Abstract
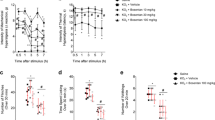
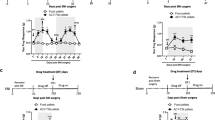
We evaluated the effect of pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate (PDTC) in superoxide anion-induced inflammatory pain. Male Swiss mice were treated with PDTC and stimulated with an intraplantar or intraperitoneal injection of potassium superoxide, a superoxide anion donor. Subcutaneous PDTC treatment attenuated mechanical hyperalgesia, thermal hyperalgesia, paw oedema and leukocyte recruitment (neutrophils and macrophages). Intraplantar injection of superoxide anion activated NF-κB and increased cytokine production (IL-1β, TNF-α and IL-10) and oxidative stress (nitrite and lipid peroxidation levels) at the primary inflammatory foci and in the spinal cord (L4–L6). PDTC treatment inhibited superoxide anion-induced NF-κB activation, cytokine production and oxidative stress in the paw and spinal cord. Furthermore, intrathecal administration of PDTC successfully inhibited superoxide anion-induced mechanical hyperalgesia, thermal hyperalgesia and inflammatory response in peripheral foci (paw). These results suggest that peripheral stimulus with superoxide anion activates the local and spinal cord oxidative- and NF-κB-dependent inflammatory nociceptive mechanisms. PDTC targets these events, therefore, inhibiting superoxide anion-induced inflammatory pain in mice.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anrather J, Racchumi G, Iadecola C (2006) NF-kappaB regulates phagocytic NADPH oxidase by inducing the expression of gp91phox. J Biol Chem 281:5657–5667
Basbaum AI, Bautista DM, Scherrer G, Julius D (2009) Cellular and molecular mechanism of pain. Cell 139:267–284
Borghi SM, Pinho-Ribeiro FA, Zarpleon AC (2015) Interleukin-10 limits intense acute swimming-induced muscle mechanical hyperalgesia in mice. Exp Physiol 100:531–544
Bruck R, Aeed H, Schey R et al. (2002) Pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate protects against thioacetamide-induced fulminant hepatic failure in rats. J Hepatol 36:370–377
Bressan E, Peres KC, Tonussi CR (2012) Evidence that LPS-reactive arthritis in rats depends on the glial activity and the fractalkine-TNF-alpha signaling in the spinal cord. Neuropharmacology 62:947–958
Cheng G, Whitehead SN, Hachinskl V et al (2006) Effects of pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate on beta-amyloid (25-35)-induced inflammatory responses and memory deficits in the rats. Neurobiol Dis 23:140–151
Chuang HH, Lin S (2009) Oxidative challenges sensitize the capsaicin receptor by covalent cysteine modification. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:20097–20102
Cunha TM, Verri WA Jr, Vivancos GG et al (2004) An electronic pressure-meter nociception paw test for mice. Braz J Med Biol Res 37:401–407
Cunha TM, Verri WA Jr, Schivo IR et al (2008) Role of neutrophils in the development of mechanical inflammatory hypernociception. J Leukoc Biol 83:824–832
Cuzzocrea S, Chatterjee PK, Mazon E et al (2002) Pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate attenuates the development of acute and chronic inflammation. Br J Pharmacol 135:496–510
Doyle T, Bryant L, Batinic-Haberle I et al (2009) Supraspinal inactivation of mitochondrial superoxide dismutate is a source of peroxynitrite in the development of morphine antinociceptive tolerance. Neurosci 164:702–710
Doyle T, Bryant L, Muscoli C et al (2010) Spinal NADPH oxidase is a source of superoxide in the development of morphine-induced hyperalgesia and antinociceptive tolerance. Neurosci Lett 483:85–89
Doyle T, Bryant L, Muscoli C et al (2012) Targeting the overproduction of peroxynitrite for the prevention and reversal of paclitaxel-induced neuropathic pain. J Neurosci 32:6149–6160
