Abstract
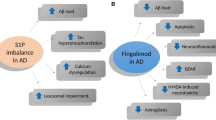
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic progressive disabling disease of the central nervous system (CNS) characterized by demyelination and neuronal injury. Dyslipidemia is observed as one of the imperative risk factors involved in MS neuropathology. Also, chronic inflammation in MS predisposes to the progress of dyslipidemia. Therefore, treatment of dyslipidemia in MS by statins may attenuate dyslipidemia-induced MS and avert MS-induced metabolic changes. Therefore, the present review aimed to elucidate the possible effects of statins on the pathogenesis and outcomes of MS. Statins adversely affect the cognitive function in MS by decreasing brain cholesterol CoQ10, which is necessary for the regulation of neuronal mitochondrial function. However, statins could be beneficial in MS by shifting the immune response from pro-inflammatory Th17 to an anti-inflammatory regulatory T cell (Treg). The protective effect of statins against MS is related to anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects with modulation of fibrinogen and growth factors. In conclusion, the effects of statins on MS neuropathology seem to be conflicting, as statins seem to be protective in the acute phase of MS through anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects. However, statins lead to detrimental effects in the chronic phase of MS by reducing brain cholesterol and inhibiting the remyelination process.

Created on BioRender.com

Created on BioRender.com

Created on BioRender.com
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Abdalla MA, Zakhary CM, Rushdi H, Hamdan JA, Youssef KN, Khan A, Khan S (2021) The effectiveness of statins as potential therapy for multiple sclerosis: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Cureus. https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.18092
Adams AC, Cheng CC, Coskun T, Kharitonenkov A (2012) FGF21 requires βklotho to act in vivo. PLoS One 7:e49977
Ahmad U, Frederiksen JL (2020) Fibrinogen: A potential biomarker for predicting disease severity in multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler Relat Disord 46:102509
Al-Kuraishy HM, Al-Gareeb AI, Hussien NR, Al-Naimi MS, Rasheed HA (2019) Statins an oft-prescribed drug is implicated in peripheral neuropathy: The time to know more. JPMA. J Pak Med Assoc 69:S108–S112
Al-Kuraishy HM, Al-Gareeb AI, Naji MT (2021) Statin therapy associated with decreased neuronal injury measured by serum S100β levels in patients with acute ischemic stroke. Int J Crit Illn Inj Sci 11:246
Al-kuraishy HM, Al-Gareeb AI, Alexiou A, Papadakis M, Alsayegh AA, Almohmadi NH, Saad HM, Batiha GE-S (2023) Pros and cons for statins use and risk of Parkinson’s disease: An updated perspective. Pharmacol Res Perspect 11:e01063
Al-kuraishy HM, Al-Gareeb AI, Saad HM, Batiha GE-S (2022) Benzodiazepines in Alzheimer’s disease: beneficial or detrimental effects. Inflammopharmacology. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-023-01163-7
Alsubaie N, Al-kuraishy HM, Al-Gareeb AI, Alharbi B, De Waard M, Sabatier J-M, Saad HM, Batiha GE-S (2022) Statins use in Alzheimer disease: bane or boon from frantic search and narrative review. Brain Sci 12:1290
Andaloro A, Russo M, Pastura C, Sessa E, Calatozzo P, Maggio MG, Bramanti P (2021) Is there a correlation between dyslipidemia and cognitive impairment in patients with multiple sclerosis? Int J Neurosci 132:201–206
