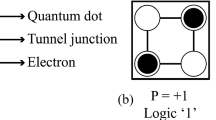
Abstract
Quantum Dot Cellular Automata (QCA) is an alternate version of the existing conventional CMOS technology due to its low power intake, faster speed, and smaller size. A multiplexer is a very important logical block in VLSI designs. In this paper, a 2:1 multiplexer (MUX) architecture is proposed, analyzed and compared with related existing architectures. The kink energy of proposed circuit has been calculated and hazard analysis has been completed successfully. All designs in this paper are simulated, checked, and verified using the popular QCADesigner tool. The comparisons of the proposed design with respect to different parameters of the existing MUX(s) along with their corresponding graphical representations prove the robustness of the proposed multiplexer.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chakraborty, B., Dalui, M., Sikdar, B.K.: Design of a reliable cache system for heterogeneous CMPs. J. Circuits Syst. Comput. 27(14), 1850219 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1142/S0218126618502195
Sasamal, T.N., Singh, A.K., Mohan, A.: Design of cost-efficient qca reversible circuits via clock-zone-based crossover. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 57(10), 3127–3140 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-018-3830-3
Sasamal, T.N., Singh, A.K., Ghanekar, U.: Design and implementation of qca d-flip-flops and ram cell using majority gates. J. Circuits Syst. Comput. 1950079 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1142/S0218126619500798
Kandasamy, N., Ahmad, F., Telagam, N.: Shannon logic based novel qca full adder design with energy dissipation analysis. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 57, 1–14 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-018-3883-3
Roohi, A., DeMara, R.F., Khoshavi, N.: Design and evaluation of an ultra-area-efficient fault-tolerant QCA full adder. Microelectron. J. 46(6), 531–542 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mejo.2015.03.023
Abedi, D., Jaberipur, G., Sangsefidi, M.: Coplanar full adder in quantum-dot cellular automata via clock-zone-based crossover. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 14(3), 497–504 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1109/TNANO.2015.2409117
Angizi, S., Sarmadi, S., Sayedsalehi, S., Navi, K.: Design and evaluation of new majority gate-based RAM cell in quantum-dot cellular automata. Microelectron. J. 46(1), 43–51 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mejo.2014.10.003
Lent, C.S., Tougaw, P.D.: A device architecture for computing with quantum dots. Proc. IEEE. 85(4), 541–557 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1109/5.573740
Wilson, M., Kannangara, K., Simmons, M., Raguse, B., Smith, G.: Nanotechnology: basic science and emerging technologies. New York: Chapman and Hall/CRC, 205–206 (2012)
Ahmadpour, S., Mosleh, M.: A novel fault-tolerant multiplexer in quantum-dot cellular automata technology. J. Supercomput. 74(9), 4696–4716 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-018-2464-9
Mukhopadhyay, D., Dinda, S., Dutta, P.: Designing and implementation of quantum cellular automata 2:1 multiplexer circuit. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 25(1), 21–24 (2011). https://doi.org/10.5120/2996-4026
Mukhopadhyay, D., Dutta, P.: Quantum cellular automata based novel unit 2:1 multiplexer. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 43(2), 22–25 (2012). https://doi.org/10.5120/6077-8196
Lent, C.S., Tougaw, P., Porod, W.: Bistable saturation in coupled quantum dots for quantum cellular automata. Appl. Phys. Lett. 62(7), 714–716 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.108848
Srivastava, S.: Probalistic modeling of quantum dot cellular automata, Graduate school thesis and dissertations, 2007. http://scholarcommons.usf.edu/etd/2372. Accessed 15 Dec 2017
Walus, K., Dysart, T.J., Jullien, G.A., Budiman, R.A.: Qcadesigner: a rapid design and simulation tool for quantum-dot cellular automata. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 3(1), 26–31 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1109/TNANO.2003.820815
Sasamal, T.N., Singh, A.K., Ghanekar, U.: Efficient design of coplanar ripple carry adderin QCA. IET Circuits Devices Syst. 12(5), 594–605 (2018)
Lent, C.S., Tougow, P.D., Porod, W., Bernstein, G.H.: Quantum cellular automata. Nanotechnology. 4(1), 49–57 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/4/1/004
Khan, A., Sur, S., Mukherjee, C., Sukla, A.S., Chakrabarty, R.: Behaviors of QCA inverter due to cell displacement and temperature variation. In proceedings of 2nd international conference on Nanotechnology 325–330 (2015). ISBN: 978- 81–927756–2-3
Chakrabarty, R., Khan, A.: Design of a fault free inverter circuit using minimum number of cells & related kink energy calculation in quantum dot cellular automata. In proceeding of International Conference on Computation and Communication Advancement (IC3A). 369–373 (2013). ISBN 13: 978–1–25-906393-0, ISBN 10: 1–25–906393-3