Fattori V, Pinho-Ribeiro FA, Borghi SM et al (2015) Curcumin inhibits superoxide anion-induced pain-like behavior and leukocyte recruitment by increasing Nrf2 expression and reducing NF-kappaB activation. Inflamm Res 64:993–1003
Funez MI, Ferrari LF, Duarte DB et al (2008) Teleantagonism: a pharmacodynamic property of the primary nociceptive neuron. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:19038–19043
Gao YJ, Ji RR (2010) Chemokines, neuronal-glial interactions and central processing of neuropathic pain. Pharmacol Ther 126:56–68
Gao X, Zhang H, Belmadani S et al (2008) Role of TNF-alpha-induced reactive oxygen species in endothelial dysfunction during reperfusion injury. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 295:H2242–H2249
Gruber-Schoffnegger D, Drdla-Schutting R, Honigsperger C et al (2013) Induction of thermal hyperalgesia and synaptic long-term potentiation in the spinal cord lamina I by TNF-alpha and IL-1beta is mediated by glial cells. J Neurosci 33:6540–6551
Guerrero AT, Verri WA Jr, Cunha TM et al (2008) Involvement of LTB4 in zymosan-induced joint nociceotion in mice: participation of neutrophils and PGE2. J Leukoc Biol 83:122–130
Hayakawa M, Miyashita H, Sakamoto I et al (2003) Evidence that reactive oxygen species do not mediate NF-kappaB activation. EMBO J 22:3356–3366
Hohmann MS, Cardoso RD, Pinho-Ribeiro FA et al (2013) 5-lipoxygenase deficiency reduces acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity and lethality. Biomed Res Int 2013:1–13
Ivan AL, Campanini MZ, Martinez RM et al (2014) Pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate inhibits UVB-induced skin inflammation and oxidative stress in hairless mice and exhibits antioxidant activity in vitro. J Photochem Photobiol B 138:124–133
Jamaluddin M, Wang S, Boldogh I, Tian B, Brasier AR (2007) TNF-alpha-induced NF-kappaB/RelA Ser(276) phosphorylation and enhanceosome formation is mediated by an ROS-dependent PKAc pathway. Cell Signal 19:1419–1433
Janes K, Neumann WL, Salvemini D (2012) Anti-superoxide and anti-peroxynitrite strategies in pain suppression. Biochim Biophys Acta 1822:815–821
Kim CH, Kim JH, Hsu CY, Ahn YS (1999a) Zinc is required in pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate inhibition of NF-kappaB activation. FEBS Lett 449:28–32
Kim CH, Kim JH, Moon SJ et al (1999b) Pyrithione, a zinc ionophore, inhibits NF-kappaB activation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 259:505–509
Kim HY, Chung JM, Chung K (2008) Increased production of mitochondrial superoxide in the spinal cord induces pain behavior in mice: the effect of mitochondrial electron transport complex inhibitors. Neurosci Lett 447:87–91
Kim HY, Wang J, Lu Y et al (2009) Superoxide signalling in pain is independent of nitric oxide signalling. NeuroReport 20:1424–1428
Kotake Y, Moore DR, Vasquez-Walden A et al (2003) Antioxidant amplifies antibiotic protection in the cecal ligation and puncture model of microbial sepsis through interleukin-10 production. Shock 19:252–256
Kvietys PR, Granger DN (2012) Role of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species in the vascular responses to inflammation. Free Radic Biol Med 52:556–592
Lee CH, Kim SH, Lee SM (2008) Effect of pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate on hepatic vascular stress gene expression during ischemia and reperfusion. Eur J Pharmacol 595:100–107
Li H, Han M, Guo L et al (2011) Oxidative stress, endothelial dysfunction and inflammatory response in rat heart to NO(2) inhalation exposure. Chemosphere 82:1589–1596
Liddell JR, Lehtonen S, Duncan C et al (2016) Pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate activates the Nrf2 pathway in astrocytes. J Neuroinflammation 13:49
