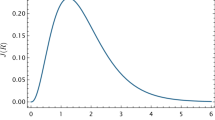
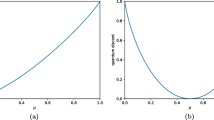
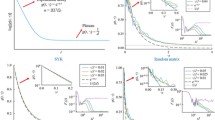
Abstract
We study the property of the many-body localization in Heisenberg Ising Chain model with periodic driving by using the method of matrix exact diagonalization. We consider a driving protocol in which the system’s Hamiltonian is periodically switched between two operators. The first segment is a disordered Ising system, and acts for time T0; It is worth noting that the Hamiltonian of the second part is an operator dependent on time, and acts for time T1, so the driving period is T = T0 + T1. We choose excited state fidelity to observe the phase transition between the localized phase and the ergodic phase of the system, which reflects the property of many-body localization in Heisenberg Ising Chains under periodic driving. Through the study, we find that when the disorder strength h is small, the system is in the ergodic phase, periodic driving can cause the occurrence of a transition from the ergodic phase to the localized phase, while the system is in the localized phase with a large disorder strength h, the transition from the localized phase to the ergodic phase will occur under the periodic driving. For these two cases, they all show that there is a critical driving period Tc, when the driving period is greater than Tc, the system will have a phase transition, meanwhile, Tc decreases with the increase of driving strength. Furthermore, we also get that the system size and disorder strength also effect the critical point of the driving period. The critical point decreases as the strength of disorder increases and decreases with the increase of the system size.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated during and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Anderson, P.W.: Absence of diffusion in certain random lattices. Phys. Rev. Lett. 109, 1492 (1958)
Abrahams, E.: 50 Years of Anderson localization World Scientific Publishing (2010)
Stolz, G.: In Entropy and the Quantum II, edited by R. Sims and D. Ueltschi, American mathematical society (2010)
Anderson, P.W., Licciardello, D.C., Ramakrishnan, T.V.: Scaling theory of localization: absence of quantum diffusion in two dimensions. Phys. Rev. Lett. 42, 673 (1979)
Basko, D.M., Aleiner, I.L., Altshuler, B.L.: Metal-insulator transition in a weakly interacting many-electron system with localized single-particle states. Ann. Phys. (Amsterdam) 321, 1126 (2006)
Pal, A., Huse, D.A.: Many-body localization phase transition. Phys. Rev. B 82, 174411 (2010)
Khemani, V., Lim, S.P., Sheng, D.N., Huse, D.A.: Critical properties of the many-body localization transition. Phys. Rev. X 7, 021013 (2017)
Nandkishore, R., Huse, D.A.: Many-body localization and thermalization in quantum statistical mechanics. Annu. Rev. of Con. Matt. Phys. 6, 15–38 (2015)
Strek, W., Cichy, B., Radosinski, L., Gluchowski, P., Marciniak, L., Lukaszewicz, M., Hreniak, D.: Laser-induced white-light emission from graphene ceramics-opening a band gap in graphene, . Light Sci. Appl. 4, e237 (2015)
Rao, W-J: Machine learning the many-body localization transition in random spin systems. J. Phys. 30, 395902 (2018)
Etezadi, D., John, B.W. IV, Ruggeri, F.S., Dietler, G., Lashuel, H.A., Altug, H.: Nanoplasmonic mid-infrared biosensor for in vitro protein secondary structure detection. Light Sci. Appl. 6, e17029 (2017)
Altman, E.: Many-body localization and quantum thermalization. Nature Phys. 14, 979–983 (2018)
Luitz, D.J., Laflorencie, N., Alet, F.: Many-body localization edge in the random-field Heisenberg chain. Phys. Rev. B 91(R), 081103 (2015)
Yurui, Q.U., Li, Q., Cai, L.U., Pan, M., Ghosh, P., Kaikai, D.U., Qiu, M.: Thermal camouflage based on the phase-changing material GST. Light Sci. Appl. 7, 26 (2018)
Dmitry, A.A., Ehud, A., Immanuel, B., Maksym, S.: Many-body localization, thermalization, and entanglement. Rev. Mod. Phys. 91, 021001 (2019)
