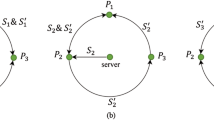
Abstract
Quantum key agreement (QKA) aims to negotiate a secure and consistent key among several participants. In this paper, we find that a type of QKA protocol is not secure when a participant is dishonest. He can make the honest participants obtain wrong final keys, which may lead to serious consequences. To resist such attacks, we design a defense strategy by introducing a trusted third party. The theoretical analysis results show that our defense strategy not only can detect the dishonest participant’s attacks, but also can identify who is dishonest. Finally we design an optical platform for participants, and show that both our attack and defense strategies are feasible with current technologies.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bennett, C.H., Brassard, G.: Quantum cryptography: public key distribution and coin tossing. In: Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Computers, Systems, and Signal processing, pp 175–179, Bangalore (1984)
Deng, F.G., Long, G.L.: Secure direct communication with a quantum one-time pad. Phys. Rev. A 69(5), 052319 (2004)
Guo, G.P., Guo, G.C.: Quantum secret sharing without entanglement. Phys. Lett. A 310(4), 247–251 (2003)
Jiang, D., Chen, Y., Gu, X., Xie, L., Chen, L.: Deterministic secure quantum communication using a single d-level system. Sci. Rep. 7, 44934 (2017)
Lo, H.K., Ma, X., Chen, K.: Decoy state quantum key distribution. Int. J. Quant. Inf. 3(supp01), 143–143 (2008)
Cerf, N.J., Bourennane, M., Karlsson, A., Gisin, N.: Security of quantum key distribution using d-level systems. Phys. Rev. Lett. 88(12), 127902 (2002)
Curty, M., Xu, F., Cui, W., Lim, C.C.W., Tamaki, K., Lo, H.K.: Finite-key analysis for measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution. Nat. Commun. 5, 3732 (2014)
Tomamichel, M., Lim, C.C.W., Gisin, N., Renner, R.: Tight finite-key analysis for quantum cryptography. Nat. Commun. 3, 634 (2012)
Gordon, K.J., Fernandez, V., Buller, G.S., Rech, I., Cova, S.D., Townsend, P.D.: Quantum key distribution system clocked at 2 GHz. Opt. Express 13(8), 3015–3020 (2005)
Schmitt-Manderbach, T., Weier, H., Fürst, M., Ursin, R., Tiefenbacher, F., Scheidl, T., et al.: Experimental demonstration of free-space decoy-state quantum key distribution over 144 km. Phys. Rev. Lett. 98(1), 010504 (2007)
Wang, S., Chen, W., Guo, J.F., Yin, Z.Q., Li, H.W., Zhou, Z., Guo, G.C., Han, Z.F.: 2 GHz clock quantum key distribution over 260 km of standard telecom fiber. Opt. Lett. 37(6), 1008–1010 (2012)
Zhou, N., Zeng, G., Xiong, J.: Quantum key agreement protocol. Electron. Lett. 40(18), 1149–1150 (2004)
Chong, S.K., Hwang, T.: Quantum key agreement protocol based on BB84. Opt. Commun. 283(6), 1192–1195 (2010)
Shi, R.H., Zhong, H.: Multi-party quantum key agreement with bell states and bell measurements. Quant. Inf. Process 12(2), 921–932 (2013)
Shukla, C., Alam, N., Pathak, A.: Protocols of quantum key agreement solely using Bell states and Bell measurement. Quant. Inf. Process. 13(11), 2391–2405 (2014)
Zhu, Z.C., Hu, A.Q., Fu, A.M.: Improving the security of protocols of quantum key agreement solely using bell states and bell measurement. Quant.Inf. Process 42(4), 1–10 (2017)
Gu, J., Hwang, T.: Improvement of “Novel Multiparty Quantum Key Agreement Protocol with GHZ States”. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 56(10), 1–9 (2017)
Cao, H., Ma, W.: Multi-party traveling-mode quantum key agreement protocols immune to collusive attack. Quantum Inf. Process 17(9), 219 (2018)
Cao, H., Ma, W.: Efficient multi-party quantum key agreement protocol based on nonorthogonal quantum entangled pairs. Laser Phys. Lett. 15(9), 095201 (2018)
Cao, H., Ma, W.: Multiparty quantum key agreement based on quantum search algorithm. Sci. Rep. 7, 45046 (2017)
