Abstract
Objective
In the present study, DNA methylation level of CD4+ T cells exposed to ultraviolet B (UVB) was investigated and its potential mechanisms were also explored.
Methods
CD4+ T cells from 12 cases of healthy subjects and 33 cases of SLE patients were isolated and exposed to different dosages (0, 50, 100 mJ/cm2) of UVB. Further, SLE patients were divided into two groups: active SLE group (22 cases, SLEDAI scores >4) and inactive SLE group (11 cases, SLEDAI scores ≤4). DNA methylation was evaluated by the Methylamp™ Global DNA Methylation Quantification Ultra Kit. The mRNA and protein expression levels of DNA methyltransferases (DNMT1 and DNMT3A) were detected by real-time PCR and western blot, respectively.
Results
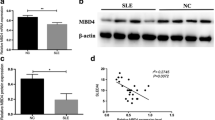
The levels of DNA methylation and DNMT3A mRNA in SLE patients were significantly decreased compared with those in healthy subjects at baseline. After different dosages of ultraviolet irradiation (0, 50 and 100 mJ/cm2), DNA methylation levels of CD4+ T cells were all reduced in a dose-dependent manner in three subgroups. Additionally, 100 mJ/cm2 ultraviolet irradiation in active SLE group contributed to a significant decrease of both DNA methylation and DNMT3A mRNA levels in CD4+ T cells. UVB exposure had no significant effects on expression levels of DNMT1 mRNA and protein and DNMT3A protein.
Conclusion
UVB decreases DNA methylation level of CD4+ T cells in SLE patients probably via inhibiting DNMT3A mRNA expression level, which needs to be further explored.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- SLE:
-
Systemic lupus erythematosus
- UVB:
-
Ultraviolet B
- DNMT1:
-
Deoxyribonucleic acid methyltransferase 1
- DNMT3:
-
Deoxyribonucleic acid methyltransferase 3
- CD4:
-
Cluster of differentiation antigen 4
References
Altorok N, Sawalha AH (2013) Epigenetics in the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Cur Opin Rheumatol 25:569–576. doi:10.1097/BOR.0b013e328364206f
Balada E, Ordi-Ros J, Serrano-Acedo S, Martinez-Lostao L, Rosa-Leyva M, Vilardell-Tarrés M (2008) Transcript levels of DNA methyltransferases DNMT1, DNMT3A and DNMT3B in CD4+ T cells from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Immunology 124:339–347. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2567.2007.02771.x
Barbhaiya M, Costenbader KH (2014) Ultraviolet radiation and systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 23:588–595. doi:10.1177/0961203314530488
Cör A (2000) The relationship between DNA methylation and expression of three different DNA methyltransferases in ovarian cancer. Radiol Oncol 34:369–374
Danchenko N, Satia JA, Anthony MS (2006) Epidemiology of systemic lupus erythematosus: a comparison of worldwide disease burden. Lupus 15:308–318
Feng PH (2007) Systemic lupus erythematosus: the face of Asia. Ann NY Acad Sci 1108:114–120
Gies P, Roy C, Javorniczky J, Henderson S, Lemus-Deschamps L, Driscoll C (2004) Global solar UV Index: Australian measurements, forecasts and comparison with the UK. Photochem Photobiol 79:32–39
Hochberg MC (1997) Updating the American College of rheumatology revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 40:1725. doi:10.1002/1529-0131(199709)40:9<1725:AID-ART29>3.0.CO;2-Y
Javierre BM et al (2010) Changes in the pattern of DNA methylation associate with twin discordance in systemic lupus erythematosus. Genome Res 20:170–179. doi:10.1101/gr.100289.109
Jeffries MA, Dozmorov M, Tang Y, Merrill JT, Wren JD, Sawalha AH (2011) Genome-wide DNA methylation patterns in CD4+ T cells from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Epigenetics 6:593–601
Medlin JL, Hansen KE, Fitz SR, Bartels CM (2016) A systematic review and meta-analysis of cutaneous manifestations in late- versus early-onset systemic lupus erythematosus. Semin Arthritis Rheum 45:691–697. doi:10.1016/j.semarthrit.2016.01.004
