Abstract
We propose an entanglement purification protocol (EPP) for purifying separate atoms embedded in single-sided optical cavities. The protocol works in an error-detected pattern, the reflection coefficients only appear as a global coefficient, the success or failure cases are heralded by the detection of photons, these merits make the protocol more robust and practical. We discuss the performance of the protocol with current experimental parameters, the results show the success probability of the present EPP is relatively high. The EPP could provide a promising building block for quantum repeaters and quantum networks in the future.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nielsen, M.A., Chuang, I.L.: Quantum computation and quantum information. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2000)
Sheng, Y.B., Zhou, L.: Distributed secure quantum machine learning. Sci. Bull. 62, 1025 (2017)
Briegel, H.J., Dur, W., Cirac, J.I., Zoller, P.: Quantum repeaters: the role of imperfect local operations in quantum communication. Phys. Rev. Lett. 81, 5932 (1998)
Niu, P.H., Zhou, Z.R., Lin, Z.S., Sheng, Y.B., Yin, L.G., Long, G.L.: Measurement-device-independent quantum communication without encryption. Sci. Bull. 63, 1345 (2018)
Bennett, C.H., Brassard, G., Mermin, N.D.: Quantum cryptography without Bell’s theorem. Phys. Rev. Lett. 68, 557–559 (1992)
Deng, F.G., Li, X.H., Li, C.Y., Zhou, P., Zhou, H.Y.: Multiparty quantum-state sharing of an arbitrary two-particle state with Einstein-Podolsky-Rosen pairs. Phys. Rev. A 72, 044301 (2005)
Deng, F.G., Li, C.Y., Li, Y.S., Zhou, H.Y., Wang, Y.: Symmetric multiparty-controlled teleportation of an arbitrary two-particle entanglement. Phys. Rev. A 72, 022338 (2005)
Deng, F.G., Li, X.H., Li, C.Y., Zhou, P., Zhou, H.Y.: Quantum state sharing of an arbitrary two-qubit state with two-photon entanglements and Bell-state measurements. Eur. Phys. J. D 39, 459–464 (2006)
Ekert, A.K.: Quantum cryptography based on Bell’s theorem. Phys. Rev. Lett. 67, 661–663 (1991)
Deng, F.G., Long, G.L.: Controlled order rearrangement encryption for quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 68, 042315 (2003)
Li, X.H., Deng, F.G., Zhou, H.Y.: Efficient quantum key distribution over a collective noise channel. Phys. Rev. A 78, 022321 (2008)
Long, G.L., Liu, X.S.: Theoretically efficient high-capacity quantum-key-distribution scheme. Phys. Rev. A 65, 032302 (2002)
Deng, F.G., Long, G.L., Liu, X.S.: Two-step quantum direct communication protocol using the Einstein-Podolsky-Rosen pair block. Phys. Rev. A 68, 042317 (2003)
Wang, C., Deng, F.G., Li, Y.S., Liu, X.S., Long, G.L.: Quantum secure direct communication with high-dimension quantum superdense coding. Phys. Rev. A 71, 044305 (2005)
Zhang, W., Ding, D.S., Sheng, Y.B., Zhou, L., Shi, B.S., Guo, G.C.: Quantum secure direct communication with quantum memory. Phys. Rev. Lett. 118, 220501 (2017)
Wu, F.Z., Yang, G.J., Wang, H.B., Xiong, J., Alzahrani, F., Hobiny, A., Deng, F.G.: High-capacity quantum secure direct communication with two-photon six-qubit hyperentangled states. Sci. China-Phys. Mech. Astron. 60, 120313 (2018)
Chen, S.S., Zhou, L., Zhong, W., Sheng, Y.B.: Three-step three-party quantum secure direct communication. Sci. China-Phys. Mech. Astron. 61, 090312 (2018)
Bennett, C.H., Bernstein, H.J., Popescu, S., Schumacher, B.: Concentrating partial entanglement by local operations. Phys. Rev. A 53, 2046–2052 (1996)
Zhao, Z., Pan, J.W., Zhan, M.S.: Practical scheme for entanglement concentration. Phys. Rev. A 64, 014301 (2001)
Yamamoto, T., Koashi, M., Imoto, N.: Concentration and purification scheme for two partially entangled photon pairs. Phys. Rev. A 64, 012304 (2001)
