Abstract
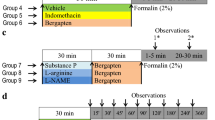
Β-sitosterol is a phytosterol, documented to possess various activities including protection against inflammation, diabetes and Alzheimer’s disease. The current investigation was designed to explore the analgesic potential of β-sitosterol and the possible molecular mechanism involved in the observed effect. β-sitosterol was administered at varying doses of 10, 20, and 40 mg/kg before subjecting the mice to acetic acid and formalin challenges. The number of writhings in acetic acid and the number of flinchings and foot tappings were quantified in the formalin test. For mechanistic studies, substance P (cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) stimulator) and L-Nitro arginine methyl ester (L-NAME) (nitric oxide synthetases (NOS) inhibitor) and L-arginine (nitric oxide precursor) were administered before β-sitosterol treatment. β-sitosterol (10, 20, 40 mg/kg) treatment significantly reduced acetic acid-induced writhings and ameliorated the formalin-induced inflammatory phase dose-dependently. Whereas, 40 mg/kg dose of β-sitosterol abrogated the formalin-induced neurogenic phase. Substance-P abrogated the effect of β-sitosterol in both neurogenic and inflammatory phases. Whereas, L-arginine only abrogated the inflammatory phase. In biochemical analysis, β-sitosterol treatment reduced the level of interleukin-6 (IL-6), thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARS) and increased the level of reduced glutathione (GSH). Furthermore, L-arginine and substance-P abrogated the GSH increasing and TBARS lowering effect of β-sitosterol (40 mg/kg). Overall, the current study delineated that β-sitosterol may induce an anti-nociceptive effect via inhibiting the IL-6, oxidative stress, cyclo-oxygenase and nitric oxide.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study is included in this article.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Adedayo LD, Ojo AO, Awobajo FO, Adeboye BA, Adebisi JA, Bankole TJ, Ayilara GO, Bamidele O, Aitokhuehi NG, Onasanwo SA (2019) Methanol extract of Cola nitida ameliorates inflammation and nociception in experimental animals. Neurobiol Pain 5:100027. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ynpai.2019.100027
Ayaz M, Junaid M, Ullah F, Subhan F, Sadiq A, Ali G, Ovais M, Shahid M, Ahmad A, Wadood A et al (2017) Anti-Alzheimer’s studies on β-Sitosterol Isolated from Polygonum hydropiper L. Front Pharmacol 8:697. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2017.00697
Brusco I, Camponogara C, Carvalho FB, Schetinger MRC, Oliveira MS, Trevisan G, Ferreira J, Oliveira SM (2017) α-Spinasterol: a COX inhibitor and a transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 antagonist presents an antinociceptive effect in clinically relevant models of pain in mice. Br J Pharmacol 174(23):4247–4262. https://doi.org/10.1111/bph.13992
Castellani ML, Conti P, Felaco M, Vecchiet J, Ciampoli C, Cerulli G, Boscolo P, Theoharides TC (2009) Substance P upregulates LTB4 in rat adherent macrophages from granuloma induced by KMnO4. Neurotox Res 15(1):49–56. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-009-9004-6
Chakraborty S, Majumdar S (2020) Natural products for the treatment of pain: chemistry and pharmacology of salvinorin A, mitragynine, and collybolide. Biochemistry 60(18):1381–1400. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biochem.0c00629
Chen L, Yang G, Grosser T (2013) Prostanoids and inflammatory pain. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat 104–105:58–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prostaglandins.2012.08.006
Cho IH, Chung YM, Park CK, Park SH, Li HY, Kim D, Piao ZG, Choi S-Y, Lee SJ, Park K, Kim JS (2006) Systemic administration of minocycline inhibits formalin-induced inflammatory pain in rat. Brain Res 1072(1):208–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2005.12.039
