Abstract
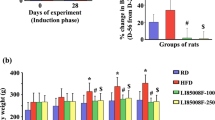
The Maytenus genus is a member of the Celastraceae family. Numerous medicinal uses were assigned to species of this genus, with the use of roots, bark, and leaves for the treatment of gastric ulcers, as anti-inflammatory, analgesic, antiallergic, antitumor, among others. Several studies have demonstrated that natural products derived from plants have an important role in the prevention and treatment of obesity. Accordingly, we evaluated the effect of Maytenus imbricata extracts in the treatment of obesity induced by diet rich in refined carbohydrate (HC). BALB/c mice were fed chow or HC diet for 8 weeks. At the beginning of the 9th week, the HC group was subdivided into three groups: (i) group of animals that continued to consume only HC diet; (ii) the group of animals fed HC diet supplemented with ethyl acetate extract of M. imbricata roots (HC + EAE); (iii) the group of animals fed HC diet supplemented with extract in hexane/ethyl ether (HC + HEE). The period of extracts supplementation was 4 weeks. It was observed that EAE and EHE when added to the HC diet modulated the metabolic and inflammatory changes, such as: reduced the adipocytes area, improved glucose intolerance, reduced the levels of triglycerides and resistin in serum, and the number of total leukocytes in blood. In the epididymal adipose tissue, the extracts reduced proinflammatory mediators’ concentration. According to the results, it was concluded that the species Maytenus imbricata has the potential to be used for the treatment of obesity.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agrawal PK (1989) Carbon-13 NMR of Flavonoids, 1st edn. New York, Elsevier
Cañete R, Gil-Campos M, Aguilera CM, Gil A (2007) Development of insulin resistance and its relation to diet in the obese child. Eur J Nutr 46:181–187
Carvalho KM, de Melo TS, de Melo KM, Quinderé AL, de Oliveira FT, Viana AF, Nunes PI, Quetz JD, Viana DA, da Silva AA, Havt A, Fonseca SG, Chaves MH, Rao VS, Santos FA (2017) Amyrins from Protium heptaphyllum reduce high-fat diet-induced obesity in mice via modulation of enzymatic, hormonal and inflammatory responses. Planta Med 83(3–04):285–291
Casaschi A, Rubio BK, Maiyoh GK, Theriault AG (2004) Inhibitory activity of diacylglycerol acyltransferase (DGAT) and microsomal triglyceride transfer protein (MTP) by the flavonoid, taxifolin, in HepG2 cells: potential role in the regulation of apolipoprotein B secretion. Atherosclerosis 176:247–253
Chantre P, Lairon D (2002) Recent findings of green tea extract AR25 (Exolise) and its activity for the treatment of obesity. Phytomedicine 9:3–8
Chawla A, Nguyen KD, Goh YP (2011) Macrophage-mediated inflammation in metabolic disease. Nat Rev Immunol 11:738–749
Choi JN, Choi Y-H, Lee J-M, Noh IC, Park JW, Choi WS et al (2012) Antiinflammatory effects of β-sitosterol-β-D-glucoside from Trachelospermum jasminoides (Apocynaceae) in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW 264.7 murine macrophages. Nat Prod Res 26:2340–2343
Dat NT, Thao NP, Quynh LTP, Minh CV, Bach TT, Joon LJ (2009) Flavonoids from Eupatorium odoratum as inhibitors of NF-KB. JUST 47:1–6
Engstrom LW, Bober L, Chen S-C, Fine JS, Li Y, Stanton MC et al (2010) Kinetic assessment and therapeutic modulation of metabolic and inflammatory profiles in mice on a high-fat and cholesterol diet. PPAR Res. https://doi.org/10.1155/2010/970164
Fan S-Y, Zeng H-W, Pei Y-H, Li L, Ye J, Pan Y-X et al (2012) The anti-inflammatory activities of na extract and compounds isolated from Platycladus orientalis (Linnaeus) Franco in vitro and ex vivo. J Ethnopharmacol 141:647–652
Ferreira AVM, Mario EG, Porto LCJ, Andrade SP, Botion LM (2011) High-carbohydrate diet selectively induces tumor necrosis factor-α production in mice liver. Inflammation 34:139–145
González-Périz A, Clària J (2010) Resolution of adipose tissue inflammation. Sci World J 10:832–856
Guilherme A, Virbasius JV, Puri V, Czech MP (2008) Adipocyte dysfunctions linking obesity to insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 9:367–377
Hasani-Ranjbar S, Nayebi N, Larijani B, Abdollahi M (2009) A systematic review of the efficacy and safety of herbal medicines used in the treatment of obesity. World J Gastroenterol 15:3073–3085
Jacobi D, Stanya KJ, Chih-Hao Lee (2012) Adipose tissue signaling by nuclear receptors in metabolic complications of obesity. Adipocyte 1:4–12
Lamb RE, Goldstein BJ (2008) Modulating an oxidative-inflammatory cascade: potential new treatment strategy for improving glucose metabolism, insulin resistance, and vascular function. Int J Clin Pract 62:1087–1095
Lemhadri A, Eddouks M, Sulpice T, Burcelin R (2007) Anti-hyperglycaemic and anti-obesity effects of Capparis spinosa and Chamaemelum nobile aqueous extracts in HFD mice. Am J Pharmacol Toxicol 2:106–110