Balasa R, Barcutean L, Mosora O, Manu D (2021) Reviewing the significance of blood–brain barrier disruption in multiple sclerosis pathology and treatment. Int J Mol Sci 22:8370
Bhardwaj S, Coleman CI, Sobieraj DM (2012) Efficacy of statins in combination with interferon therapy in multiple sclerosis: a meta-analysis. Am J Health Syst Pharm 69:1494–1499
Birnbaum G, Cree B, Altafullah I, Zinser M, Reder A (2008) Combining beta interferon and atorvastatin may increase disease activity in multiple sclerosis. Neurology 71:1390–1395
Black DM (1998) Statins and fibrinogen. The Lancet 351:1430
Borghini I, Barja F, Pometta D, James RW (1995) Characterization of subpopulations of lipoprotein particles isolated from human cerebrospinal fluid. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Lipids Lipid Metabol 1255:192–200
Boshra H, Awad M, Hussein M, Elyamani E (2022) Vascular dysfunction and dyslipidemia in multiple sclerosis: are they correlated with disease duration and disability status? Egyptian Heart J 74:9
Chen J, Zhang C, Jiang H, Li Y, Zhang L, Robin A, Katakowski M, Lu M, Chopp M (2005) Atorvastatin induction of VEGF and BDNF promotes brain plasticity after stroke in mice. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 25:281–290
Chihara N (2018) Dysregulated T cells in multiple sclerosis. Clin Experim Neuroimmunol 9:20–29
Ciurleo R, Bramanti P, Marino S (2014) Role of statins in the treatment of multiple sclerosis. Pharmacol Res 87:133–143
Conway DS, Thompson NR, Cohen JA (2017) Influence of hypertension, diabetes, hyperlipidemia, and obstructive lung disease on multiple sclerosis disease course. Mult Scler J 23:277–285
Cucchiara B, Kasner SE (2001) Use of statins in CNS disorders. J Neurol Sci 187:81–89
D’haeseleer M, Cambron M, Vanopdenbosch L, De Keyser J (2011) Vascular aspects of multiple sclerosis. Lancet Neurol 10:657–666
de Oliveira FF, Bertolucci PHF, Chen ES, Smith MC (2022) Pharmacogenetic analyses of therapeutic effects of lipophilic statins on cognitive and functional changes in Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 87:1–14
Dobson R, Giovannoni G (2019) Multiple sclerosis–a review. Eur J Neurol 26:27–40
Dunn SE, Youssef S, Goldstein MJ, Prod’homme T, Weber MS, Zamvil SS, Steinman L (2006) Isoprenoids determine Th1/Th2 fate in pathogenic T cells, providing a mechanism of modulation of autoimmunity by atorvastatin. J Exp Med 203:401–412
Dziedzic A, Miller E, Saluk-Bijak J, Bijak M (2020) The GPR17 receptor—a promising goal for therapy and a potential marker of the neurodegenerative process in multiple sclerosis. Int J Mol Sci 21:1852
Edwards NC, Munsell M, Menzin J, Phillips AL (2018) Comorbidity in US patients with multiple sclerosis. Patient Relat Outcome Meas 9:97–102
Eyal Leibovitz M, Neli Hazanov M, Angela Frieman M, Itzhak Elly M, Dov Gavish M (2004) Atorvastatin reduces fibrinogen levels in patients with severe hypercholesterolemia: additional evidence to support the anti-inflammatory effects of statins
Feng X, Vander Heyden N, Ratner L (2003) AlphaInterferon inhibits human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 assembly by preventing gag interaction withrafts. J Virol 77:13389–13395
Feng X, Han D, Kilaru BK, Franek BS, Niewold TB, Reder AT (2012) Inhibition of interferon-beta responses in multiple sclerosis immune cells associated with high-dose statins. Arch Neurol 69:1303–1309
