Abstract
The novel emerging technology, QCA technology, is a candidate for replacing CMOS technology. Full Adder (FA) circuits are also widely used circuits in arithmetic circuits design. In this paper, two new multilayer QCA architectures are presented: one-bit FA and 4-bit Ripple Carry Adder (RCA). The designed one-bit multilayer FA architecture is based on a new XOR gate architecture. The designed 4-bit multilayer QCA RCA is also developed based on the designed one-bit multilayer QCA FA. The functionality of the designed architectures are verified using QCADesigner tool. The results indicate that the designed architecture for 4-bit multilayer QCA RCA requires 5 clock phases, 125 QCA cells, and 0.17 μm2 area. The comparison results confirm that the designed architectures provide improvements compared with other adder architectures in terms of cost, cell count, and area.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Compano, R., Molenkamp, L., Paul, D.: Roadmap for nanoelectronics. European commission IST programme, future and emerging technologies (2000)
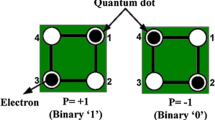
Lent, C.S., Tougaw, P.D., Porod, W., Bernstein, G.H.: Quantum cellular automata. Nanotechnology. 4(1), 49–57 (1993)
Lent, C.S., Tougaw, P.D.: A device architecture for computing with quantum dots. Proc. IEEE. 85(4), 541–557 (1997)
Balali, M., Rezai, A., Balali, H., Rabiei, F., Emadi, S.: A novel design of 5-input majority gate in quantum-dot cellular automata technology. In: Computer Applications & Industrial Electronics (ISCAIE), 2017 IEEE Symposium on 2017, Pp. 13–16. IEEE (2017)
Rashidi, H., Rezai, A.: Design of novel efficient multiplexer architecture for quantum-dot cellular automata. J. Nano- Electron. Phys. 9(1), 1012–1011 (2017)
Rashidi, H., Rezai, A.: High-performance full adder architecture in quantum-dot cellular automata. J. Eng. 1(1), (2017)
Mokhtari, D., Rezai, A., Rashidi, H., Rabiei, F., Emadi, S., Karimi, A.: Design of novel efficient full adder architecture for quantum-dot cellular automata technology. Facta Univ. Ser.: Electron. Energ. (FU Elec. Energ). 31(2), 279–285 (2018)
Balali, M., Rezai, A., Balali, H., Rabiei, F., Emadi, S.: Towards coplanar quantum-dot cellular automata adders based on efficient three-input XOR gate. Results Phys. 7, 1389–1395 (2017)
Mohammadi, M., Mohammadi, M., Gorgin, S.: An efficient design of full adder in quantum-dot cellular automata (QCA) technology. Microelectron. J. 50, 35–43 (2016)
Roohi, A., DeMara, R.F., Khoshavi, N.: Design and evaluation of an ultra-area-efficient fault-tolerant QCA full adder. Microelectron. J. 46(6), 531–542 (2015)
Navi, K., Farazkish, R., Sayedsalehi, S., Azghadi, M.R.: A new quantum-dot cellular automata full-adder. Microelectron. J. 41(12), 820–826 (2010)
Hashemi, S., Tehrani, M., Navi, K.: An efficient quantum-dot cellular automata full-adder. Sci. Res. Essays. 7(2), 177–189 (2012)
Rashidi, H., Rezai, A., Soltany, S.: High-performance multiplexer architecture for quantum-dot cellular automata. J. Comput. Electron. 15(3), 968–981 (2016)
Niknezhad Divshali, M., Rezai, A., Karimi, A.: Towards multilayer QCA SISO shift register based on efficient D-FF circuits. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 57, 3326–3339 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-018-3846-8
Ahmad, F., Bhat, G.M., Ahmad, P.Z.: Novel adder circuits based on quantum-dot cellular automata (QCA). Circuits Syst. 5(06), 142–152 (2014)
Arani, I.E., Rezai, A.: Novel circuit design of serial–parallel multiplier in quantum-dot cellular automata technology. J. Comput. Electron. 1–9 (2018)
Ahmad, F., Bhat, G.M., Khademolhosseini, H., Azimi, S., Angizi, S., Navi, K.: Towards single layer quantum-dot cellular automata adders based on explicit interaction of cells. J. Comput. Sci. 16, 8–15 (2016)
Balali, M., Rezai, A.: Design of low-complexity and high-speed coplanar four-bit ripple carry adder in QCA technology. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 1–13 (2018)
Sheikhfaal, S., Angizi, S., Sarmadi, S., Moaiyeri, M.H., Sayedsalehi, S.: Designing efficient QCA logical circuits with power dissipation analysis. Microelectron. J. 46(6), 462–471 (2015)
Mustafa, M., Beigh, M.: Design and implementation of quantum cellular automata based novel parity generator and checker circuits with minimum complexity and cell count. (2013)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roshany, H.R., Rezai, A. Novel Efficient Circuit Design for Multilayer QCA RCA. Int J Theor Phys 58, 1745–1757 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-019-04069-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-019-04069-9