Cilla A, Attanzio A, Barberá R, Tesoriere L, Livrea MA (2015) Anti-proliferative effect of main dietary phytosterols and β-cryptoxanthin alone or combined in human colon cancer Caco-2 cells through cytosolic Ca+2 – and oxidative stress-induced apoptosis. J Funct Foods 12:282–293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jff.2014.12.001
Cury Y, Picolo G, Gutierrez VP, Ferreira SH (2011) Pain and analgesia: the dual effect of nitric oxide in the nociceptive system. Nitric Oxide 25(3):243–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.niox.2011.06.004
Demsie DG, Yimer EM, Berhe AH, Altaye BM, Berhe DF (2019) Anti-nociceptive and anti-inflammatory activities of crude root extract and solvent fractions of Cucumis ficifolius in mice model. J Pain Res 12:1399–1409. https://doi.org/10.2147/jpr.s193029
Du J, Yu Y, Ke Y, Wang C, Zhu L, Qian ZM (2007) Ligustilide attenuates pain behavior induced by acetic acid or formalin. J Ethnopharmacol 112(1):211–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2007.02.007
Feng Y, Cui M, Willis WD (2003) Gabapentin markedly reduces acetic acid–induced visceral nociception. Anesthesiology 98(3):729–733. https://doi.org/10.1097/00000542-200303000-00023
França DS, Souza ALS, Almeida KR, Dolabella SS, Martinelli C, Coelho MM (2001) B vitamins induce an antinociceptive effect in the acetic acid and formaldehyde models of nociception in mice. Eur J Pharmacol 421(3):157–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0014-2999(01)01038-x
Freire MAM (2009) Pain modulation by nitric oxide in the spinal cord. Front Neurosci 3(2):175–181. https://doi.org/10.3389/neuro.01.024.2009
Ghorbanzadeh B, Mansouri MT, Sahraei H, Alboghobeish S (2016) Involvement of opioid receptors in the systemic and peripheral antinociceptive actions of montelukast in the animal models of pain. Eur J Pharmacol 779:38–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2016.03.010
Gupta E (2020) β-Sitosterol: predominant phytosterol of therapeutic potential. Innov Food Technol. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-6121-4_32
Ikeda Y, Ueno A, Naraba H, Oh-ishi S (2001) Involvement of vanilloid receptor VR1 and prostanoids in the acid-induced writhing responses of mice. Life Sci 69(24):2911–2919. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0024-3205(01)01374-1
Jahromi B, Pirvulescu I, Candido KD, Knezevic NN (2021) Herbal medicine for pain management: efficacy and drug interactions. Pharmaceutics 13(2):251. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13020251
Jones PJ, AbuMweis SS (2009) Phytosterols as functional food ingredients: linkages to cardiovascular disease and cancer. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care 12(2):147–151. https://doi.org/10.1097/mco.0b013e328326770f
Kaur B, Kaur M, Kaur N, Garg S, Bhatti R, Singh P (2019) Engineered substrate for cyclooxygenase-2: a pentapeptide isoconformational to arachidonic acid for managing inflammation. J Med Chem 62(13):6363–6376. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.9b00823
Khan A, Ullah MZ, Afridi R, Rasheed H, Khalid S, Ullah H, Ali H, AlSharari SD, Kim YS, Khan S (2018) Antinociceptive properties of 25-methoxy hispidol A, a triterpinoid isolated from Poncirus trifoliata (Rutaceae) through inhibition of NF-κB signalling in mice. Phytother Res 33(2):327–341. https://doi.org/10.1002/ptr.6223
Kiasalari Z, Rahmani T, Mahmoudi N, Baluchnejadmojarad T, Roghani M (2017) Diosgenin ameliorates development of neuropathic pain in diabetic rats: involvement of oxidative stress and inflammation. Biomed Pharmacother 86:654–661. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2016.12.068
Koon HW, Zhao D, Zhan Y, Rhee SH, Moyer MP, Pothoulakis C (2006) Substance P stimulates cyclooxygenase-2 and prostaglandin E2 expression through JAK-STAT activation in human colonic epithelial cells. J Immunol 176:5050–5059. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.176.8.5050
Kuehn B (2018) Chronic pain prevalence. J Am Med Assoc 320(16):1632. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2018.16009