Maffeis C, Silvagni D, Bonadonna R, Grezzani A, Banzato C, Tatò L (2007) Fat cell size, insulin sensitivity, and inflammation in obese children. J Pediatr 151:647–652
Matsusaka T, Fujikawa K, Nishio Y, Mukaida N, Matsushima K, Kishimoto T et al (1993) Transcription factors NF-IL6 and NF-κB synergistically activate transcription of the inflammatory cytokines, interleukin 6 and interleukin 8. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:10193–10197
Moro CO, Basile G (2000) Obesity and medicinal plants. Fitoterapia 71:S73–S82
Olefsky JM, Glass CK (2010) Macrophages, inflammation, and insulin resistance. Annu Rev Physiol 72:219–246
Oliveira MC, Menezes-Garcia Z, Henriques MCC, Soriani FM, Pinho V, Faria AMC et al (2013) Acute and sustained inflammation and metabolic dysfunction induced by high refined carbohydrate containing diet in mice. Obesity 21:E396–E406
Oliveira VB, Ferreira AVM, Oliveira MC, Teixeira MM, Brandão MGL (2014) Effects of Xylopia aromática (Lam.) Mart. fruit on metabolic and inflammatory dysfunction induced by high refined carbohydrate-containing-diet in mice. Food Res Int 62:541–550
Pinto SAH, Pinto LMS, Cunha GMA, Chaves MH, Santos FA, Rao VS (2008) Antiinflammatory effect of a, b-Amyrin, a pentacyclic triterpene from Protium heptaphyllum in rat model of acute periodontitis. Inflammopharmacology 16:48–52
Rodrigues VG, Duarte LP, Silva GDF, Silva FC, Góes JF, Takahashi JA et al (2012) Evaluation of antimicrobial activity and toxic potential of extracts and triterpenes isolated fromMaytenus imbricata. Quim Nova 35:1375–1380
Satoh H, Nguyen MT, Miles PD, Imamura T, Usui I, Olefsky JM (2004) Adenovirusmediated chronic “hyper-resistinemia” leads to in vivo insulin resistance in normal rats. J Clin Invest 114:224–231
Schmidt CA, Murillo R, Bruhn T, Bringmann G, Goettert M, Heinzmann B et al (2010) Catechin derivatives from Parapiptadenia rigida with in vitro wound-healing properties. J Nat Prod 73:2035–2041
Schuster DP (2010) Obesity and the development of type 2 diabetes: the effects of fatty tissue inflammation. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes 3:253–262
Shankar K, Harrel A, Kang P, Singhal R, Ronis MJJ, Badger TM (2010) Carbohydrate responsive gene expression in the adipose tissue of rats. Endocrinology 151:153–164
Sharma N, Sharma VK, Sung-Yum Seo (2005) Screening of some medicinal plants for anti-lipase activity. J Ethnopharmacol 97:453–456
Sheng H, Sun H (2011) Synthesis, biology and clinical significance of pentacyclic triterpenes: a multi-target approach to prevention and treatment of metabolic and vascular diseases. Nat Prod Rep 28:543–593
Steppan CM, Bailey ST, Bhat S, Brown EJ, Banerjee RR, Wright CM et al (2001) The hormone resistin links obesity to diabetes. Nature 409:307–312
Valerio M, Awad AB (2011) β-Sitosterol down-regulates some pro-inflammatory signal transduction pathways by increasing the activity of tyrosine phosphatase SHP-1 in J774A.1 murine macrophages. Int Immunopharmacol 11:1012–1017
Veloso CC, Oliveira MC, Oliveira CC, Rodrigues VG, Giusti-Paiva A, Teixeira MM et al (2014a) Hydroethanolic extract of Pyrostegia venusta (Ker Gawl.) Miers flowers improves inflammatory and metabolic dysfunction induced by high refined carbohydrate diet. J Ethnopharmacol 151:722–728
Veloso CC, Rodrigues VG, Azevedo AO, Oliveira CO, Gomides LF, Duarte LP, Duarte ID, Klein A, Perez AC (2014b) Antinociceptive effects of Maytenus imbricata Mart. ex. Reissek (Celastraceae) root extract and its tingenone constituent. JMPR 8:68–76
Xu H, Barnes GT, Yang Q, Tan G, Yang D, Chou CJ et al (2003) Chronic inflammation in fat plays a crucial role in the development of obesity-related insulin resistance. J Clin Invest 112:1821–1830
Yadav A, Kataria MA, Saini V, Yadav A (2013) Role of leptin and adiponectin in insulin resistance. Clin Chim Acta 417:80–84
Yoshikawa M, Shimoda H, Nishida N, Takada M, Matsuda H (2002) Salacia reticulata and its polyphenolic constituents with lipase inhibitory and lipolytic activities have mild antiobesity effects in rats. J Nutr 132:1819–1824
Zhou L, Li Y, Xia T, Feng S, Chen X, Yang Z (2006) Resistin overexpression impaired glucose tolerance in hepatocytes. Eur Cytokine Netw 17:189–195
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES-Brazil) and Conselho Nacional de Pesquisa (CNPq-Brazil).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
All authors declared that they have no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Veloso, C.C., Oliveira, M.C., Rodrigues, V.G. et al. Evaluation of the effects of extracts of Maytenus imbricata (Celastraceae) on the treatment of inflammatory and metabolic dysfunction induced by high-refined carbohydrate diet. Inflammopharmacol 27, 539–548 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-018-0496-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-018-0496-7