Abstract.
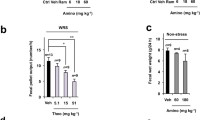
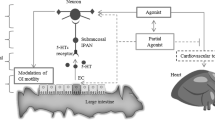
Ramosetron is a potent and selective serotonin (5-HT)3 receptor antagonist that has been shown to affect abnormal colonic function and abdominal pain in animals. Ramosetron (0.3 to 100 µg/kg, p.o.) has been found to significantly suppress abnormal defecation induced by conditioned-fear stress (CFS), restraint stress, corticotropin releasing factor (CRF) and 5-HT in rats and mice, and these effects were more potent than those of alosetron, cilansetron or loperamide. On the other hand, ramosetron (3,000 µg/kg, p. o., once daily for 7 days) did not inhibit normal defecation in dogs while tiquizium significantly inhibited it. Ramosetron (3 to 100 µg/kg, p. o.) also significantly prevented CFS-induced acceleration of colonic transit and CRF-induced abnormal water transport in rats, respectively. Moreover, ramosetron (0.3 to 3 µg/kg, p. o.) significantly suppressed restraint stress-induced decrease in colonic pain threshold, an effect not observed with loperamide. These results indicate that ramosetron produce beneficial clinical effects on IBS symptoms.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Received 12 July 2006; accepted 21 August 2006
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hirata, T., Funatsu, T., Keto, Y. et al. Pharmacological profile of ramosetron, a novel therapeutic agent for IBS. Inflammopharmacol 15, 5–9 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-006-1537-1
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-006-1537-1