Sheng, Y.B., Deng, F.G., Zhou, H.Y.: Nonlocal entanglement concentration scheme for partially entangled multipartite systems with nonlinear optics. Phys. Rev. A 77, 062325 (2008)
Sheng, Y.B., Zhou, L., Zhao, S.M., Zheng, B.Y.: Efficient single-photon-assisted entanglement concentration for partially entangled photon pairs. Phys. Rev. A 85, 012307 (2012)
Deng, F.G.: Optimal nonlocal multipartite entanglement concentration based on projection measurements. Phys. Rev. A 85, 022311 (2012)
Ren, B.C., Du, F.F., Deng, F.G.: Hyperentanglement concentration for two-photon four-qubit systems with linear optics. Phys. Rev. A 88, 012302 (2013)
Ren, B.C., Long, G.L.: General hyperentanglement concentration for photon systems assisted by quantum dot spins inside optical microcavities. Opt. Express 22, 6547–6561 (2014)
Ren, B.C., Long, G.L.: Highly efficient hyperentanglement concentration with two steps assisted by quantum swap gates. Sci. Rep. 5, 16444 (2015)
Ren, B.C., Wang, H., Alzahrani, F., Hobiny, A., Deng, F.G.: Hyperentanglement concentration of nonlocal two-photon six-qubit systems with linear optics. Ann. Phys. 385, 86–94 (2017)
Bennett, C.H., Brassard, G., Popescu, S., Schumacher, B., Smolin, J.A., Wootters, W.K.: Purification of noisy entanglement and faithful teleportation via noisy channels. Phys. Rev. Lett. 76, 722–725 (1996)
Deutsch, D., Ekert, A., Jozsa, R., Macchiavello, C., Popescu, S., Sanpera, A.: Quantum privacy amplification and the security of quantum cryptography over noisy channels. Phys. Rev. Lett. 77, 2818–2821 (1996)
Fujii, K., Yamamoto, K.: Entanglement purification with double selection. Phys. Rev. A 80, 042308 (2009)
Pan, J.W., Simon, C., Brukner, C., Zeilinger, A.: Entanglement purification for quantum communication. Nature (London) 410, 1067–1070 (2001)
Simonm, C., Pan, J.W.: Polarization entanglement purification using spatial entanglement. Phys. Rev. Lett. 89, 257901 (2002)
Cirac, J.I., Ekert, A.K., Macchiavello, C.: Optimal purification of single qubits. Phys. Rev. Lett. 82, 4344 (1999)
Dür, W., Aschauer, H., Briegel, H.J.: Multiparticle entanglement purification for graph states. Phys. Rev. Lett. 91, 107903 (2003)
Goyal, K., McCauley, A., Raussendorf, R.: Purification of large bicolorable graph states. Phys. Rev. A 74, 032318 (2006)
Pan, J.W., Gasparonl, S., Ursin, R., Weihs, G., Zellinger, A.: Experimental entanglement purification of arbitrary unknown states. Nature (London) 423, 417–422 (2003)
Sheng, Y.B., Deng, F.G., Zhou, H.Y.: Efficient polarization-entanglement purification based on parametric down-conversion sources with cross-Kerr nonlinearity. Phys. Rev. A 77, 042308 (2008)
Wang, C., Zhang, Y., Jin, G.S.: Polarization-entanglement purification and concentration using cross-Kerr nonlinearity. Quantum Inf. Comput. 11, 988–1002 (2011)
Cao, C., Wang, C., He, L.Y., Zhang, R.: Polarization-entanglement purification for ideal sources using weak cross-Kerr nonlinearity. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 52, 1265–1273 (2013)
Deng, F.G.: Efficient multipartite entanglement purification with the entanglement link from a subspace. Phys. Rev. A 84, 052312 (2011)
Sheng, Y.B., Deng, F.G.: Deterministic entanglement purification and complete nonlocal Bell-state analysis with hyperentanglement. Phys. Rev. A 81, 032307 (2010)
Sheng, Y.B., Deng, F.G.: One-step deterministic polarization-entanglement purification using spatial entanglement. Phys. Rev. A 82, 044305 (2010)
Li, X.H.: Deterministic polarization-entanglement purification using spatial entanglement. Phys. Rev. A 82, 044304 (2010)
Deng, F.G.: One-step error correction for multipartite polarization entanglement. Phys. Rev. A 83, 062316 (2011)
Sheng, Y.B., Zhou, L.: Deterministic entanglement distillation for secure double-server blind quantum computation. Sci. Rep. 5, 7815 (2015)