Fessler MB, Parks JS (2011) Intracellular lipid flux and membrane microdomains as organizing principles in inflammatory cell signaling. J Immunol 187:1529–1535
Franklin RJ (2002) Why does remyelination fail in multiple sclerosis? Nat Rev Neurosci 3:705–714
Franklin RJ, Gallo V (2014) The translational biology of remyelination: past, present, and future. Glia 62:1905–1915
Frohman EM, Racke MK, Raine CS (2006) Multiple sclerosis—the plaque and its pathogenesis. N Engl J Med 354:942–955
Gao S, Yu R, Zhou X (2016) The role of geranylgeranyltransferase I-mediated protein prenylation in the brain. Mol Neurobiol 53:6925–6937
Gao Y-H, Li X (2023) Cholesterol metabolism: Towards a therapeutic approach for multiple sclerosis. Neurochem Int 164:105501
Ghittoni R, Napolitani G, Benati D, Uliveri C, Patrussi L, Laghi Pasini F, Lanzavecchia A, Baldari CT (2006) Simvastatin inhibits the MHC class II pathway of antigen presentation by impairing Ras superfamily GTPases. Eur J Immunol 36:2885–2893
Hardoňová M, Šiarnik P, Sivakova M, Sucha B, Vlček M, Imrich R, Turčáni P, Havranova A, Rádiková Ž (2021) Autonomic Nervous system function in newly diagnosed multiple sclerosis: association with lipid levels and insulin resistance. Physiol Res 70:875
He W, Tian X, Yuan B, Chu B, Gao F, Wang H (2019) Rosuvastatin improves neurite extension in cortical neurons through the Notch 1/BDNF pathway. Neurol Res 41:658–664
Hinson ER, Joshi NS, Chen JH, Rahner C, Jung YW, Wang X, Kaech SM, Cresswell P (2010) Viperin is highly induced in neutrophils and macrophages during acute and chronic lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus infection. J Immunol 184:5723–5731
Hirrlinger J, Nave KA (2014) Adapting brain metabolism to myelination and long-range signal transduction. Glia 62:1749–1761
Höftberger R, Lassmann H, Berger T, Reindl M (2022) Pathogenic autoantibodies in multiple sclerosis—from a simple idea to a complex concept. Nat Rev Neurol 11:1–8
Husain I, Akhtar M, Vohora D, Abdin MZ, Islamuddin M, Akhtar MJ, Najmi AK (2017) Rosuvastatin attenuates high-salt and cholesterol diet induced neuroinflammation and cognitive impairment via preventing nuclear factor KappaB pathway. Neurochem Res 42:2404–2416
Hussien NR, Al-Niemi MS, Al-Kuraishy HM, Al-Gareeb AI (2021) Statins and Covid-19: The neglected front of bidirectional effects. J Pak Med Assoc 71:133
Ifergan I, Wosik K, Cayrol R, Kébir H, Auger C, Bernard M, Bouthillier A, Moumdjian R, Duquette P, Prat A (2006) Statins reduce human blood–brain barrier permeability and restrict leukocyte migration: relevance to multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol 60:45–55
Kadhim SS, Al-Windy SA, Al-Nami MS, Al-kuraishy HM, Al-Gareeb AI (2019) Possible role of statins on the inflammatory biomarkers in patients with periodontal disease: a cross-sectional study. Dent Hypotheses 10:70
Kadhim SS, Al-Windy SA, Al-Nami MS, Al Kuraishy HM, Al Gareeb AI (2020) Statins improve periodontal disease–induced inflammatory changes and associated lipid peroxidation in patients with dyslipidemia: Two birds by one stone. J Int Oral Health 12:66
Kajinami K, Akao H, Polisecki E, Schaefer EJ (2005) Pharmacogenomics of statin responsiveness. Am J Cardiol 96:65–70
