Abstract
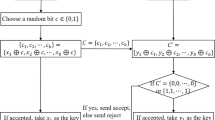
A novel practical quantum secure direct communication (QSDC) protocol is constructed by utilizing the evolution law of atom via cavity QED. It transmits the atoms from one communicant to the other communicant in a two-step manner. It adopts two-atom product states as the initial quantum resource and the decoy atom technique to guarantee the security against the outside attack. It only needs single-atom measurements, and neither the quantum entanglement swapping nor the unitary operations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bennett, C.H., Brassard, G.: Quantum cryptography: public-key distribution and coin tossing. Proc IEEE Int Conf Comput Syst and Signal Process, 175–179 (1984)
Long, G.L., Liu, X.S.: Theoretically efficient high-capacity quantum-key-distribution scheme. Phys. Rev. A 65(3), 032302 (2002)
Deng, F.G., Long, G.L., Liu, X.S.: Two-step quantum direct communication protocol using the Einstein-Podolsky-Rosen pair block. Phys. Rev. A 68(4), 042317 (2003)
Wang, J., Zhang, Q., Tang, C.J.: Quantum secure direct communication based on order rearrangement of single photons. Phys. Lett. A 358(4), 256–258 (2006)
Tan, X.Q., Zhang, X.Q.: Controlled quantum secure direct communication by entanglement distillation or generalized measurement. Quantum Inf. Process. 15(5), 2137–2154 (2016)
Wang, L.L., Ma, W.P., Wang, M.L., Shen, D.S.: Three-party quantum secure direct communication with single photons in both polarization and spatial-mode degrees of freedom. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 55, 2490–2499 (2016)
Wu, F.Z., Yang, G.J., Wang, H.B., Xiong, J., Alzahrani, F., Hobiny, A., Deng, F.G.: High-capacity quantum secure direct communication with two-photon six-qubit hyperentangled states. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 60, 120313 (2017)
Chen, S.S., Zhou, L., Zhong, W., Sheng, Y.B.: Three-step three-party quantum secure direct communication. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 61, 90312 (2018)
Khorasani, F.M., Houshmand, M., Anzabi-Nezhad, N.S.: Authenticated controlled quantum secure direct communication protocol based on five-particle brown states. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 59, 1612–1622 (2020)
Bebrov, G., Dimova, R.: Efficient quantum secure direct communication protocol based on quantum channel compression. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 59, 426–435 (2020)
Shu, J.: Quantum State Preparation and Quantum Information Processing in Cavity QED, pp. 19–20. University of science and technology of China, Heifei (2007)
Zheng, S.B., Guo, G.C.: Efficient scheme for two-atom entanglement and quantum information processing in cavity QED. Phys. Rev. Lett. 85, 2392–2395 (2000)
Zheng, S.B.: Generation of entangled states for many multilevel atoms in a thermal cavity and ions in thermal motion. Phys. Rev. A 68, 035801 (2003)
Shan, C.J., Liu, J.B., Chen, T., Liu, T.K., Huang, Y.X., Li, H.: Controlled quantum secure direct communication with local separate measurements in cavity QED. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 49, 334–342 (2010)
Shan, C.J., Liu, J.B., Cheng, W.W., Liu, T.K., Huang, Y.X., Li, H.: Bidirectional quantum secure direct communication in driven cavity QED. Mod. Phys. Lett. B 23, 3225–3234 (2009)
Shor, P.W., Preskill, J.: Simple proof of security of the BB84 quantum key distribution protocol. Phys. Rev. Lett. 85(2), 441–444 (2000)
Lin, J., Hwang, T.: An enhancement on Shi et al.’s multiparty quantum secret sharing protocol. Opt. Commun. 284(5), 1468–1471 (2011)
Chen, J.H., Lee, K.C., Hwang, T.: The enhancement of Zhou et al.’s quantum secret sharing protocol. Int. J. Mod. Phy. C 20(10), 1531–1535 (1999)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The author declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yin-Ju, L. A Novel Practical Quantum Secure Direct Communication Protocol. Int J Theor Phys 60, 1159–1163 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-021-04741-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-021-04741-z