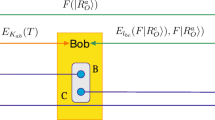
Abstract
Different from traditional signature schemes, the paper gives a novel protocol which uses quantum logic gates to perform operations on quantum states, and it realizes the quantum state representation of two classical information and uses mixed entangled states to measure information. The binary measurement results of the protocol are converted into blocks of a certain length, and these blocks are encrypted by quantum Fourier transform and transmitted through N-dimensional quantum states. In the proposed protocol, the quantum channel uses N-dimensional quantum states, which is more efficient than the currently proposed two-dimensional information carrier channel protocol. The security analysis of this article shows that the program is anti-counterfeit, undeniable and blind. In addition, compared with other existing efficiency analysis schemes, this scheme has higher signature efficiency.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shor, P.W.: Algorithms for quantum computation: discrete logarithms and factoring. Foundations of Computer Science. 124–134 (1994)
Wen, K.: Security Analysis and Improvement of Arbitration Quantum Signature Protocol, pp. 1–5. Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, Beijing (2019)
Chuang I L, Gottesman D. Quantum Digital Signatures. arXiv: Quantum Physics, 2002
Zeng, G.H., Keitel, C.H.: Arbitrated quantum-signature scheme. Phys. Rev. A. 64(4), 042312 (2002)
Amiri, R., Wallden, P., Kent, A., Andersson, E.: Secure quantum signatures using insecure quantum channels. Phys. Rev. A. 93(3), 032325 (2016)
Puthoor, I.V., Amiri, R., Wallden, P., Curty, M., Andersson, E.: Measurement-device-independent quantum digital signatures. Phys. Rev. A. 94(2), 022328 (2016)
Zhu, Z.D., Zhao, S.H., Gu, W.Y., et al.: Orbital angular momentum encoded measurement-device-independent quantum key distributions under atmospheric turbulence. Acta Opt. Sin. 38(12), 1227002 (2019)
Zhang, X.Z., Xu, Q.: Liu B Y. Influence of Fog on Performance of Free-Space Quantum Communication Acta Optica Sinica. 40(7), 0727001 (2020)
Wen, X.J., Niu, X.M., Ji, L.P., et al.: A weak blind signature scheme based on quantum cryptography. Opt. Commun. 282(4), 666–669 (2009)
Su, Q., Huang, Z., Wen, Q.Y., et al.: Quantum blind signature based on two-state vector formalism. Opt. Commun. 283(21), 4408–4410 (2010)
Wang, M.M., Chen, X.B., Yang, Y.X.: A blind quantum signature protocol using the GHZ states. Science China-Physics Mechanics & Astronomy. 09, 32–37 (2013)
Siavash, K., Ali, Z.: A sessional blind signature based on quantum cryptography. Quantum Inf. Process. 13(1), 121–130 (2014)
Tian, Y., Chen, H., Ji, S.F., et al.: A broadcasting multiple blind signature scheme based on quantum teleportation. Opt. Quant. Electron. 46(6), 769–777 (2014)
Zhang, W., Qiu, D., Zou, X., Mateus, P.: Analyses and improvement of a broadcasting multiple blind signature scheme based on quantum GHZ entanglement. Quantum Inf. Process. 16(6), 150 (2017)
Chen F, Wang Z, Hu Y, et al. A New Quantum Blind Signature Scheme with BB84-State. Entropy, 2019, 21(4)
Liang, X., Wu, Y., Zhang, Y., et al.: Quantum multi-proxy blind signature scheme based on four-qubit cluster states. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 58(1), 31–39 (2019)
Liu, G., Ma, W., Cao, H., et al.: A novel quantum group proxy blind signature scheme based on five-qubit entangled state. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 58(6), 1999–2008 (2019)
Zhang, J.L., Zhang, J.Z., Xie, S.C., et al.: Improvement of a quantum proxy blind signature scheme. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 57(6), 1612–1621 (2018)
Yang, Y.Y., Xie, S.C., Zhang, J.Z., et al.: An improved quantum proxy blind signature scheme based on genuine seven-qubit entangled state. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 56(7), 2293–2302 (2017)
Li, X.Y., Chang, Y., Zhang, S.B., Dai, J.Q., Zheng, T.: Quantum blind signature scheme based on quantum Wa1k. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 59, 2059–2073 (2020)
Niu, X.F., Ma, W.P., Chen, B.Q., et al.: A quantum proxy blind signature scheme based on Superdense coding. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 59(4), 1–8 (2020)
Tian, Y., Chen, H., Ji, S.F., et al.: A broadcasting multiple blind signature scheme based on quantum teleportation. Opt. Quant. Electron. 46(6), 769–777 (2014)
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the Basic Scientific Research Project of Liaoning Provincial Department of Education (Grant No. LJC202007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, H., Zhang, Y. & Li, Z. Efficient Quantum Blind Signature Scheme Based on Quantum Fourier Transform. Int J Theor Phys 60, 2311–2321 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-021-04854-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-021-04854-5