Monthus, C.: Many-body-localization transition: sensitivity to twisted boundary conditions. J. Phys. A : Math. Theor. 50, 095002 (2017)
Rispoli, M., Lukin, A., Schittko, R., et al: Quantum critical behaviour at the many-body localization transition. Nature 573, 385–389 (2019)
Rigol, M., Dunjko, V., Olshanii, M.: Thermalization and its mechanism for generic isolated quantum systems. Nature (London) 452, 854 (2008)
Pal, A., Huse, D.A.: Many-body localization phase transition. Phys. Rev. B 82, 174411 (2010)
Ponte, P, Papic, Z., Huveneers, F., Abain, D.A.: Many-body localization in periodically driven system. Phys. Rev. Lett. 114, 140401 (2015)
Ponte, P., Chandran, A., Papic, Z., Abanin, D.A.: Periodically driven ergodic and many-body localized quantunm system. Ann. Phys. 196–204, 353 (2015)
Bairey, E., Refael, G., Netanel, H.: Lindner driving induced many-body localization. Phys. Rev. B 96(R), 020201 (2017)
Biasco, S, Beere, H.E., Ritchie, D.A., Li, L., Davies, G.A., Linfield, E.H., Vitiello, M.S.: Frequency-tunable continuous-wave random lasers at terahertz frequencies. Light Sci. Appl. 8, 43 (2019)
Thimothee, T., Franrois, H., Markus, M., Wojciech, D.R.: Many-body delocalization as a quantum avalanche. Phys. Rev. Lett. 121, 140601 (2018)
Rubin, S., Hong, B., Fainman, Y.: Subnanometer imaging and controlled dynamical patterning of thermocapillary driven deformation of thin liquid films. Light Sci. Appl. 8, 77 (2019)
Grifoni, M., Hanggi, P.: Driven quantum tunneling. Phys. Rep. 304, 229–354 (1998)
D’Alessio, L., Rigol, M.: Long-time behavior of isolated periodically driven interacting lattice systems. Phys. Rev. X 4, 041048 (2014)
Petsch, S., Schuhladen, S., Dreesen, L., Zappe, H.: The engineered eyeball, a tunable imaging system using soft-matter micro-optics. Light Sci. Appl. 5, e16068 (2016)
Bukov, M., D’Alessio, L., Polkovnikov, A.: Universal high-frequency behavior of periodically driven systems: from dynamical stabilization to floquet engineering. Adv. Phys. 64 (2015)
Dutt, A., Minkov, M., Williamson, IA, Fan, S.: Higher-order topological insulators in synthetic dimensions. Light Sci. Appl. 9, 131 (2020)
Sajeed, S, Jennewein, T: Observing quantum coherence from photons scattered in free-space. Light: Science & Applications 10, 121 (2021)
Chen, L, Lin, W, Wang, H, Li, J, Kang, J: Reversing abnormal hole localization in high-Al-content AlGaN quantum well to enhance deep ultraviolet emission by regulating the orbital state coupling. Light: Science & Applications 9, 104 (2020)
Hu, T.T., Xue, K., Li, X.D., Zhang, Y., Ren, H.: Fidelity of the diagonal ensemble signals the many-body localization transition. Phys. Rev. E 94, 052119 (2016)
Hu, T.T., Xue, K., Li, X., et al: Excited-state fidelity as a signal for the many-body localization transition in a disordered Ising chain. Sci. Rep. 7, 577 (2017)
Zheng, Y., Yang, J., Shen, Z., et al.: Optically induced transparency in a micro-cavity. Light: Science & Applications 5, 16072 (2016)
Chen, L., Lei, J., Romero, J.: Quantum digital spiral imaging. Light: Science & Applications 3, 153 (2014)
De Grandi, C., Polkovnikov, A., Sandvik, A.W.: . Phys. Rev. B 84, 224303 (2011)
Mukherjee, V., Polkovnikov, A., Dutta, A.: . Phys. Rev. B 83, 075118 (2011)
Lai, Y., Lan, Y., Lu, T.: Strong light-matter interaction in ZnO microcavities. Light: Science & Applications 2, 76 (2013)
Saeed, S., de Weerd, C., Stallinga, P., et al.: Carrier multiplication in germanium nanocrystals. Light: Science & Applications 4, 251 (2015)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the NSF of China (Grant No. 62175233) and by the Plan for Scientific and Technological Development of Jilin Province (No. 20220101111JC).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ni, S., Hu, T., Ren, H. et al. Property of Many-Body Localization in Heisenberg Ising Chain Under Periodic Driving. Int J Theor Phys 62, 56 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-023-05309-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-023-05309-9