drusen in only 33 eyes (73.3 %, p = 0.0001). The 10 MHz probe showed surface drusen in 10 eyes (22.2 %), while the 20 MHz probe showed surface drusen in 14 eyes (31.1 %) (sensitivity 71.4 %; 95 % CI [47.6–95.1 %]). The 10 MHz probe showed buried drusen in 23 eyes (23.1 %), while the 20 MHz probe showed buried drusen in 29 eyes (64.4 %) (sensitivity 79.3 %; 95 % CI [56.6–86.2 %]). The sensitivity was 76.7 % with 10 MHz probe compared to a 20 MHz as gold standard. The use of 20 MHz probe increased the sensitivity of buried disc drusen by 1.5 times and surface disc drusen by nearly 2 times. Using the 10 MHz probe alone the false negative error rate was 83.3 %. The 20 MHz probe has shown itself to be an excellent method for the diagnosis of ONHD; it is more sensitive and reliable than 10 MHz probe and should be considered in the management of patients with clinical evidence of ONHD.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Claudia A-H, Flemming S, Heinrich W (2002) Optic Disc Drusen. Surv ophthalmol 47:515–532
Johnson LN, Diehl ML, Hamm CW, Sommerville DN, Petroski GF (2009) Differentiating optic disc edema from optic nerve head drusen on optical coherence tomography. Arch Ophthalmol 127:45–49
Sato T, Mrejen S, Spaide RF (2013) Multimodal imaging of optic disc drusen. Am J Ophthalmol 156:275–282
Friedman AH, Beckerman B, Gold DH, Walsh JB, Gartner S (1977) Drusen of the optic disc. Surv Ophthalmol 21:373–390
Mustonen E, Nieminen H (1982) Optic disc drusen- a photographic study: autofluorescence pictures and fluorescein angiography. Acta Ophthalmol (Copenh) 60:849–858
McNicholas MM, Power WJ, Griffin JF (1994) Sonography in optic disk drusen: imaging findings and role in diagnosis when funduscopic findings are normal. AJR Am J Roentgenol 162:161–163
Merchant KY, Su D, Park SC, Qayum S, Banik R, Liebmann JM, Ritch R (2013) Enhanced depth imaging optical coherence tomography of optic nerve head drusen. Ophthalmology 120:1409–1414
Kurz-Levin MM, Landau K (1999) A comparison of imaging techniques for diagnosing drusen of the optic nerve head. Arch Ophthalmol 117:1045–1049
Boldt HC, Byrne SF, DiBernardo C (1991) Echographic evaluation of optic disc drusen. J Clin Neuroophthalmol 11:85–91
Hewick SA, Fairhead AC, Culy JC, Atta HR (2004) A comparison of 10 MHz and 20 MHz ultrasound probes in imaging the eye and orbit. Br J Ophthalmol 88:551–555
Lorentzen SE (1966) Drusen of the optic disk: a clinical and genetic study. Acta Ophthalmol (Copenh) Suppl 90:1–180
Friedman AH, Gartner S, Modi SS (1975) Drusen of the optic disc. A retrospective study in cadaver eyes. Br J Ophthalmol 59:413–421
Atta HR (1988) Imaging of the optic nerve with standardised echography. Eye (Lond) 2:358–366
Kheterpal S, Good PA, Beale DJ, Kritzinger EE (1995) Imaging of optic disc drusen: a comparative study. Eye (Lond) 9:67–69
Acknowledgments
This work has been supported by the Ministry of Higher Education and Scientific Research of Tunisia.
Conflict of interest
The authors report no conflicts of interest. The authors alone are responsible for the content and writing of the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zaouali, S., Abroug, N., Khochtali, S. et al. Optic nerve head drusen: a comparative study of 10 MHz and 20 MHz ultrasound probes. Int Ophthalmol 35, 229–232 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10792-014-9939-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10792-014-9939-3