Abstract
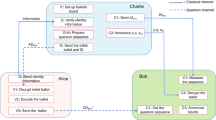
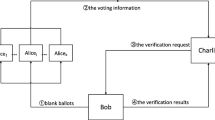
We propose a quantum voting scheme with Greenberger-Horne-Zeilinger (GHZ) states. In this scheme, quantum sequences that are formed by different particles of different GHZ states are sent to other participants respectively. Because of the correlation of different particles in a GHZ state, different participants perform a same measurement on each particle in the sequence that they received in order to obtain a same measurement outcome. To reduce the overhead of quantum transmissions, the participants publish their results on a bulletin board. According to the information on the bulletin board, voters can check whether their voting information is correct. If an attacker tampers with the voting information, his behavior can be discovered during the verification process. Analyses show that our new scheme has high efficiency and can withstand all the known attacks.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jan, J.K., Tai, C.C.: A secure electronic voting protocol with IC cards. J. Syst. Software. 39(12), 93–101 (1997)
Ku, W.C., Wang, S.D.: A secure and practical electronic voting scheme. Comput. Commun. 22(3), 279–286 (1999)
Hillery, M.: Quantum voting and privacy ptotection: first steps. Int. Soc. Opt. Eng. (2006)
Vaccaro, J.A., Spring, J., Chefles, A.: Quantum protocols for anonymous voting and surveying. Phys. Rev. A 75(1), 012333 (2007)
Tian, J.H., Zhang, J.Z., Li, Y.P.: A voting protocol based on the controlled quantum operation teleportation. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 55(5), 2303–2310 (2016)
Wen, X.J., Cai, X.J.: Secure quantum voting protocol. J. Shangdong Univ. (Natural Science) 46(9), 9–13 (2011)
Yi, Z., He, G.Q., Zeng, G.H.: Quantum voting protocol using two-mode squeezed states. Acta. Phys. Sin. 58(5), 3166–3172 (2009)
Horoshko, D., Kilin, S.: Quantum anonymous voting with anonymity check. Phys. Lett. A 375, 1172–1175 (2011)
Guo, F.Z., Qin, S.J., Wen, Q.Y., Zhu, F.C.: Cryptanalysis and improvement of two GHZ-State-Based QSDC protocols. Chinese Phys. Lett. 27(9), 090307 (2010)
Gao, F., Qin, S.J., Wen, Q.Y.: Cryptanalysis of multiparty controlled quantum secure direct communication using Greenberger-Horne-Zeilinger state. Opt. Commun. 283(1), 192–195 (2010)
Yang, Y.G., Wang, H.Y., Jia, X.: A quantum protocol for (t,n)-threshold identity authentication based on greenberger-horne-zeilinger states. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 52(2), 524–530 (2013)
Fan, L., Zhang, K.J., Qin, S.J.: A novel quantum blind signature scheme with four-particle GHZ states. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 55(2), 1028–1035 (2016)
Wang, T.Y., Wen, Q.Y., Chen, X.B.: Cryptanalysis and improvement of a multi-user quantum key distribution protocol. Opt. Commun. 283(24), 5261–5263 (2010)
Chen, X.B., et al.: Cryptanalysis of secret sharing with a single d-level quantum system. Quantum Inf. Process. 17, 225 (2018)
Jiang, D.H., Hu, Q.Z., Liang, X.Q., Xu, G.B.: A novel quantum multi-signature protocol based on locally indistinguishable orthogonal product states. Quantum Inf. Process. 18, 268 (2019)
Xia, Z.H., Wang, X.H., Zhang, L.G., et al.: A privacy-preserving and copy-deterrence content-based image retrieval scheme in cloud computing. IEEE. T. Inf. Foren. Sec. 11(11), 2594–2608 (2016)
Wang, T.Y., Li, Y.P., Zhang, R.L.: Analysis of counterfactual quantum certificate authorization. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 55(12), 5331–5335 (2016)
Cao, H.J., Ding, L.Y., Yu, Y.F., et al.: A electronic voting scheme achieved by using quantum proxy signature. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 55(9), 4081–4088 (2016)
Cao, H.J., Ding, L.Y., Jiang, X.L., Li, P.F.: A new proxy electronic voting scheme achieved by six-particle entangled states. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 57 (3), 674–681 (2018)
Zhang, J.L., Xie, S.C., Zhang, J.Z.: An elaborate secure quantum voting scheme. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 56(10), 3019–3028 (2017)
Jiang, D.H., Xu, Y.L., Xu, G.B.: Arbitrary quantum signature based on local indistinguishability of orthogonal product states. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 58 (3), 1036–1045 (2019)
Zhang, K.J., Zhang, X., Jia, H.Y., Zhang, L.: A new n-party quantum secret sharing model based on multiparty entangled states. Quantum Inf. Process. 18(3), 21 (2019)
Zhang, K.J., Zhang, L., Song, T.T., Yang, Y.H.: A potential application in quantum networks-Deterministic quantum operation sharing schemes with Bell states. Sci. China Phys. Mech. 59(6), 660302 (2016)
Chong, S.K., Tsai, C.W., Hwang, T.: Improvement on quantum key agreement protocol with maximally entangled states. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 50(6), 1793–1802 (2011)
Jiang, D.H., Wang, J., Liang, X.Q., et al.: Quantum voting scheme based on locally indistinguishable orthogonal product states. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 59, 436–444 (2020)
Lin, J., Hwang, T.: An enhancement on Shi et al.’s multiparty quantum secret sharing protocol. Opt. Commun. 284(5), 1468–1471 (2011)
Shi, W.M., Zhou, Y.H., Yang, Y.G.: A restricted quantum deniable authentication protocol applied in electronic voting system. Optik 142, 9–12 (2017)
Zhang, L., Sun, H.W., Zhang, K.J., Jia, H.Y.: An improved arbitrated quantum signature protocol based on the key-controlled chained CNOT encryption. Quantum Inf. Process. 16(3), 70 (2017)
Zhang, J.L., Zhang, J.Z., Xie, S.C.: A choreographed distributed electronic voting scheme. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 57(9), 2676–2686 (2018)
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundation (Grants No. ZR2019MF023), National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grants No. 61701343) and SDUST Research Fund.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Xu, GB. & Jiang, DH. Quantum Voting Scheme with Greenberger-Horne-Zeilinger States. Int J Theor Phys 59, 2599–2605 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-020-04529-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-020-04529-7