Richardson B (2003) DNA methylation and autoimmune disease. Clin Immunol 109:72–79
Richardson BC, Liebling MR, Hudson JL (1990) CD4+ cells treated with DNA methylation inhibitors induce autologous B cell differentiation. Clin Immunol Immunopathol 55:368–381
Runger TM, Epe B, Moller K (1995) Processing of directly and indirectly ultraviolet-induced DNA damage in human cells. Recent Results Cancer Res 139:31–42
Schwarz T (2008) 25 years of UV-induced immunosuppression mediated by T cells-from disregarded T suppressor cells to highly respected regulatory T cells. Photochem Photobiol 84:10–18. doi:10.1111/j.1751-1097.2007.00223.x
Ueno A et al (2013) Increased prevalence of circulating novel IL-17 secreting Foxp3 expressing CD4 + T cells and defective suppressive function of circulating Foxp3 + regulatory cells support plasticity between Th17 and regulatory T cells in inflammatory bowel disease patients. Inflamm Bowel Dis 19:2522–2534. doi:10.1097/MIB.0b013e3182a85709
Wang GS, Zhang M, Li XP, Zhang H, Chen W, Kan M, Wang YM (2009) Ultraviolet B exposure of peripheral blood mononuclear cells of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus inhibits DNA methylation. Lupus 18:1037–1044. doi:10.1177/0961203309106181
Wu Z, Li X, Qin H, Zhu X, Xu J, Shi W (2013) Ultraviolet B enhances DNA hypomethylation of CD4+ T cells in systemic lupus erythematosus via inhibiting DNMT1 catalytic activity. J Dermatol Sci 71:167–173. doi:10.1016/j.jdermsci.2013.04.022
Wu H, Zhao M, Chang C, Lu Q (2015a) The real culprit in systemic lupus erythematosus: abnormal epigenetic regulation. Int J Mol Sci 16:11013–11033. doi:10.3390/ijms160511013
Wu Z, Mei X, Zhao D, Sun Y, Song J, Pan W, Shi W (2015b) DNA methylation modulates HERV-E expression in CD4+ T cells from systemic lupus erythematosus patients. J Dermatol Sci 77:110–116. doi:10.1016/j.jdermsci.2014.12.004
Wu H, Zhao M, Tan L, Lu Q (2016) The key culprit in the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus: aberrant DNA methylation. Autoimmun Rev 15:684–689. doi:10.1016/j.autrev.2016.03.002
Yamane H, Paul WE (2013) Early signaling events that underlie fate decisions of naive CD4(+) T cells toward distinct T-helper cell subsets. Immunol Rev 252:12–23. doi:10.1111/imr.12032
Zhang Y, Zhao M, Sawalha AH, Richardson B, Lu Q (2013) Impaired DNA methylation and its mechanisms in CD4(+)T cells of systemic lupus erythematosus. J Autoimmun 41:92–99. doi:10.1016/j.jaut.2013.01.005
Zhang T et al (2016) G9a/GLP complex maintains imprinted DNA methylation in embryonic stem cells. Cell Rep 15:77–85. doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2016.03.007
Zhao M et al (2014) DNA methylation and mRNA and microRNA expression of SLE CD4+ T cells correlate with disease phenotype. J Autoimmun 54:127–136. doi:10.1016/j.jaut.2014.07.002
Acknowledgements
The authors are very grateful to Dr. Wei Wang (Department of Medical Oncology of Anhui Provincial Hospital, Hefei, PR.China) and Dr. Ning Yu (Department of Rheumatology, Keck School of Medicine, University of Southern California, Los Angeles, CA, USA), for their kind assistance in language editing. This work was partly supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 81202349 and 81373186), Anhui Provincial Natural Science Foundation of Institution of Higher Education (No. KJ2012Z154) and the School Research Fund of Anhui Medical University (No. 2011xkj066).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, M., Fang, X., Wang, GS. et al. Ultraviolet B decreases DNA methylation level of CD4+ T cells in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Inflammopharmacol 25, 203–210 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-017-0321-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-017-0321-8