Sheng, Y.B., Zhou, L.: Deterministic polarization entanglement purification using time-bin entanglement. Laser Phys. Lett. 11, 085203 (2014)
Ren, B.C., Du, F.F., Deng, F.G.: Two-step hyperentanglement purification with the quantum-state-joining method. Phys. Rev. A 90, 052309 (2014)
Wang, T.J., Liu, L.L., Zhang, R., Cao, C., Wang, C.: One-step hyperentanglement purification and hyperdistillation with linear optics. Opt. Express 23, 9284–9294 (2015)
Wang, G.Y., Liu, Q., Deng, F.G.: Hyperentanglement purification for two-photon six-qubit quantum systems. Phys. Rev. A 94, 032319 (2016)
Zhou, L., Sheng, Y.B.: Purification of logic-qubit entanglement. Sci. Rep. 6, 28813 (2016)
Zhou, L., Sheng, Y.B.: Polarization entanglement purification for concatenated Greenberger-Horne-Zeilinger state. Ann. Phys. 385, 10 (2017)
Wu, X.D., Zhou, L., Zhong, W., Sheng, Y.B.: Purification of the concatenated Greenberger-Horne-Zeilinger state with linear optics. Quantum Inf. Process. 17, 255 (2018)
Cao, C., Wang, C., He, L.Y., Zhang, R.: Atomic entanglement purification and concentration using coherent state input-output process in low-Q cavity QED regime. Opt. Express 21, 4093–4105 (2013)
Wang, C., Zhang, Y., Zhang, R.: Entanglement purification based on hybrid entangled state using quantum-dot and microcavity coupled system. Opt. Express 19, 25685–25695 (2011)
Wang, C., Zhang, Y., Jin, G.S.: Entanglement purification and concentration of electron-spin entangled states using quantum-dot spins in optical microcavities. Phys. Rev. A 84, 032307 (2011)
Wang, C., Zhang, Y., Jin, G.S., Zhang, R.: Efficient entanglement purification of separate nitrogen-vacancy centers via coupling to microtoroidal resonators. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 29, 3349–3354 (2012)
Steane, A.M.: Overhead and noise threshold of fault-tolerant quantum error correction. Phys. Rev. A 68, 042322 (2003)
Jones, N.C., Van Meter, R., Fowler, A.G., McMahon, P.L., Kim, J., Ladd, T.D., Yamamoto, Y.: Layered architecture for quantum computing. Phys. Rev. X 2, 031007 (2012)
Knill, E.: Quantum computing with realistically noisy devices. Nature (London) 434, 39–44 (2005)
Li, Y., Aolita, L., Chang, D.E., Kwek, L.C.: Robust-fidelity atom-photon entangling gates in the weak-coupling regime. Phys. Rev. Lett. 109, 160504 (2012)
Li, T., Deng, F.G.: Error-rejecting quantum computing with solid-state spins assisted by low-Q optical microcavities. Phys. Rev. A 94, 062310 (2016)
Li, T., Yang, G J., Deng, F.G.: Heralded quantum repeater for a quantum communication network based on quantum dots embedded in optical microcavities. Phys. Rev. A 93, 012302 (2016)
Li, T., Deng, F.G.: Heralded high-efficiency quantum repeater with atomic ensembles assisted by faithful single-photon transmission. Sci. Rep. 5, 15610 (2015)
Wang, G.Y., Ai, Q., Ren, B.C., Li, T., Deng, F.G.: Error-detected generation and complete analysis of hyperentangled Bell states for photons assisted by quantum-dot spins in double-sided optical microcavities. Opt. Express 24, 28444–28458 (2016)
Jiang, Y., Guo, L.P., Gao, C.Y., Wang, H.B., Alzahrani, F., Hobiny, A., Deng, F.G.: Self-error-rejecting photonic qubit transmission in polarization-spatial modes with linear optical elements. Sci. China-Phys. Mech. Astron. 60, 120312 (2017)
Duan, L.M., Wang, B., Kimble, H.J.: Scalable photonic quantum computation through cavity-assisted interactions. Phys. Rev. Lett. 92, 127902 (2004)
An, J.H., Feng, M., Oh, C.H.: Quantum-information processing with a single photon by an input-output process with respect to low-Q cavities. Phys. Rev. A 79, 032303 (2009)
Chen, Q., Yang, W.L., Feng, M., Du, J.F.: Entangling separate nitrogen-vacancy centers in a scalable fashion via coupling to microtoroidal resonators. Phys. Rev. A 83, 054305 (2011)