Kumar VL, Guruprasad B, Wahane VD (2010) Atorvastatin exhibits anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidant properties in adjuvant-induced monoarthritis. Inflammopharmacology 18(6):303–308. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-010-0057-1
Lam HHD, Hanley DF, Trapp BD, Saito S, Raja S, Dawson TM, Yamaguchi H (1996) Induction of spinal cord neuronal nitric oxide synthase (NOS) after formalin injection in the rat hind paw. Neurosci Lett 210(3):201–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-3940(96)12702-6
Lee IA, Kim EJ, Kim DH (2012) Inhibitory effect of β-sitosterol on TNBS-induced colitis in mice. Planta Med 78(09):896–898. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0031-1298486
Lesma G, Luraghi A, Bavaro T, Bortolozzi R, Rainoldi G, Roda G, Viola G, Ubiali D, Silvani A (2018) Phytosterol and γ-oryzanol conjugates: synthesis and evaluation of their antioxidant, antiproliferative, and anticholesterol activities. J Nat Prod 81(10):2212–2221. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jnatprod.8b00465
Lucetti DL, Lucetti EC, Bandeira MAM, Veras HN, Silva AH, Leal LKA, Lopes AA, Alves VC, Silva GS, Brito GA, Viana GB (2010) Anti-inflammatory effects and possible mechanism of action of lupeol acetate isolated from Himatanthus drasticus (Mart.) Plumel. J Inflamm 7:60. https://doi.org/10.1186/1476-9255-7-60
Lugrin J, Rosenblatt-Velin N, Parapanov R, Liaudet L (2014) The role of oxidative stress during inflammatory processes. Biol Chem 395(2):203–230. https://doi.org/10.1515/hsz-2013-0241
Moore J, Gaines C (2019) Gabapentin for chronic neuropathic pain in adults. Br J Commun Nurs 24(12):608–609. https://doi.org/10.12968/bjcn.2019.24.12.608
Moreau RA, Whitaker BD, Hicks KB (2002) Phytosterols, phytostanols, and their conjugates in foods: structural diversity, quantitative analysis, and health-promoting uses. Progress Lipid Res 41(6):457–500. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0163-7827(02)00006-1
Nirmal SA, Pal SC, Mandal SC, Patil AN (2011) Analgesic and anti-inflammatory activity of β-sitosterol isolated from Nyctanthes arbortristis leaves. Inflammopharmacology 20(4):219–224. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-011-0110-8
Norregaard R, Kwon TH, Frøkiær J (2015) Physiology and pathophysiology of cyclooxygenase-2 and prostaglandin E2 in the kidney. Kidney Res Clin Pract 34(4):194–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.krcp.2015.10.004
Owoyele B, Olaleye S, Oke J, Elegbe R (2010) Anti-inflammatory and analgesic activities of leaf extracts of Landolphia Owariensis. Afr J Biomed Res. https://doi.org/10.4314/ajbr.v4i3.53896
Paniagua-Pérez R, Madrigal-Bujaidar E, Reyes-Cadena S, Molina-Jasso D, Gallaga JP, Silva-Miranda A, Velazco O, Hernández N, Chamorro G (2005) Genotoxic and cytotoxic studies of beta-sitosterol and pteropodine in mouse. Biomed Res Int 2005:242–247. https://doi.org/10.1155/JBB.2005.242
Park SK, Park SJ, Park SM, Cho IJ, Park CI, Kim YW, Kim SC (2013) Inhibition of acute phase inflammation by Laminaria japonica through regulation of iNOS-NF-κB Pathway. Evid-Based Complement Altern Med 2013:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/439498
Piao X, Zou Y, Sui X, Liu B, Meng F, Li S, Zhang Q, Ma C, Wu T (2021) Hydrostatin-SN10 ameliorates pancreatitis-induced lung injury by affecting IL-6-induced JAK2/STAT3-associated inflammation and oxidative stress. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2021:1–2. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/8541783
Pigatto GR, Silva CS, Parizotto NA (2019) Photobiomodulation therapy reduces acute pain and inflammation in mice. J Photochem Photobiol B 196:111513. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2019.111513
Posadas I, Terencio MC, Guillén I, Ferrándiz ML, Coloma J, Payá M, Alcaraz MJ (2000) Co-regulation between cyclo-oxygenase-2 and inducible nitric oxide synthase expression in the time-course of murine inflammation. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 361(1):98–106. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002109900150
