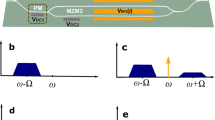
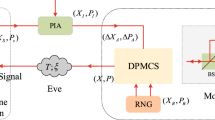
Abstract
How to remove local oscillator (LO) side channel attacks has been a notoriously hard problem in continuous-variable quantum key distribution (CV-QKD). In the self-referenced CV-QKD schemes, the LO signal is locally generated at the receiver by an independent laser so that it is not co-transmitted with the quantum signal. This simple solution removes all LO side channels. However it also introduces some other practical vulnerabilities. Especially the polarization states of the quantum signal and LO signal may not be identical across the detector because of the presence of the polarization aberrations. Thus, the detection efficiency which is arguably the most critical experiment parameter of the practical implementation will be impaired. In this paper, we analyze the impact of polarization aberrations on the detection efficiency for CV-QKD and propose a self-referenced CV-QKD scheme in the presence of polarization aberrations by using an off-axis optical system. In the proposed scheme, the polarization states of the quantum signal would change with the off-axis optical system, thus impairing the heterodyne efficiency. Our security analysis shows a gap between the theory and practice of CV-QKD.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bennett, C.H., Brassard, G.: Quantum cryptography: public key distribution and coin tossing. In: Proc. of the IEEE Int. Conf. on Computers, Systems and Signal Processing, pp. 175–179. IEEE Press, New York (1984)
Yuen, H.P.: Security of quantum key distribution. IEEE Access 4, 724–749 (1998)
Zhou, N.R., Wang, L.J., Ding, J., Gong, L.H., Zuo, X.W.: Novel quantum deterministic key distribution protocols with entangled states. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 49, 2035–2044 (2010)
He, G.Q., Zhu, S.W., Guo, H.B., Zeng, G.H.: Security of quantum key distribution using two-mode squeezed states against optimal beam splitter attack. Chin. Phys. B 17, 1263–1268 (2008)
Gong, L.H., Song, H.C., He, C.S., Liu, Y., Zhou, N.R.: A continuous variable quantum deterministic key distribution based on two-mode squeezed states. Phys. Scr. 89, 035101 (2014)
Gong, L.H., Li, J.F., Zhou, N.R.: Continuous variable quantum network dialogue protocol based on single-mode squeezed states. Laser Phys. Lett. 15, 105204 (2018)
Huang, P., He, G.Q., Fang, J., Zeng, G.H.: Performance improvement of continuous-variable quantum key distribution via photon subtraction. Phys. Rev. A 87, 530–537 (2013)
Gong, L.H., Tian, C., Li, J.F., Zou, X.F.: Quantum network dialogue protocol based on continuous variable GHZ states. Quantum Inf. Process 17, 331 (2018)
Huang, P., Huang, J.Z., Wang, T., Li, H.S., Huang, D., Zeng, G.H.: Robust continuous-variable quantum key distribution against practical attacks. Phys. Rev. A 95, 052302 (2017)
Guo, Y., Xie, C.L., Liao, Q., Zhao, W., Huang, D.: Entanglement-distillation attack on continuous-variable quantum key distribution in a turbulent atmospheric channel. Phys. Rev. A 96, 022320 (2017)
Guo, Y., Liao, Q., Wang, Y.J., Huang, D., Huang, P., Zeng, G.H.: Performance improvement of continuous-variable quantum key distribution with an entangled source in the middle via photon subtraction. Phys. Rev. A 95, 032304 (2017)
Liao, Q., Wang, Y.J., Huang, D., Guo, Y.: Dual-phase-modulated plug-and-play measurement-device-independent continuous-variable quantum key distribution. Opt. Express 26, 19907 (2018)
Weedbrook, C., Lance, A.M., Bowen, W.P., Symul, T., Ralph, T.C., Lam, P.K.: Quantum cryptography without switching. Phys. Rev. Lett. 93, 170504 (2004)
Weedbrook, C., Lance, A.M., Bowen, W.P., Symul, T., Ralph, T.C., Lam, P.K.: Coherent-state quantum key distribution without random basis switching. Phys. Rev. A 73, 022316 (2006)