Little JW, Chen Z, Doyle T et al (2012a) Supraspinal peroxynitrite modulates pain signaling by suppressing the endogenous opioid pathway. J Neurosci 32:10797–10808
Little JW, Doyle T, Salvemini D (2012b) Reactive nitroxidative species and nociceptive processing: determining the roles for nitric oxide, superoxide, and peroxynitrite in pain. Amino Acids 42:75–94
Little JW, Cuzzocrea S, Bryant L et al (2013) Spinal mitochondrial-derived peroxynitrite enhances neuroimmune activation during morphine hyperalgesia and antinociceptive tolerance. Pain 154:978–986
Lundberg JO, Weitzberg E, Gladwin MT (2008) The nitrate-nitrite-nitric oxide pathway in physiology and therapeutics. Nat Rev Drug Discov 7:156–167
Maioli NA, Zarpelon AC, Mizokami SS et al (2015) The superoxide anion donor, potassium superoxide, induces pain and inflammation in mice through production of reactive oxygen species and cyclooxygenase-2. Braz J Med Biol Res 48:321–331
Mantovani A, Cassatella MA, Constantini C et al (2011) Neutrophil in the activation and regulation of innate and adaptative immunity. Nat Rev Immunol 11:519–531
Naito Y, Takagi T, Higashimura Y (2014) Heme oxygenase-1 and anti-inflammatory M2 macrophages. Arch Biochem Biophys 15:83–88
Ndengele MM, Muscoli C, Wang ZQ et al (2005) Superoxide potentiates NF-kappaB activation and modulates endotoxin-induced cytokine production in alveolar macrophages. Shock 23:186–193
Ndengele MM, Cuzzocrea S, Esposito E et al (2008) Cyclooxygenases 1 and 2 contribute to peroxynitrite-mediated inflammatory pain hypersensitivity. FASEB J 22:3154–3164
Németh ZH, Haskó G, Vizi ES et al (1998) Pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate augments IL-10, inhibits TNF-α, MIP-1alpha, IL-12, and nitric oxide production and protects from the lethal effect of endotoxin. Shock 10:49–53
Pinho-Ribeiro FA, Hohmann MS, Borghi SM et al (2015) Protective effects of the flavonoid hesperidin methyl chalcone in inflammation and pain in mice: role of TRPV1, oxidative stress, cytokines and NF-kappaB. Chem Biol Interact 228:88–99
Qiu M, Chen Y, Cheng L et al (2013) Pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate inhibits herpes simplex virus 1 and 2 replication, and its activity may be mediated through dysregulation of the ubiquitin-proteasome system. J Virol 87:8675–8686
Rees H, Sluka KA, Westlund KN et al (1994) Do dorsal root reflexes augment peripheral inflammation? NeuroReport 21:821–824
Ruiz-Miyazawa KW, Pinho-Ribeiro FA, Zarpelon AC et al (2015) Vinpocetine reduces lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory pain and neutrophil recruitment in mice by targeting oxidative stress, cytokines and NF-κB. Chem Biol Interact 237:9–17
Salvemini D, Riley DP, Cuzzocrea S (2002) SOD mimetics are coming of age. Nat Rev Drug Discov 1:367–374
Salvemini D, Little JW, Doyle T et al (2011) Roles of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species in pain. Free Rad Biol Med 51:951–966
Schreck R, Meier B, Mannel DN et al (1992) Dithiocarbamates as potent inhibitors of nuclear factor κB activation in intact cells. J Exp Med 175:1181–1194
Serafim KG, Navarro SA, Zarpelon AC et al (2015) Bosentan, a mixed endothelin receptor antagonist, inhibits superoxide anion-induced pain and inflammation in mice. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 388:1211–1221
Sluka KA, Rees H, Westlund KN et al (1995) Fiber types contributing to dorsal root reflexes induced by joint inflammation in cats and monkeys. J Neurophysiol 74:981–989
Souza GR, Talbot J, Lotufo CM et al (2013) Fractalkine mediates inflammatory pain through activation of satellite glial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110:11193–11198