Karimi N, Ashourizadeh H, Pasha BA, Haghshomar M, Jouzdani T, Shobeiri P, Teixeira AL, Rezaei N (2022) Blood levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) in people with multiple sclerosis (MS): A systematic review and meta-analysis. Mult Scler Relat Disord 65:103984
Kata D, Földesi I, Feher L, Hackler L Jr, Puskas L, Gulya K (2016) Rosuvastatin enhances anti-inflammatory and inhibits pro-inflammatory functions in cultured microglial cells. Neuroscience 314:47–63
Katsiki N, Mantzoros C (2019) Fibroblast growth factor 21: A role in cardiometabolic disorders and cardiovascular risk prediction? Metabol Clin Exp 93:iii–v
Kaur G, Saravana S, Banerjee P, Kumar M, Khurana D (2019) Influence of dyslipidemia on multiple sclerosis disease activity. J Neurol Sci 405:308
Kendall A, Ekman S, Skiöldebrand E (2023) Nerve growth factor receptors in equine synovial membranes vary with osteoarthritic disease severity. J Orthop Res 41:316–324
Kennedy PG, George W, Yu X (2022) The possible role of neural cell apoptosis in multiple sclerosis. Int J Mol Sci 23:7584
Khalilian B, Madadi S, Fattahi N, Abouhamzeh B (2021) Coenzyme Q10 enhances remyelination and regulate inflammation effects of cuprizone in corpus callosum of chronic model of multiple sclerosis. J Mol Histol 52:125–134
Kitzmiller JP, Mikulik EB, Dauki AM, Murkherjee C, Luzum JA (2016) Pharmacogenomics of statins: understanding susceptibility to adverse effects. Pharmgenom Pers Med 9:97–106
Kumar DR, Aslinia F, Yale SH, Mazza JJ (2011) Jean-Martin Charcot: the father of neurology. Clin Med Res 9:46–49
Kuroda M, Muramatsu R, Maedera N, Koyama Y, Hamaguchi M, Fujimura H, Yoshida M, Konishi M, Itoh N, Mochizuki H (2017) Peripherally derived FGF21 promotes remyelination in the central nervous system. J Clin Investig 127:3496–3509
Kurosu H, Choi M, Ogawa Y, Dickson AS, Goetz R, Eliseenkova AV, Mohammadi M, Rosenblatt KP, Kliewer SA, Kuro-o M (2007) Tissue-specific expression of βKlotho and fibroblast growth factor (FGF) receptor isoforms determines metabolic activity of FGF19 and FGF21. J Biol Chem 282:26687–26695
Lanzillo R, Orefice G, Quarantelli M, Rinaldi C, Prinster A, Ventrella G, Spitaleri D, Lus G, Vacca G, Carotenuto B (2010) Atorvastatin combined to interferon to verify the efficacy (ACTIVE) in relapsing—remitting active multiple sclerosis patients: a longitudinal controlled trial of combination therapy. Mult Scler 16:450–454
Leoni V, Caccia C (2013) 24S-hydroxycholesterol in plasma: a marker of cholesterol turnover in neurodegenerative diseases. Biochimie 95:595–612
Li H, Kuwajima T, Oakley D, Nikulina E, Hou J, Yang WS, Lowry ER, Lamas NJ, Amoroso MW, Croft GF (2016) Protein prenylation constitutes an endogenous brake on axonal growth. Cell Rep 16:545–558
Mäkelä J, Tselykh TV, Maiorana F, Eriksson O, Do HT, Mudò G, Korhonen LT, Belluardo N, Lindholm D (2014) Fibroblast growth factor-21 enhances mitochondrial functions and increases the activity of PGC-1α in human dopaminergic neurons via Sirtuin-1. Springerplus 3:1–12
Marik C, Felts PA, Bauer J, Lassmann H, Smith KJ (2007) Lesion genesis in a subset of patients with multiple sclerosis: a role for innate immunity? Brain 130:2800–2815
Marrie R, Rudick R, Horwitz R, Cutter G, Tyry T, Campagnolo D, Vollmer T (2010) Vascular comorbidity is associated with more rapid disability progression in multiple sclerosis. Neurology 74:1041–1047