Liu, B., Gao, F., Huang, W., Wen, Q.Y.: Multiparty quantum key agreement with single particles. Quantum Inf. Process 12(4), 1797–1805 (2013)
Yu, K.F., Yang, C.W., Hwang, T., Li, C.M., Gu, J.: Design of quantum key agreement protocols with strong fairness property. arXiv:quant-ph/1510.02353v2 (2017)
Zhu, Z.C., Hu, A.Q., Fu, A.M.: Improving the security of protocols of quantum key agreement solely using bell states and bell measurement. Quantum Inf. Process 42 (4), 1–10 (2017)
He, Y.F., Ma, W.P.: Two-party quantum key agreement with five-particle entangled states. Int. J,. Quant. Inf. 15(3), 1750018 (2017)
Cai, T., Jiang, M., Cao, G.: Multi-party quantum key agreement with five-qubit brown states [J]. Quantum Inf. Process 17(5), 103 (2018)
Min, S.Q., Chen, H.Y., Gong, L.H.: Novel multi-party quantum key agreement protocol with G-like States and Bell States. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 57(6), 1811–1822 (2018)
Wang, S.S., Xu, G.B., Liang, X.Q., Wu, Y.L.: Multiparty quantum key agreement with four-qubit symmetric W state. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 57(12), 3716–3726 (2018)
Yin, X.R., Ma, W.P.: Multiparty quantum key agreement based on three-photon entanglement with unidirectional qubit transmission. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 58(2), 631–638 (2019)
Zhao, X.Q., Zhou, N.R., Chen, H.Y., Gong, L.H.: Multiparty quantum key agreement protocol with entanglement swapping. Int. J. Theor. Phys., 1–15 (2018)
Huang, W., Su, Q., Liu, B., He, Y.H., Fan, F., Xu, B.J.: Efficient multiparty quantum key agreement with collective detection. Sci. Rep. 7(1), 15264 (2017)
Abulkasim, H., Farouk, A., Alsuqaih, H., Hamdan, W., Hamad, S., Ghose, S.: Improving the security of quantum key agreement protocols with single photon in both polarization and spatial-mode degrees of freedom. Quant. Inf. Process 17(11), 316 (2018)
Sun, Z., Zhang, C., Wang, B., Li, Q., Long, D.: Improvements on “multiparty quantum key agreement with single particles”. Quant. Inf. Process 12(11), 3411–3420 (2013)
Deng, F.G., Li, X.H., Zhou, H.Y., Zhang, Z.j.: Improving the security of multiparty quantum secret sharing against trojan horse attack. Phys. Rev. A 72(4), 044302 (2005)
Lin, S., Guo, G.D., Xu, Y.Z., Sun, Y., Liu, X.F.: Cryptanalysis of quantum secret sharing with d-level single particles. Phys. Rev. A 93(6), 062343 (2016)
Shor, P.W., Preskill, J.: Simple proof of security of the bb84 quantum key distribution protocol. Phys. Rev. Lett. 85(2), 441–444 (2000)
Gao, G.: Two quantum dialogue protocols without information leakage. Opt. Commun. 283(10), 2288–2293 (2010)
Shi, G.F., Xi, X.Q., Tian, X.L., Yue, R.H.: Bidirectional quantum secure communication based on a shared private bell state. Opt. Commun. 282(12), 2460–2463 (2009)
Xiu, X.M., Dong, H.K., Dong, L., Gao, Y.J., Chi, F.: Deterministic secure quantum communication using four-particle genuine entangled state and entanglement swapping. Opt. Commun. 282(12), 2457–2459 (2009)
Nguyen, B.A.: Quantum exam. Phys. Lett. A 350(3), 174–178 (2006)
Qin, S.J., Gao, F., Guo, F.Z., Wen, Q.Y.: Comment on “two-way protocols for quantum cryptography with a nonmaximally entangled qubit pair”. Phys. Rev. A 82(82), 036301 (2010)
Acknowledgements
This research is financially supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (NO. 2017YFA0303700), the Major Program of National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 11690030, 11690032), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 61771236), and the Excellence Research Program of Nanjing University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, Wc., Yang, Yk., Jiang, D. et al. Designing Secure Quantum Key Agreement Protocols Against Dishonest Participants. Int J Theor Phys 58, 4093–4104 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-019-04275-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-019-04275-5