Hu, C.Y., Young, A., O’Brien, J.L., Munro, W.J., Rarity, J.G.: Giant optical Faraday rotation induced by a single-electron spin in a quantum dot: applications to entangling remote spins via a single photon. Phys. Rev. B 78, 085307 (2008)
Lin, X.M., Zhou, Z.W., Ye, M.Y., Xiao, Y.F., Guo, G.C.: One-step implementation of a multiqubit controlled-phase-flip gate. Phys. Rev. A 73, 012323 (2006)
Walls, D.F., Milburn, G.J.: Quantum optics. Springer, Berlin (1994)
Loo, V., Lanco, L., Lematire, A., Sagnes, I., Krebs, O., Voisin, P., Senellart, P.: Quantum dot-cavity strong-coupling regime measured through coherent reflection spectroscopy in a very high-Q micropillar. Appl. Phys. Lett. 97, 241110 (2010)
Cao, C., Liu, X.H., Duan, Y.W., Chen, X., Zhang, R.: Entanglement concentration of unknown states on separate nitrogen-vacancy centers via error-detected entanglement swapping. Laser Phys. 27, 055202 (2017)
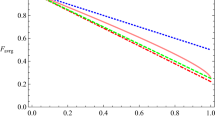
Although, Alice and Bob cannot distinguish the outcomes of the single-photon measurements with each other in these situations, if the atoms are preserved, after this entanglement purification process, the new fidelity of the atomic qubits that was kept becomes \(F^{\prime }=F^{2}(8\nu ^{2}+ 2\tau ^{2})/[F^{2}(8\nu ^{2}+ 2\tau ^{2})+ 16F(1-F)\nu ^{2}+(1-F)^{2}(8\nu ^{2}+ 2\tau ^{2})]\). Under the ideal situation, i.e., η = 1,Δ = 0, λ 2 ≫ κ γ, this equation reduces to (23). So the atoms are discarded. This would decrease the success probability of the present EPP but increase the fidelity of the EPP
Buck, J.R., Kimble, H.J.: Optimal sizes of dielectric microspheres for cavity QED with strong coupling. Phys. Rev. A 67, 033806 (2003)
Reithmaier, J.P., Sek, G., Loffler, A., Hofmann, C., Kuhn, S., Reitzenstein, S., Keldysh, L. V., Kulakovskii, V.D., Reinecke, T.L., Forchel, A.: Strong coupling in a single quantum dot-semiconductor microcavity system. Nature (London) 432, 197 (2004)
Dayan, B., Parkins, A.S., Aoki, T., Ostby, E.P., Vahala, K.I., Kimble, H.J.: A photon turnstile dynamically regulated by one atom. Science 319, 1062 (2008)
Maunz, P., Puppe, T., Schuster, I., Syassen, N., Pinkse, P.W.H., Rempe, G.: Normal-mode spectroscopy of a single-bound-atom-cavity system. Phys. Rev. Lett. 94, 033002 (2005)
Law, C.K., Eberly, J.H.: Synthesis of arbitrary superposition of Zeeman states in an atom. Opt. Express 2, 368–371 (1998)
Law, C.K., Eberly, J.H.: Arbitrary control of a quantum electromagnetic field. Phys. Rev. Lett. 76, 1055–1058 (1996)
Bergmann, K., Theuer, H., Shore, B.W.: Coherent population transfer among quantum states of atoms and molecules. Rev. Mod. Phys. 70, 1003–1025 (1998)
Vitanov, N.V., Suominen, K.A., Shore, B.W.: Creation of coherent atomic superpositions by fractional stimulated Raman adiabatic passage. J. Phys. B 32, 4535–4546 (1999)
Young, A.B., Thijssen, A.C.T., Beggs, D.M., Androvitsaneas, P., Kuipers, L., Rarity, J.G., Hughes, S., Oulton, R.: Polarization engineering in photonic crystal waveguides for spin-photon entanglers. Phys. Rev. Lett. 115, 153901 (2015)
Acknowledgments
We thank Li-Li Sun for helpful discussions. This work is supported by the Scientific Research Foundation of Shanxi Institute of Technology No. 201706001, the Fund for Shanxi “1331 Project” Key Subjects Construction, the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation under Grant No. 2017M612411, the Education Department Foundation of Henan Province Under Grant No. 18A140009, and the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grants No. 61821280, 11604190 and No. 61465013.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, AP., Guo, Q., Su, SL. et al. Entanglement Purification on Separate Atoms in an Error-Detected Pattern. Int J Theor Phys 58, 1404–1417 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-019-04030-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-019-04030-w