Turpaev KT (2013) Keap1-Nrf2 signaling pathway: mechanisms of regulation and role in protection of cells against toxicity caused by xenobiotics and electrophiles. Biochemistry (Mosc). 78:111–126
Verri WA Jr, Cunha TM, Parada CA et al (2006) Hypernociceptive role of cytokines and chemokines: targets for analgesic drug development? Pharmacol Ther 112:116–138
Verri WA Jr, Cunha TM, Ferreira SH et al (2007) IL-15 mediates antigen-induced neutrophil migration by triggering IL-18 production. Eur J Immunol 12:3373–3380
Wang ZQ, Porreca F, Cuzzocrea S et al (2004) A newly identified role for superoxide in inflammatory pain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 309:869–878
Wieseler-Frank J, Maier SF, Watkins LR (2004) Glial activation and pathological pain. Neurochem Int 45:389–395
Wild AC, Moinova HR, Mulcahy RT (1999) Regulation of gamma-glutamylcysteine synthetase subunit gene expression by the transcription factor Nrf2. J Biol Chem 274:33627–33636
Yamacita-Borin FY, Zarpelon AC, Pinho-Ribeiro FA et al (2015) Superoxide anion-induced pain and inflammation depends on TNFalpha/TNFR1 signaling in mice. Neurosci Lett 605:53–58
Yang SR, Valvo S, Yao H et al (2008) IKK alpha causes chromatin modification on pro-inflammatory genes by cigarette smoke in mouse lung. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 38:689–698
Yoshino Y, Yamamoto S, Kohsaka S et al (2011) Superoxide anion contributes to the induction of tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFalpha) through activation of the MKK3/6-p38 MAPK cascade in rat microglia. Brain Res 1422:1–12
Yu XJ, Zhang DM, Jia LL et al (2015) Kang, Inhibition of NF-kappaB activity in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus attenuates hypertension and cardiac hypertrophy by modulating cytokines and attenuating oxidative stress. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 284:315–322
Zarpelon AC, Rodrigues FC, Lopes AH et al (2016) Spinal cord oligodendrocyte-derived alarmin IL-33 mediates neurophatic pain. FASEB J 30:54–65
Zipper LM, Mulcahy RT (2000) Inhibition of ERK and p38 MAP kinases inhibits binding of Nrf2 and induction of GCS genes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 278:484–492
Zipper LM, Mulcahy RT (2003) Erk activation is required for Nrf2 nuclear localization during pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate induction of glutamate cysteine ligase modulatory gene expression in HepG2 cells. Toxicol Sci 73:124–134
Acknowledgments
Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq), São Paulo Research Foundation (FAPESP) under grant agreements number 2011/19670-0 (Thematic project) and 2013/08216-2 (Center for Research in Inflammatory Disease-CRID), Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES), Ministério da Ciência, Tecnologia e Inovação (MCTI), Secretaria da Ciência, Tecnologia e Ensino Superior (SETI), Fundação Araucária and Parana State Government grants supported this study (Brazil). A.C.Z. received a post-doc fellowship from CAPES/Fundação Araucária, S.M.B. received a post-doc fellowship from CAPES, and L.S.F. received a post-doc fellowship from CNPq. It is noteworthy to mention that this manuscript has been read and approved by all the authors, which contributed substantially to the work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pinho-Ribeiro, F.A., Fattori, V., Zarpelon, A.C. et al. Pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate inhibits superoxide anion-induced pain and inflammation in the paw skin and spinal cord by targeting NF-κB and oxidative stress. Inflammopharmacol 24, 97–107 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-016-0266-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-016-0266-3