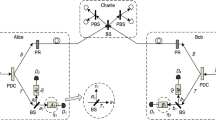
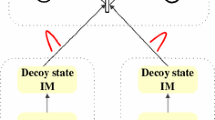
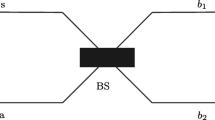
Abstract
We propose a quantum key distribution based on Mach-Zehnder (MZ) interferometry and interaction-free measurement on single photon. The raw key comes from the photons on which MZ interferometry happened. And the interaction-free measurements are used to detect eavesdroppers. The analysis indicates that the protocol is secure, and can prevent some familiar attacks, such as photon number splitting (PNS) attack. This scheme is easy to be realized in current experiments.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bennett, C.H., Brassard, G.: Quantum cryptography: public-key distribution and coin tossing. In: IEEE International Conference on Computers, Systems and Signal Processing, p. 175C179. IEEE, New York, Bangalore, India (1984)
Bennett, C.H.: Quantum cryptography using any two nonorthogonal states. Phys. Rev. Lett. 68, 3121–3124 (1992)
Goldenberg, L., Vaidman, L.: Quantum cryptography based on orthogonal states. Phys. Rev. Lett. 75, 1239–1243 (1995)
Koashi, M., Imoto, N.: Quantum cryptography based on split transmission of one-bit information in two steps. Phys. Rev. Lett. 79, 2383–2386 (1997)
Guo, G.C., Shi, B.S.: Quantum cryptography based on interaction-free measurement. Phys. Lett. A 256, 109–112 (1999)
Yuen, H.P.: In: Tombesi, P., Hirota, O. (eds.) Proceedings of QCMC00, Capri, 2001. Plenum Press, New York (2001)
Hwang, W.Y.: Quantum key distribution with high loss: Toward global secure communication. Phys. Rev. Lett. 91, 057901 (2003)
Noh, T.G.: Counterfactual quantum cryptography. Phys. Rev. Lett. 103, 230501 (2009)
Allati, A.E., Baz, M.E., Hassouni, Y.: Quantum key distribution via tripartite coherent states. Quantum Inf. Process 10(5), 589–602 (2011)
Lo, H.K., Curty, M., Qi, B.: Measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. Lett. 108, 130503 (2012)
Lin, S., Liu, X.F.: A modified quantum key distribution without public announcement bases against photon-number-splitting attack. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 51, 2514–2523 (2012)
Mishra, M.K., Prakash, H.: Bipartite coherent-state quantum key distribution with strong reference pulse. Quantum Inf. Process 12(2), 907–920 (2013)
Li, Y.B.: Analysis of counterfactual quantum key distribution using error correcting theory. Quantum Inf. Process 13(10), 2325–2342 (2014)
Fuchs, C.A.: Information gain vs. state disturbance in quantum theory. Fortschr. Phys. 46, 535–565 (1998)
Lo, H.K., Chau, H.F.: Unconditional security of quantum key distribution over arbitrarily long distances. Science 283, 2050 (1999)
Brassard, G., Lütkenhaus, N., Mor, T., Sanders, B.C.: Limitations on practical quantum cryptography. Phys. Rev. Lett. 85, 1330–1333 (2000)
Huttner, B., Imoto, N., Gisin, N., Mor, T.: Quantum cryptography with coherent states. Phys. Rev. A 51, 1863 (1995)
Gisin, N., Fasel, S., Kraus, B., Zbinden, H., Ribordy, G.: Trojan-horse attacks on quantum-key-distribution systems. Phys. Rev. A 73, 022320 (2006)
Wang, T.Y., Wen, Q.Y.: Security of a kind of quantum secret sharing with single photons. Quantum Inf. Comput. 11(5–6), 0434–0443 (2011)
Yang, Y.G., Teng, Y.W., Chai, H.P., Wen, Q.Y.: Revisiting the security of secure direct communication based on ping-pong protocol. Quant. Inf. Proc. 10(3), 317–323 (2011)
Makarov, V., Anisimov, A., Skaar, J.: Effects of detector efficiency mismatch on security of quantum cryptosystems. Phys. Rev. A 74, 022313 (2006)
Brassard, G., Salvail, L.: Secret-key reconciliation by public discussion. Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. 765, 410 (1994)
Bennett, C.H., Brassard, G., Crépeau, C., Maurer, U.M.: Generalized privacy amplification. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 41, 1915 (1995)
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by NSFC (Grant Nos. 61272057, 61170270, 61370188), Beijing Higher Education Young Elite Teacher Project (Grant Nos. YETP0475, YETP0477), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Grant No. 328201506), China scholarship council.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, YB., Xu, SW., Wang, QL. et al. Quantum Key Distribution Based on Interferometry and Interaction-Free Measurement. Int J Theor Phys 55, 98–106 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-015-2636-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-015-2636-9