Massey J, Jackson K, Singh M, Hughes B, Withers B, Ford C, Khoo M, Hendrawan K, Zaunders J, Muylder C-D (2022) Haematopoietic stem cell transplantation results in extensive remodelling of the clonal T cell repertoire in multiple sclerosis. Front Immunol 13:232
Melchor GS, Khan T, Reger JF, Huang JK (2019) Remyelination pharmacotherapy investigations highlight diverse mechanisms underlying multiple sclerosis progression. ACS Pharmacol Trans Sci 2:372–386
Mincu RI, Magda LS, Florescu M, Velcea A, Mihaila S, Mihalcea D, Popescu BO, Chiru A, Tiu C, Cinteza M (2015) Cardiovascular dysfunction in multiple sclerosis. Maedica 10:364
Miron VE, Zehntner SP, Kuhlmann T, Ludwin SK, Owens T, Kennedy TE, Bedell BJ, Antel JP (2009) Statin therapy inhibits remyelination in the central nervous system. Am J Pathol 174:1880–1890
Mohammadhosayni M, Khosrojerdi A, Lorian K, Aslani S, Imani D, Razi B, Babaie F, Torkamandi S (2020) Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) family gene polymorphisms and the risk of multiple sclerosis: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Neurol 20:1–10
Musabak U, Demirkaya S, Genç G, Ilikci RS, Odabasi Z (2011) Serum adiponectin, TNF-α, IL-12p70, and IL-13 levels in multiple sclerosis and the effects of different therapy regimens. NeuroImmunoModulation 18:57–66
Naegelin Y, Saeuberli K, Schaedelin S, Dingsdale H, Magon S, Baranzini S, Amann M, Parmar K, Tsagkas C, Calabrese P (2020) Levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in patients with multiple sclerosis. Ann Clin Trans Neurol 7:2251–2261
Neuhaus O, Stüve O, Zarnvil SS, Hartung H-P (2004) Are statins a treatment option for multiple sclerosis? Lancet Neurol 3:369–371
Noori H, Gheini MR, Rezaeimanesh N, Saeedi R, Aliabadi HR, Sahraian MA, Moghadasi AN (2019) The correlation between dyslipidemia and cognitive impairment in multiple sclerosis patients. Mult Scler Relat Disord 36:101415
Ntolkeras G, Barba C, Mavropoulos A, Vasileiadis GK, Dardiotis E, Sakkas LI, Hadjigeorgiou G, Bogdanos DP (2019) On the immunoregulatory role of statins in multiple sclerosis: the effects on Th17 cells. Immunol Res 67:310–324
Okudan N, Belviranli M (2020) High dose simvastatin and rosuvastatin impair cognitive abilities of healthy rats via decreasing hippocampal neurotrophins and irisin. Brain Res Bull 165:81–89
Olsson T, Barcellos LF, Alfredsson L (2017) Interactions between genetic, lifestyle and environmental risk factors for multiple sclerosis. Nat Rev Neurol 13:25–36
Ortiz GG, Pacheco-Moisés FP, Macías-Islas MÁ, Flores-Alvarado LJ, Mireles-Ramírez MA, González-Renovato ED, Hernández-Navarro VE, Sánchez-López AL, Alatorre-Jiménez MA (2014) Role of the blood–brain barrier in multiple sclerosis. Arch Med Res 45:687–697
Paul F, Waiczies S, Wuerfel J, Bellmann-Strobl J, Dörr J, Waiczies H, Haertle M, Wernecke KD, Volk H-D, Aktas O (2008) Oral high-dose atorvastatin treatment in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. PLoS One 3:e1928
Paul R, Choudhury A, Boruah DC, Devi R, Bhattacharya P, Choudhury MD, Borah A (2017) Hypercholesterolemia causes psychomotor abnormalities in mice and alterations in cortico-striatal biogenic amine neurotransmitters: relevance to Parkinson’s disease. Neurochem Int 108:15–26
Penesova A, Vlcek M, Imrich R, Vernerova L, Marko A, Meskova M, Grunnerova L, Turcani P, Jezova D, Kollar B (2015) Hyperinsulinemia in newly diagnosed patients with multiple sclerosis. Metab Brain Dis 30:895–901