Santiago RF, de Brito TV, Dias JM, Dias GJ, da Cruz JS, Batista JA, Silva RO, Souza MHLP, de Albuquerque Ribeiro R, Gutierrez SJC et al (2015) Riparin B, a synthetic compound analogue of riparin, inhibits the systemic inflammatory response and oxidative stress in mice. Inflammation 38(6):2203–2215. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-015-0203-4
Shefer S, Salen G, Nguyen L, Batta AK, Packin V, Tint GS, Hauser S (1988) Competitive inhibition of bile acid synthesis by endogenous cholestanol and sitosterol in sitosterolemia with xanthomatosis. Effect on cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase. J Clin Investig 82(6):1833–1839. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci113799
Singh G, Singh G, Bhatti R, Gupta V, Mahajan A, Singh P, Singh Ishar MP (2017) Rationally designed benzopyran fused isoxazolidines and derived β 2,3,3 -amino alcohols as potent analgesics: synthesis, biological evaluation and molecular docking analysis. Eur J Med Chem 127:210–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2016.12.052
Singh P, Kaur S, Kumari P, Kaur B, Kaur M, Singh G, Bhatti R, Bhatti M (2018a) Tailoring the substitution pattern on 1,3,5-triazine for targeting cyclooxygenase-2: discovery and structure-activity relationship of triazine–4-aminophenylmorpholin-3-one hybrids that reverse algesia and inflammation in Swiss albino mice. J Med Chem 61(17):7929–7941. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.8b00922
Singh G, Bhatti R, Mannan R, Singh D, Kesavan A, Singh P (2018b) Osthole ameliorates neurogenic and inflammatory hyperalgesia by modulation of iNOS, COX-2, and inflammatory cytokines in mice. Inflammopharmacology 27(5):949–960. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-018-0486-9
Sio SW, Ang SF, Lu J, Moochhala S, Bhatia M (2010) Substance p upregulates cyclooxygenase-2 and prostaglandin E metabolite by activating ERK1/2 and NF-κB in a mouse model of burn-induced remote acute lung injury. J Immunol 185(10):6265–6276. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1001739
Stevens EB, Stephens GJ (2018) Recent advances in targeting ion channels to treat chronic pain. Br J Pharmacol 175(12):2133–2137. https://doi.org/10.1111/bph.14215
Tripathi P, Tripathi P, Kashyap L, Singh V (2007) The role of nitric oxide in inflammatory reactions. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 51(3):443–452. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-695x.2007.00329.x
Wilt TJ, MacDonald R, Ishani A (2001) β-sitosterol for the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia. BJU Int 83(9):976–983. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1464-410x.1999.00026.x
Yam M, Loh Y, Tan C, Khadijah Adam S, Abdul Manan N, Basir R (2018) General pathways of pain sensation and the major neurotransmitters involved in pain regulation. Int J Mol Sci 19(8):2164. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19082164
Funding
Nil.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
KK, LS, AK performed all the experiments and helped in writing the manuscript. RB conceptualized the study.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
The entire study involving the use of mice was approved by the Institutional Animal Ethics Committee (Approval No. (226/CPCSEA/2018/41) and the experiments were conducted according to ethical guidelines of the Ministry of Environment and Forests, Government of India.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to publish
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kaur, K., Singh, L., Kaur, A. et al. Exploring the possible mechanism involved in the anti-nociceptive effect of β-sitosterol: modulation of oxidative stress, nitric oxide and IL-6. Inflammopharmacol 31, 517–527 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-022-01122-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-022-01122-8