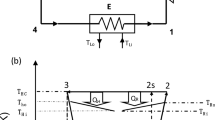
Abstract
Performance optimization of heat devices is of great significance for the efficient utilization of energy. In the context of irreversible thermodynamics, the thermodynamic behaviors of coupled autonomous(CAU) heat engines(refrigerators) under the trade-off criterion are studied. The analytical formulas of power(cooling power) and efficiency [coefficient of performance(COP)] are not only formulated, but also the thermodynamic bounds of efficiency(COP) are presented. In the physically allowed space, optimal characteristics of CAU heat engines(refrigerators) are detailedly elucidated, and the energetic advantages of trade-off optimization are highlighted. Besides, when the temperature of the intermediate reservoir is set to be specific mean values of the hot and cold temperatures, both efficiency and COP are definitely given. These results have certain theoretical and practical significance for designing and manipulating real-life heat engines(refrigerators).



Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Vaudrey, A., Lanzetta, F., Feidt, M.: HB Reitlinger and the origins of the efficiency at maximum power formula for heat engines. J. Non-Equilib. Thermodyn. 39, 199–203 (2014)
Curzon, F.L., Ahlborn, B.: Efficiency of a carnot engine at maximum power output. Am. J. Phys. 43, 22–24 (1975)
Andresen, B.: Current trends in finite-time thermodynamics. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 50, 2690–2704 (2011)
Andresen, B., Salamon, P.: Future perspectives of finite-time thermodynamics. Entropy 24, 690 (2022)
Ma, Y.H., Dong, H., Sun, C.P.: Can we build a heat engine with both high power and high efficiency? The development and prospects of finite-time thermodynamics. Phys. Chin. 50, 1–9 (2021)
Ding, Z.M., Chen, L.G., Wang, W.H., Sun, F.R.: Progress in study on finite time thermodynamic performance optimization for three kinds of microscopic energy conversion systems. Sci. China-Phys. Mech. Astron. 45, 889–918 (2015)
Esposito, M., Kawai, R., Lindenberg, K., den Broeck, C.V.: Efficiency at maximum power of low-dissipation Carnot engines. Phys. Rev. Lett. 105, 150603 (2010)
den Broeck, C.V.: Thermodynamic efficiency at maximum power. Phys. Rev. Lett. 95, 190602 (2005)
de Cisneros, B.J., Arias-Hernandez, L.A., Heranadez, A.C.: Linear irreversible thermodynamics and coefficient of performance. Phys. Rev. E 73, 057103 (2006)
Izumida, Y., Okuda, K., Roco, J.M.M., Hernandez, A.C.: Heat devices in nonlinear irreversible thermodynamics. Phys. Rev. E 91, 052140 (2015)
Izumida, Y., Okuda, K.: Efficiency at maximum power of minimally nonlinear irreversible heat engines. Europhys. Lett. 97, 10004 (2012)
Proesmans, K., Dreher, Y., Gavrilov, M., Bechhoefer, J., den Broeck, C.V.: Brownian duet: a novel tale of thermodynamic efficiency. Phys. Rev. X 6, 041010 (2016)
Malgaretti, P., Nowakowski, P., Stark, H.: Mechanical pressure and work cycle of confined active Brownian particles. Europhys. Lett. 134, 20002 (2021)
Fang, X., Kruse, K., Lu, T., Wang, J.: Nonequilibrium physics in biology. Rev. Mod. Phys. 91, 045004 (2019)
Mugnai, M.L., Hyeon, C., Hinczewski, M., Thirumalai, D.: Theoretical perspectives on biological machines. Rev. Mod. Phys. 92, 025001–1 (2020)
Benenti, G., Casati, G., Saito, K., Whitney, R.S.: Fundamental aspects of steady-state conversion of heat to work at the nanoscale. Phys. Rep. 694, 1–124 (2017)
Myers, N.M., Abah, O., Deffner, S.: Quantum thermodynamic devices: from theoretical proposals to experimental reality. AVS Quantum Sci. 4, 027101–1 (2022)
Bhattacharjee, S., Dutta, A.: Quantum thermal machines and batteries. Eur. Phys. J. B 94, 239 (2021)
Kosloff, R., Levy, A.: Quantum heat engines and refrigerators: continuous devices. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 65, 365 (2014)
Wang, Y., Li, M., Tu, Z.C., Hernandez, A.C., Roco, J.M.M.: Coefficient of performance at maximum figure of merit and its bounds for low-dissipation Carnot-like refrigerators. Phys. Rev. E 86, 011127 (2012)
Yan, Z., Chen, J.: A class of irreversible Carnot refrigeration cycles with a general heat transfer law. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 23, 136–141 (1990)
Angulo-Brown, F.: An ecological optimization criterion for finite-time heat engines. J. Appl. Phys. 69, 7465–7469 (1991)
Chen, C.K., Chen, C.Y.: The ecological optimization of an irreversible Carnot heat engine. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 30, 1602 (1997)