Petersen MA, Ryu JK, Akassoglou K (2018) Fibrinogen in neurological diseases: mechanisms, imaging and therapeutics. Nat Rev Neurosci 19:283–301
Pieters M, Wolberg AS (2019) Fibrinogen and fibrin: An illustrated review. Res Pract Thromb Haemost 3:161–172
Pihl-Jensen G, Tsakiri A, Frederiksen JL (2015) Statin treatment in multiple sclerosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. CNS Drugs 29:277–291
Posvar EL, Radulovic LL, Cilla DD Jr, Whitfield LR, Sedman AJ (1996) Tolerance and pharmacokinetics of single-dose atorvastatin, a potent inhibitor of HMG-CoA reductase, in healthy subjects. J Clin Pharmacol 36:728–731
Radikova Z, Penesova A, Vlcek M, Havranova A, Sivakova M, Siarnik P, Zitnanova I, Imrich R, Kollar B, Turcani P (2018) LDL and HDL lipoprotein subfractions in multiple sclerosis patients with decreased insulin sensitivity. Endocr Regul 52:139–145
Restelli LM, Oettinghaus B, Halliday M, Agca C, Licci M, Sironi L, Savoia C, Hench J, Tolnay M, Neutzner A (2018) Neuronal mitochondrial dysfunction activates the integrated stress response to induce fibroblast growth factor 21. Cell Rep 24:1407–1414
Rojas-Fernandez CH, Cameron J-CF (2012) Is statin-associated cognitive impairment clinically relevant? A narrative review and clinical recommendations. Ann Pharmacother 46:549–557
Sanoobar M, Eghtesadi S, Azimi A, Khalili M, Jazayeri S, Reza Gohari M (2013) Coenzyme Q10 supplementation reduces oxidative stress and increases antioxidant enzyme activity in patients with relapsing–remitting multiple sclerosis. Int J Neurosci 123:776–782
Sanoobar M, Dehghan P, Khalili M, Azimi A, Seifar F (2016) Coenzyme Q10 as a treatment for fatigue and depression in multiple sclerosis patients: A double blind randomized clinical trial. Nutr Neurosci 19:138–143
Schol-Gelok S, de Maat MP, Biedermann JS, van Gelder T, Leebeek FW, Lijfering WM, van der Meer FJ, Rijken DC, Versmissen J, Kruip MJ (2020) Rosuvastatin use increases plasma fibrinolytic potential: a randomised clinical trial. Br J Haematol 190:916–922
Segatto M, Leboffe L, Trapani L, Pallottini V (2014) Cholesterol homeostasis failure in the brain: implications for synaptic dysfunction and cognitive decline. Curr Med Chem 21:2788–2802
Sellner J, Greeve I, Findling O, Kamm CP, Minten C, Engelhardt B, Grandgirard D, Leib SL, Mattle HP (2008) Effect of interferon-β and atorvastatin on Th1/Th2 cytokines in multiple sclerosis. Neurochem Int 53:17–21
Singhal G, Fisher FM, Chee MJ, Tan TG, El Ouaamari A, Adams AC, Najarian R, Kulkarni RN, Benoist C, Flier JS (2016) Fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) protects against high fat diet induced inflammation and islet hyperplasia in pancreas. PLoS One 11:e0148252
Sorensen PS, Lycke J, Erälinna J-P, Edland A, Wu X, Frederiksen JL, Oturai A, Malmeström C, Stenager E, Sellebjerg F (2011) Simvastatin as add-on therapy to interferon beta-1a for relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis (SIMCOMBIN study): a placebo-controlled randomised phase 4 trial. Lancet Neurol 10:691–701
Stavroulopoulos A, Petras D, Kakavas I, Agroyannis I, Stamatelou K, Vyssoulis G, Papadakis IT, Stefanadis C (2010) Monocyte expression of adhesion molecules during low-and high-flux polysulfone hemodialysis and the effect of atorvastatin administration. Blood Purif 29:274–279
Stüve O, Prod’homme T, Slavin A, Youssef S, Dunn S, Steinman L, Zamvil SS (2003) Statins and their potential targets in multiple sclerosis therapy. Expert Opin Ther Targets 7:613–622
