Abstract
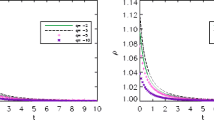
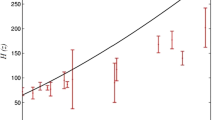
In this paper, we study holographic Ricci dark energy model with non-constant c 2 term in dark energy density formula. We consider FRW metric in flat space-time and calculate density. Also we find scale factor and Hubble expansion parameter.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Riess, A.G., et al. (Supernova Search Team): Astron. J. 116, 100938 (1998)
Riess, A.G., et al.: Astrophys. J. 607, 665 (2004)
Perlmutter, S., et al. (The Supernova Cosmology Project): Astrophys. J. 517, 56586 (1999)
Perlmutter, S., et al.: Nature 391, 51 (1998)
Spergel, D.N., et al.: Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe (WMAP) three year results: implications for cosmology. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 170, 377 (2007). astro-ph/0603449
Spergel, D.N., et al.: Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 148, 175 (2003)
Komatsu, E., et al. (WMAP Collaboration): Five-year Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe (WMAP) observations: cosmological interpretation. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 180, 330 (2009). arXiv:0803.0547 [astro-ph]
Adelman-McCarthy, J.K., et al. (SDSS Collaboration): The sixth data release of the sloan digital sky survey. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 175, 297 (2008). arXiv:0707.3413 [astro-ph]
Tegmark, M., et al.: Cosmological parameters from SDSS and WMAP. Phys. Rev. D 69, 103501 (2004). astro-ph/0310723
Tegmark, M., et al.: The 3D power spectrum of galaxies from the SDSS. Astrophys. J. 606, 702 (2004). astro-ph/0310725
Frieman, J.A., et al.: Phys. Rev. Lett. 75, 2077 (1995)
Caldwell, R.R., Dave, R., Steinhardt, P.J.: Phys. Rev. Lett. 80, 1582 (1998)
Caldwell, R.R., Linder, E.V.: Phys. Rev. Lett. 95, 141301 (2005)
Carvalho, F.C., et al.: Phys. Rev. Lett. 97, 081301 (2006)
Jassal, H.K., Bagla, J.S., Padmanabhan, T.: Understanding the origin of CMB constraints on Dark Energy. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 405, 2639–2650 (2010). astro-ph/0601389
Davis, T.M., et al.: Scrutinizing exotic cosmological models using ESSENCE supernova data combined with other cosmological probes. Astrophys. J. 666, 716 (2007). astro-ph/0701510
Samushia, L., Ratra, B.: Constraints on dark energy from galaxy cluster gas mass fraction versus Redshift data. Astrophys. J. 680(1), L1–L4 (2008). arXiv:0803.3775 [astro-ph]
Sadeghi, J., Saadat, H., Pourhassan, B.: Relation between dark matter density and temperature with power law. Chaos Solitons Fractals 42, 1080 (2009)
Saadat, H.: Solar system and dark matter. Chaos Solitons Fractals 42, 2236 (2009)
Saadat, H., et al.: The effect of dark matter on solar system and perihelion precession of Earth planet. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 49(10), 2506 (2010)
Saadat, H.: Relation between the dark energy density and temperature. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 50(1), 140 (2011)
Thomas, S.D.: Phys. Rev. Lett. 89, 081310 (2002)
Horava, P., Minic, D.: Phys. Lett. 85, 1610 (2000)
Zhao, W.: Phys. Lett. B 655, 99 (2007)
Li, H., Guo, Z.K., Zhang, Y.Z.: Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 15, 869 (2006)
Hu, B., Ling, Y.: Phys. Rev. D 73, 123510 (2006)
Wang, B., Gong, Y., Abdalla, E.: Phys. Lett. 624, 141 (2005)
Saadat, H., Saadat, A.M.: Time-dependent dark energy density and holographic DE model with interaction. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 50, 1358–1366 (2011)
Saadat, H.: Holographic dark energy density. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 50, 1769–1775 (2011)
Jassal, H.K., Bagla, J.S., Padmanabhan, T.: Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 356, L11 (2005)
Saadat, H., et al.: Holographic dark energy density and JBP parametrization. Int. J. Theor. Phys. (2001) doi:10.1007/s10773-011-0787-x
Saadat, H.: Hubble expansion parameter in a new model of dark energy. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 51, 78–82 (2012). doi:10.1007/s10773-011-0879-7
Barboza, E.M. Jr., Alcaniz, J.S.: Probing the time dependence of dark energy arXiv:1103.0257 [astro-ph.CO]
Zhang, X.: Phys. Rev. D 79, 103509 (2009)
Xu, L., Wang, Y.: J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 06, 002 (2010)
Gao, C., Wu, F., Chen, X., Shen, Y.-G.: Phys. Rev. D 79, 043511 (2009)
Wang, Y., Xu, L.: Phys. Rev. D 81, 083523 (2010)
Chimento, L.P., Monica Forte, a., Richarte, M.G.: A modified Ricci scalar as an interacting model of holographic dark energy. arXiv:1106.0781 [astro-ph.CO]
Rong-Gen, C., Bin, H., Yi, Z.: Holography, UV/IR relation, causal entropy bound, and dark energy. Commun. Theor. Phys. 51, 954–960 (2009)
Saadat, H.: Holographic Ricci dark energy model. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 51, 731–737 (2012). doi:10.1007/s10773-011-0952-2
Radicella, N., Pavon, D.: On the c 2 term in the holographic formula for dark energy. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 10, 005 (2010)
Pavon, D., Zimdahl, W.: Holographic dark energy and cosmic coincidence. Phys. Lett. B 628, 206 (2005). arXiv:gr-qc/0505020
Pavon, D.: Holographic dark energy and late cosmic acceleration. J. Phys. A 40, 6865 (2007). arXiv:gr-qc/0610008
Guberina, B., Horvat, R., Nikolic, H.: Nonsaturated holographic dark energy. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 01, 012 (2007). arXiv:astro-ph/0611299
Xu, L.: Holographic dark energy model with hubble horizon as an IR cut-off. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 09, 016 (2009). arXiv:0907.1709
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saadat, H. Holographic Ricci Dark Energy Model with Non-constant c 2 Term. Int J Theor Phys 52, 1027–1032 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-012-1416-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-012-1416-z