Stucki, J.W.: The optimal efficiency and the economic degrees of coupling of oxidative phosphorylation. Eur. J. Biochem 109, 269–283 (1980)
Yilmaz, T., Durmusoglu, Y.: Efficient power analysis for an irreversible Carnot heat engine. Int. J. Energy Res. 32, 623–628 (2008)
Yilmaz, T.: A new performance criterion for heat engines: efficient power. J. Energy Inst. 79, 38–41 (2006)
Singh, V., Johal, R.S.: Low-dissipation Carnot-like heat engines at maximum efficient power. Phys. Rev. E 98, 062132 (2018)
Ryabov, A., Holubec, V.: Maximum efficiency of steady-state heat engines at arbitrary power. Phys. Rev. E 93, 050101(R) (2016)
Zhang, R., Li, Q.W., Tang, F.R., Yang, X.Q., Bai, L.: Route towards the optimization at given power of thermoelectric heat engines with broken time-reversal symmetry. Phys. Rev. E 96, 022133 (2017)
Hernandez, A.C., Medina, A., White, J.A., Velasco, S.: Unified optimization criterion for energy converters. Phys. Rev. E 63, 037102 (2001)
de Tomas, C., Roco, J.M.M., Hernandez, A.C., Wang, Y., Tu, Z.C.: Low-dissipation heat devices: Unified trade-off optimization and bounds. Phys. Rev. E 87, 012105 (2013)
Gonzalez-Ayala, J., Hernandez, A.C., Roco, J.M.M.: From maximum power to a trade-off optimization of low-dissipation heat engines: influence of control parameters and the role of entropy generation. Phys. Rev. E 95, 022131 (2017)
Apertet, Y., Ouerdane, H., Goupil, C., Lecoeur, P.: True nature of the Curzon-Ahlborn efficiency. Phys. Rev. E 96, 022119 (2017)
Yan, Z.: Comment on “ An ecological optimization criterion for finitetime heat engines” [ J. Appl. Phys. 69, 7465 (1991)]. J. Appl. Phys. 73, 3583 (1993)
Yan, Z.: Comment on “ A general property of endoreversible thermal engines” [J. Appl. Phys. 81, 2973(1997)]. J. Appl. Phys. 89, 1518–1519 (2001)
Long, R., Liu, W.: Efficiency and its bounds of minimally nonlinear irreversible heat engines at arbitrary power. Phys. Rev. E 94, 052114 (2016)
Long, R., Liu, Z.C., Liu, W.: Performance optimization of minimally nonlinear irreversible heat engines and refrigerators under a trade-off figure of merit. Phys. Rev. E 89, 062119 (2014)
Long, R., Liu, W.: Unified trade-off optimization for general heat devices with nonisothermal processes. Phys. Rev. E 91, 042127 (2015)
Kaur, K., Singh, V., Ghai, J., Jena, S., Mustecaplioğlu, Ö.E.: Unified trade-off optimization of a three-level quantum refrigerator. Phys. A: Stat. Mech. Appl. 576, 125892 (2021)
Harman, T.C.: Multiple stage thermoelectric generation of power. J. Appl. Phys. 29, 1471–1473 (1958)
Apertet, Y., Ouerdane, H., Goupil, C., Lecoeur, P.: Efficiency at maximum power of thermally coupled heat engines. Phys. Rev. E 85, 041144 (2012)
Khlifi, Y., Seddik, S., ElAllati, A.: Steady state entanglement behavior between two quantum refrigerators. Phys. A: Stat. Mech. Appl. 596, 127199 (2022)
Ye, Z.L., Holubec, V.: Maximum efficiency of absorption refrigerators at arbitrary cooling power. Phys. Rev. E 103, 052125 (2021)
Johal, R.S., Rai, R.: Efficiency at optimal performance: a unified perspective based on coupled autonomous thermal machines. Phys. Rev. E 105, 044145 (2022)
Singh, V., Johal, R.S.: Feynman-Smoluchowski engine at high temperatures and the role of constraints. J. Stat. Mech. 2018, 073205 (2018)
Chen, L., Yan, Z.: The effect of heat-transfer law on performance of a two-heat-source endoreversible cycle. J. Chem. Phys. 90, 3740 (1989)
den Broeck, C.V.: Efficiency at maximum power in the lowdissipation limit. Europhys. Lett. 101, 10006 (2013)
Tu, Z.C.: Efficiency at maximum power of Feynman’s ratchet as a heat engine. J. Phys. A: Math. Theor. 41, 312003 (2008)
den Broeck, C.V., Findenberg, K.: Efficiency at maximum power for classical particle transport. Phys. Rev. E 86, 041144 (2012)
Cavina, V., Mari, A., Giovannetti, V.: Slow dynamics and thermodynamics of open quantum systems. Phys. Rev. Lett. 119, 050601 (2017)
Funding
This work is financially supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Grant No. 2020ZDPYMS32).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
L.B. and L.Z. conducted the calculations and the processing of the results. R.Z. provided the useful analysis and wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethics approval
Not applicable
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bai, L., Zhang, L. & Zhang, R. Thermodynamic Performances of Coupled Autonomous Heat Devices: Insights from the Trade-off Optimization. Int J Theor Phys 63, 13 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-023-05541-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-023-05541-3