Stüve O, Youssef S, Weber MS, Nessler S, von Büdingen H-C, Hemmer B, Prodhomme T, Sobel RA, Zamvil SS (2006) Immunomodulatory synergy by combination of atorvastatin and glatiramer acetate in treatment of CNS autoimmunity. J Clin Investig 116:1037–1044
Sun Y, Wang Y, Chen S-T, Chen Y-J, Shen J, Yao W-B, Gao X-D, Chen S (2020) Modulation of the astrocyte-neuron lactate shuttle system contributes to neuroprotective action of fibroblast growth factor 21. Theranostics 10:8430
Taheri M, Ghafouri-Fard S, Sayad A, Arsang-Jang S, Mazdeh M, Toghi M, Omrani MD (2018) Assessment of protein prenylation pathway in multiple sclerosis patients. J Mol Neurosci 64:581–590
Tan W, Xue-bin C, Tian Z, Xiao-wu C, Pei-pei H, Zhi-bin C, Bei-sha T (2016) Effects of simvastatin on the expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase and brain-derived neurotrophic factor in a lipopolysaccharide-induced rat model of Parkinson disease. Int J Neurosci 126:278–286
Tettey P, Simpson S Jr, Taylor B, Blizzard L, Ponsonby A-L, Dwyer T, Kostner K, van der Mei I (2014) An adverse lipid profile is associated with disability and progression in disability, in people with MS. Mult Scler J 20:1737–1744
Tettey P, Simpson S, Taylor B, Ponsonby A-L, Lucas RM, Dwyer T, Kostner K, van der Mei IA, group Ai (2017) An adverse lipid profile and increased levels of adiposity significantly predict clinical course after a first demyelinating event. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 88:395–401
Teunissen C, Dijkstra C, Polman C, Hoogervorst E, Von Bergmann K, Lütjohann D (2003) Decreased levels of the brain specific 24S-hydroxycholesterol and cholesterol precursors in serum of multiple sclerosis patients. Neurosci Lett 347:159–162
Togha M, Karvigh SA, Nabavi M, Moghadam NB, Harirchian MH, Sahraian MA, Enzevaei A, Nourian A, Ghanaati H, Firouznia K (2010) Simvastatin treatment in patients with relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis receiving interferon beta 1a: a double-blind randomized controlled trial. Mult Scler J 16:848–854
Vollmer T, Singh I (2004) Statins for multiple sclerosis. The Lancet 364:412–413
Voskuhl RR, Itoh N, Tassoni A, Matsukawa MA, Ren E, Tse V, Jang E, Suen TT, Itoh Y (2019) Gene expression in oligodendrocytes during remyelination reveals cholesterol homeostasis as a therapeutic target in multiple sclerosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci 116:10130–10139
Wagstaff LR, Mitton MW, Arvik BM, Doraiswamy PM (2003) Statin-associated memory loss: analysis of 60 case reports and review of the literature. Pharmacotherapy J Hum Pharmacol Drug Therapy 23:871–880
Wang X-M, Xiao H, Liu L-L, Cheng D, Li X-J, Si L-Y (2016) FGF21 represses cerebrovascular aging via improving mitochondrial biogenesis and inhibiting p53 signaling pathway in an AMPK-dependent manner. Exp Cell Res 346:147–156
Wang J, Xiao Y, Luo M, Luo H (2011) Statins for multiple sclerosis. Cochrane Database System Rev
Weinstock-Guttman B, Zivadinov R, Mahfooz N, Carl E, Drake A, Schneider J, Teter B, Hussein S, Mehta B, Weiskopf M (2011) Serum lipid profiles are associated with disability and MRI outcomes in multiple sclerosis. J Neuroinflammation 8:1–7
Wens I, Keytsman C, Deckx N, Cools N, Dalgas U, Eijnde B (2016) Brain derived neurotrophic factor in multiple sclerosis: effect of 24 weeks endurance and resistance training. Eur J Neurol 23:1028–1035
