Abstract
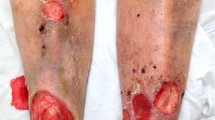
This study was conducted to evaluate the effects of the prepared ointments from Mentha piperita essential oil (M. piperita) on wound healing in the infected mice models. Each circular full-thickness wound was inoculated with 25 × 107 units of Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteria strains. The tissue bacterial count, histological analyses and expression levels of IL-10, TNF-α, TGF-β1, IL-1β, CCL2, CXCL1, VEGF and FGF-2 were assessed to identify the different doses of M. piperita on wound healing. Total tissue bacterial count, edema and inflammation level were declined, but the migration of fibroblasts, collagen synthesis and re-epithelization were increased in treated animals with M. piperita. The expression levels of CCL2, CXCL1, IL-1β, TGF-β1 and IL-10 genes were up-regulated in the M. piperita-treated animals compared to the control group. While the expression of TNF-α, VEGF and FGF-2 was down-regulated in comparison to the control group. This study indicated that M. piperita can be used for treatment of the infected wound.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bielefeld KA, Amini-Nik S, Alman BA (2013) Cutaneous wound healing: recruiting developmental pathways for regeneration. Cell Mol Life Sci 6:1–23
Campos M, Calixto J (2000) Neurokinin mediation of edema and inflammation. Neuropeptide 34(5):314–322
Çetin B, Kaya Y, Çakir A, Özer H, Aksakal Ö, Mete E (2016) Antimicrobial activities of essential oils and hexane extracts of two Turkish spice plants, cymbocarpum erythraeum (DC.) Boiss. and Echinophora tenuifolia L. against foodborne microorganisms. Rec Nat Prod 10(4):426–435
Charo IF, Ransohoff RM (2006) The many roles of chemokines and chemokine receptors in inflammation. N Engl J Med 354:610–621
Eo H, Lee H-J, Lim Y (2016) Ameliorative effect of dietary genistein on diabetes induced hyper-inflammation and oxidative stress during early stage of wound healing in alloxan induced diabetic mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 478:1021–1027
Fang Y, Shen J, Yao M, Beagley K, Hambly B, Bao S (2010) Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor enhances wound healing in diabetes via upregulation of proinflammatory cytokines. Br J Dermatol 162(3):478–486
Farahpour MR, Mirzakhani N, Doostmohammadi J, Ebrahimzadeh M (2015) Hydroethanolic Pistacia atlantica hulls extract improved wound healing process; evidence for mast cells infiltration, angiogenesis and RNA stability. Int J Surg 17:88–98
Farahpour MR, Vahid M, Oryan A (2017) Effectiveness of topical application of ostrich oil on the healing of Staphylococcus aureus-and Pseudomonas aeruginosa-infected wounds. Connect Tissue Res 31:1–10
Gillitzer R, Goebeler M (2001) Chemokines in cutaneous wound healing. J Leukoc Biol 69(4):513–521
Godwin JW, Rosenthal N (2014) Scar-free wound healing and regeneration in amphibians: immunological influences on regenerative success. Differentiation 87(1):66–75
Herro E, Jacob SE (2010) Mentha piperita (peppermint). Dermatitis 21(6):327–329
Hozzeina WN, Badrc G, Al Ghamdid A, Sayede A, Al-Wailif NS, Garraudg O (2015) Topical application of propolis enhances cutaneous wound healing by promoting TGF-Beta/smad-mediated collagen production in a streptozotocin-induced type I diabetic mouse model. Cell Physiol Biochem 37:940–954
Jianu C, Pop G, Gruia AT, Horhat FG (2013) Chemical composition and antimicrobial activity of essential oils of lavender (Lavandula angustifolia) and lavandin (Lavandula × intermedia) grown in Western Romania. Int J Agric Biol 15(4):772–776
Kimmel AR, Brasaemle DL, McAndrews-Hill M, Sztalryd C, Londos C (2010) Adoption of PERILIPIN as a unifying nomenclature for the mammalian PAT-family of intracellular lipid storage droplet proteins. J Lipid Res 51:468–471
Lauer G, Sollberg S, Cole M, Flamme I, Stürzebecher J, Mann K, Krieg T, Eming SA (2000) Expression and proteolysis of vascular endothelial growth factor is increased in chronic wounds. J Invest Dermatol 115:12–18
Liang R, Xu S, Shoemaker CF, Li Y, Zhong F, Huang Q (2012) Physical and antimicrobial properties of peppermint oil nanoemulsions. J Agric Food Chem 60:7548–7755
Lucas T, Waisman A, Ranjan R, Roes J, Krieg T, Müller W et al (2010) Differential roles of macrophages in diverse phases of skin repair. J Immunol 184(7):3964–3977
Milatovic S, Nanney LB, Yu Y, White JR, Richmond A (2003) Impaired healing of nitrogen mustard wounds in CXCR2 null mice. Wound Repair Regen 11(3):213–219
Nathan C (2006) Neutrophils and immunity: challenges and opportunities. Nat Rev Immunol 6(3):173–182
Okuda K, Murata M, Sugimoto M, Saito Y, Kabasawa Y, Yoshie H, Saku T, Hara K (1998) TGF‐β1 influences early gingival wound healing in rats: an immunohistochemical evaluation of stromal remodelling by extracellular matrix molecules and PCNA. J Oral Pathol Med 27:463–469
Oryan A, Moshiri A (2011) A long term study on the role of exogenous human recombinant basic fibroblast growth factor on the superficial digital flexor tendon healing in rabbits. J Musculoskelet Neuron Interact 11(2):185–195
Raman D, Sobolik-Delmaire T, Richmond A (2011) Chemokines in health and disease. Exp Cell Res 317(5):575–589
Satish L (2015) Chemokines as therapeutic targets to improve healing efficiency of chronic wounds. Adv Wound Care 4(11):651–659
Sato Y, Ohshima T, Kondo T (1999) Regulatory role of endogenous interleukin-10 in cutaneous inflammatory response of murine wound healing. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 265(1):194–199
Schmid P, Cox D, Bilbe G, McMaster G, Morrison C, Stähelin H, Lüscher N, Seiler W (1993) TGF-betas and TGF-beta type II receptor in human epidermis: differential expression in acute and chronic skin wounds. J Pathol 171:191–197
Schultz GS, Wysocki A (2009) Interactions between extracellular matrix and growth factors in wound healing. Wound Repair Regen 17:153–162
Shalayel MHF, Asaad AM, Qureshi MA, Elhussein AB (2017) Anti-bacterial activity of peppermint (Mentha piperita) extracts against some emerging multi-drug resistant human bacterial pathogens. J Herb Med 7:27–30
Sun Z, Wang H, Wang J, Zhou L, Yang P (2014) Chemical composition and anti-inflammatory, cytotoxic and antioxidant activities of essential oil from leaves of Mentha piperita grown in China. PLoS One 9(12):e114767
Acknowledgement
This study was extracted from DVM thesis of Mr Mohammad Moddaresi in Veterinary Faculty of Islamic Azad University, Urmia Branch. The authors are grateful to Dr. Farahnaz Tahery for ointment formulation and Dr. Sheryl Thomas for the native language edition.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Modarresi, M., Farahpour, MR. & Baradaran, B. Topical application of Mentha piperita essential oil accelerates wound healing in infected mice model. Inflammopharmacol 27, 531–537 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-018-0510-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-018-0510-0