Abstract
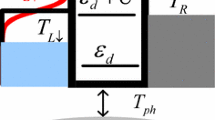
Spin-dependent electron temperature effect on the spin pump in a single quantum dot connected to Normal and/or Ferromagnetic leads are investigated with the help of master equation method. Results show that spin heat accumulation breaks the tunneling rates balance at the thermal equilibrium state thus the charge current and the spin current are affected to some extent. Pure spin current can be obtained by adjusting pumping intensity or chemical potential of the lead. Spin heat accumulation of certain material can be detected by measuring the charge current strength in symmetric leads architectures. In practical devices, spin-dependent electron temperature effect is quite significant and our results should be useful in quantum information processing and spin Caloritronics.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bauer, G.E.W., MacDonald, A.H., Maekawa, S.: Spin caloritronics. Solid State Commun. 150, 459–460 (2010)
Bauer, G.E.W., Saitoh, E., van Wees, B.J.: Spin caloritronics[J]. Nat. Mater. 11(5), 391–399 (2012)
Tserkovnyak, Y., Brataas, A., Bauer, G.E.W.: Enhanced Gilbert damping in thin ferromagnetic films[J]. Phys. Rev. Lett. 88(11), 117601 (2002)
Stevens, M.J., Smirl, A.L., Bhat, R.D.R., et al.: Quantum interference control of ballistic pure spin currents in semiconductors[J]. Phys. Rev. Lett. 90(13), 136603 (2003)
Hübner, J., Rühle, W.W., Klude, M., et al.: Direct observation of optically injected spin-polarized currents in semiconductors[J]. Phys. Rev. Lett. 90(21), 216601 (2003)
Uchida, K., Takahashi, S., Harii, K., et al.: Observation of the spin Seebeck effect[J]. Nature 455(7214), 778–781 (2008)
Uchida, K., Xiao, J., Adachi, H., et al.: Spin seebeck insulator[J]. Nat. Mater. 9(11), 894–897 (2010)
Uchida, K., Adachi, H., Ota, T., et al.: Observation of longitudinal spin-Seebeck effect in magnetic insulators[J]. Appl. Phys. Lett. 97(17), 172505 (2010)
Gravier, L., Serrano-Guisan, S., Reuse, F., et al.: Spin-dependent Peltier effect of perpendicular currents in multilayered nanowires[J]. Phys. Rev. B 73(5), 052410 (2006)
Flipse, J., Bakker, F.L., Slachter, A., et al.: Direct observation of the spin-dependent Peltier effect[J]. Nat. Nanotechnol. 7(3), 166–168 (2012)
Giazotto, F., Taddei, F., D’Amico, P., et al.: Nonequilibrium spin-dependent phenomena in mesoscopic superconductor–normal metal tunnel structures[J]. Phys. Rev. B 76(18), 184518 (2007)
Zhang, H.R., Xue, H.J., Chi, F.: Spin-Polarized Transport through a quantum dot coupled to leads with Spin-Dependent electron Temperature[J]. J. Low Temp. Phys. 180(5–6), 321–329 (2015)
Dejene, F.K., Flipse, J., Bauer, G.E.W., et al.: Spin heat accumulation and spin-dependent temperatures in nanopillar spin valves[J]. Nat. Phys. 9(10), 636–639 (2013)
Vera-Marun, I.J., van Wees, B.J., Jansen, R.: Spin heat accumulation induced by tunneling from a ferromagnet[J]. Phys. Rev. Lett. 112(5), 056602 (2014)
van der Wiel, W.G., De Franceschi, S., Elzerman, J.M., et al.: Electron transport through double quantum dots[J]. Rev. Mod. Phys. 75(1), 1 (2002)
Dong, B., Cui, H.L., Lei, X.L.: Pumped spin-current and shot-noise spectra of a single quantum dot[J]. Phys. Rev. Lett. 94(6), 066601 (2005)
Liu, J., Cheng, J.: Thermal bias on the pumped spin-current in a single quantum dot[J]. Commun. Theor. Phys. 62(1), 86–90 (2014)
Gurvitz, S.A., Prager, Y.S.: Microscopic derivation of rate equations for quantum transport[J]. Phys. Rev. B 53(23), 15932 (1996)
Wang, B., Wang, J., Guo, H.: Quantum spin field effect transistor[J]. Phys. Rev. B 67(9), 092408 (2003)
Zhang, P., Xue, Q.K., Xie, X.C.: Spin current through a quantum dot in the presence of an oscillating magnetic field[J]. Phys. Rev. Lett. 91(19), 196602 (2003)
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China Project (Grant No.11564029, 11147010), the Natural Science Foundation of Inner Mongolia (Grant No.2012MS0113), and the Research Program of science and technology at Universities of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region (Grant No.NJZY12111).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, J., Wang, S. & Du, X. Pumped Spin-Current in Single Quantum Dot with Spin-Dependent Electron Temperature. Int J Theor Phys 55, 4036–4043 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-016-3032-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-016-3032-9