Woo Y, Xu A, Wang Y, Lam KS (2013) Fibroblast growth factor 21 as an emerging metabolic regulator: clinical perspectives. Clin Endocrinol (oxf) 78:489–496
Woodbury ME, Ikezu T (2014) Fibroblast growth factor-2 signaling in neurogenesis and neurodegeneration. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 9:92–101
Wu F, Luo T, Mei Y, Liu H, Dong J, Fang Y, Peng J, Guo Y (2018) Simvastatin alters M1/M2 polarization of murine BV2 microglia via Notch signaling. J Neuroimmunol 316:56–64
Xue-Shan Z, Qi W, Zhong R, Li-hong P, Zhi-han T, Zhi-sheng J, Gui-xue W, Lu-shan L (2016) Imbalanced cholesterol metabolism in Alzheimer’s disease. Clin Chim Acta 456:107–114
Yang D, Han Y, Zhang J, Chopp M, Seyfried DM (2012) Statins enhance expression of growth factors and activate the PI3K/Akt-mediated signaling pathway after experimental intracerebral hemorrhage. World J Neurosci. https://doi.org/10.4236/wjns.2012.22011
Yates RL, Esiri MM, Palace J, Jacobs B, Perera R, DeLuca GC (2017) Fibrin (ogen) and neurodegeneration in the progressive multiple sclerosis cortex. Ann Neurol 82:259–270
Youssef S, Stüve O, Patarroyo JC, Ruiz PJ, Radosevich JL, Hur EM, Bravo M, Mitchell DJ, Sobel RA, Steinman L (2002) The HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor, atorvastatin, promotes a Th2 bias and reverses paralysis in central nervous system autoimmune disease. Nature 420:78–84
Yu Y, He J, Li S, Song L, Guo X, Yao W, Zou D, Gao X, Liu Y, Bai F (2016) Fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) inhibits macrophage-mediated inflammation by activating Nrf2 and suppressing the NF-κB signaling pathway. Int Immunopharmacol 38:144–152
Zambón D, Quintana M, Mata P, Alonso R, Benavent J, Cruz-Sánchez F, Gich J, Pocoví M, Civeira F, Capurro S (2010) Higher incidence of mild cognitive impairment in familial hypercholesterolemia. Am J Med 123:267–274
Zamvil SS, Steinman L (2002) Cholesterol-lowering statins possess anti-inflammatory activity that might be useful for treatment of MS. AAN Enterprises 59:970–971
Zhang X, Jin J, Peng X, Ramgolam VS, Markovic-Plese S (2008) Simvastatin inhibits IL-17 secretion by targeting multiple IL-17-regulatory cytokines and by inhibiting the expression of IL-17 transcription factor RORC in CD4+ lymphocytes. J Immunol 180:6988–6996
Zhornitsky S, McKay KA, Metz LM, Teunissen CE, Rangachari M (2016) Cholesterol and markers of cholesterol turnover in multiple sclerosis: relationship with disease outcomes. Mult Scler Relat Disord 5:53–65
Ziros P, Zagoriti Z, Lagoumintzis G, Kyriazopoulou V, Iskrenova RP, Habeos EI, Sykiotis GP, Chartoumpekis DV, Habeos IG (2016) Hepatic Fgf21 expression is repressed after simvastatin treatment in mice. PLoS One 11:e0162024
Funding
Nil.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HMA and AIA: conceptualization, data collection, and writing of the manuscript. HMS and GEB: writing, supervision, and editing of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Nil.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Al-Kuraishy, H.M., Al-Gareeb, A.I., Saad, H.M. et al. The potential therapeutic effect of statins in multiple sclerosis: beneficial or detrimental effects. Inflammopharmacol 31, 1671–1682 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-023-01240-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-023-01240-x