Grosshans, F.: Collective attacks and unconditional security in continuous variable quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. Lett. 94, 020504 (2005)
Navascués, M., Grosshans, F., Acín, A.: Optimality of Gaussian attacks in continuous-variable quantum cryptography. Phys. Rev. Lett. 97, 190502 (2006)
García-Patrón, R., Cerf, N.J.: Unconditional optimality of Gaussian attacks against continuous-variable quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. Lett. 97, 190503 (2006)
Qin, H., Kumar, R., Alléaume, R.: Quantum hacking: saturation attack on practical continuous-variable quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 94, 012325 (2016)
Braunstein, S.L., Pirandola, S.: Side-channel-free quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. Lett. 108, 130502 (2012)
Pirandola, S., Ottaviani, C., Spedalieri, G., Weedbrook, C., Braunstein, S.L., Gehring, T., Jacobsen, C.S., Andersen, U.L.: Reply to discrete and continuous variables for measurement-device-independent quantum cryptography. Nature Photon. 9, 773–775 (2015)
Soh, D.B.S., Brif, C., Coles, P.J., Lutkenhaus, N., Camacho, R.M., Urayama, J., Sarovar, M.: Self-referenced continuous-variable quantum key distribution protocol. Phys. Rev. X 5, 041010 (2015)
Yang, Y., Yan, C.X., Hu, C.H., Wu, C.J.: Modified heterodyne effociency for coherent laser communication in the presence of polarization aberrations. Opt. Express 25, 7567–7591 (2017)
Yun, G., Crabtree, K., Chipman, R.A.: Skew aberration: a form of polarization aberration. Opt. Lett. 36, 4062–4064 (2011)
McIntyre, G.R., Kye, J., Levinson, H., Neureuther, A.R.: Polarization aberrations in hyper-numericalaperture projection printing: a comparison of various representations. J. Microlith. Microfab. Microsyst. 5, 033001 (2006)
Fink, D.: Coherent detection signal-to-noise. Appl. Opt. 14, 689–690 (1975)
Yun, G., Crabtree, K., Chipman, R.A.: Three-dimensional polarization ray-tracing calculus i: definition and diattenuation. Appl. Opt. 50, 2855–2865 (2011)
Yun, G., McClain, S.C., Chipman, R.A.: Three-dimensional polarization ray-tracing calculus II: retardance. Appl. Opt. 50, 2866–2874 (2011)
Ruoff, J., Totzeck, M.: Orientation Zernike polynomials: a useful way to describe the polarization effects of optical imaging systems. JM3 8, 031404 (2009)
Yamamoto, N., Kye, J., Levison, H.J.: Polarization aberration analysis using Pauli-Zernike representation. In: Conference on Optical Microlithography XX, p 65200Y. SPIE, California (2007)
Yang, Y., Yan, C.: Polarization property analysis of a periscopic scanner with three-dimensional polarization ray-tracing calculus. Appl. Opt. 55, 1343–1350 (2016)
Tanaka, K., Ohta, N.: Effects of tilt and offset of signal field on heterodyne efficiency. Appl. Opt. 26, 627–632 (1987)
Leverrier, A., Grosshans, F., Grangier, P.: Finite-size analysis of a continuous-variable quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 81, 062343 (2010)
Scarani, V., Renner, R.: Quantum cryptography with finite resources: unconditional security bound for discrete variable protocols with one-way postprocessing. Phys. Rev. Lett. 100, 200501 (2008)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities of Central South University (Grant No. 2018zzts533), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 61871407, 61572529), and the Natural Science Foundation of the Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions of China (Grant No. 18KJB510045).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J., Li, S., Guo, Y. et al. Practical Security Analysis of Self-Referenced CV-QKD System in the Presence of Polarization Aberration. Int J Theor Phys 58, 2091–2105 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-019-04101-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-019-04101-y