Chakrabarty, R., De, D., Khan, A., Mukherjee, C., Pramanik, S.: Effect of temperature & kink energy in multilevel digital circuit using quantum dot cellular automata. In proceedings of 5th International Conference on Computers and Devices for Communication (CODEC). 1–4 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1109/CODEC.2012.6509297
Khan, A., Chakrabarty, R.: Design of ring and Johnson counter in a single reconfigurable logic circuit in quantum dot cellular automata. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Technol. 4(1), 363–367 (2013) ISSN: 2229-4333
Khan, A., Chakrabarty, R.: Design of high polarized binary wires using minimum number of cells & related kink energy calculations in quantum dot cellular automata. Int. J. Electron. Commun. Technol. 4(Spl.2), 54–57 (2013) ISSN: 2230–9543
Angizi, S., Moaiyeri, M.H., Farrokhi, S., Navi, K., Bagherzadeh, N.: Designing quantum-dot cellular automata counters with energy consumption analysis. Microprocess. Microsyst. 39(7), 512–520 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micpro.2015.07.011
Khan, A., Chakrabarty, R.: Novel design of high polarized inverter using minimum number of rotated cells and related kink energy calculation in quantum dot cellular automata. Int. J. Soft Comput. Eng. 3(1), 165–169 (2013)
Sheikhfaal, S., Angizi, S., Sarmadi, S., Moaiyeri, M.H., Sayedsalehi, S.: Designing efficient qca logical circuits with power dissipation analysis. Microelectron. J. 46(6), 462–471 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mejo.2015.03.016
Orlov, A.O., Amlani, I., Kummamuru, R.K., Ramasubramaniam, R., Toth, G., Lent, C.S., Bernstein, G.H., Snider, G.L.: Experimental demonstration of clocked single-electron switching in quantum-dot cellular automata. Appl. Phys. Lett. 77(2), 295–297 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.126955
Rashidi, H., Rezai, A.: Design of novel efficient multiplexer architecture for quantum-dot cellular automata. J. Nano Electron. Phys., 9(1), 01012_1-01012_7 (2017). https://doi.org/10.21272/jnep.9(1).01012, 01012-7
Rashidi, H., Rezai, A., Soltany, S.: High performance multiplexer architecture for quantum-dot cellular automata. J. Comput. Electron. 15(3), 968–981 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10825-016-0832-3
Singh, S., Pandey, S., Wairya, S.: Modular design of 2n:1 quantum dot cellular automata multiplexers and its application, via clock zone based crossover. Int. J. Mod. Educ. Comput. Sci. 8(7), 41–52 (2016). https://doi.org/10.5815/ijmecs.2016.07.05
Roohi, A., Khademolhosseini, H., Sayedsalehi, S., Navi, K.: A novel architecture for quantum-dot cellular automata multiplexer. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Issues. 8(6), 55–60 (2011)
Chabi, A.M., Sayedsalehi, S., Angizi, S., Navi, K.: Efficient QCA exclusive-or and multiplexer circuits based on a nanoelectronic-compatible designing approach. Int. Sch. Res. Notices. 2014, 1–9 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/463967
Ghosh, M., Mukhopadhyay, D., Dutta, P.: A study on 2 dimensional 2 dot 1 electron quantum dot cellular automata based reversible 2:1 mux design: an energy analytical approach. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 38(2–3), 82–95 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1080/1206212x.2016.1218239
Sen, B., Dutta, M., Saran, D., Sikdar, B.K.: An efficient multiplexer in quantum-dot cellular automata. Progress in VLSI design and test. Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. 7373, 350–351 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-31494-0_40
Khan, A., Mandal, S., Nag, S., Chakrabarty, R.: Efficient multiplexer design and analysis using quantum dot cellular automata. In proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Distributed Computing, VLSI, Electrical Circuits and Robotics (IEEE-DISCOVER 2016). 163–168 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/DISCOVER.2016.7806233
Khan, A., Mandal, S.: Elimination of static hazard in 2:1 multiplexer using quantum dot cellular automata. In proceedings of IEEE Students’ Technology Symposium. 229–234 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/TechSym.2016.7872687
Khan, A., Mukherjee, C., Chakraborty, A. K., Chakrabarty, R., De, D.: Elimination of static hazards in asynchronous sequential circuits using quantum dot cellular automata. In Proceedings of 2nd International Conference on Microelectronics, Circuits and Systems. Vol.-II. 140–145 (2015). ISBN: 81-85824-46-0
Khan, A., Chakrabarty, R., De, D.: Static hazard elimination for a logical circuit using quantum dot cellular automata. Microsyst. Technol. 23(9), 4169–4177 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-016-3057-2
Farazkish, R., Sayedsalehi, S., Navi, K.: Novel design for quantum dots cellular automata to obtain fault-tolerant majority gate. J. Nanotechnol. 2012, 1–7 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/943406
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khan, A., Mandal, S. Robust Multiplexer Design and Analysis Using Quantum Dot Cellular Automata. Int J Theor Phys 58, 719–733 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-018-3970-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-018-3970-5