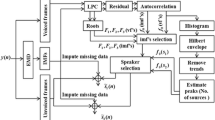
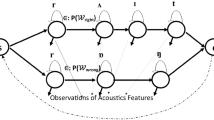
Abstract
Separating individual source signals is a challenging task in musical and multitalker source separation. This work studies unsupervised monaural (co-channel) speech separation (UCSS) in reverberant environment. UCSS is the problem of separating the individual speakers from multispeaker speech without using any training data and with minimum information regarding mixing condition and sources. In this paper, state-of-art UCSS algorithms based on auditory and statistical approaches are evaluated for reverberant speech mixtures and results are discussed. This work also proposes to use multiresolution cochleagram and Constant Q Transform (CQT) spectrogram feature with two-dimensional Non-negative matrix factorization. Results show that proposed algorithm with CQT spectrogram feature gave an improvement of 1.986 and 1.262 in terms of speech intelligibility and 0.296 db and 0.561 db in terms of signal to interference ratio compared to state-of-art statistical and auditory approach respectively at T60 of 0.610s.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen, J., Wang, Y., & Wang, D. (2014). A feature study for classification-based speech separation at very low signal-to-noise ratio. In IEEE International conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing ICASSP 2014, Florence, Italy, May 4–9 (pp. 7039–7043). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICASSP.2014.6854965.
Cherry, E. C. (1953). Some experiments on the recognition of speech, with one and with two ears. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 25(5), 975–979. https://doi.org/10.1121/1.1907229.
Chien, J. T., & Hsieh, H. L. (2012). Convex divergence ica for blind source separation. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 20(1), 302–313. https://doi.org/10.1109/TASL.2011.2161080.
Delfarah, M., & Wang, D. (2017). Features for masking-based monaural speech separation in reverberant conditions. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 25(5), 1085–1094.
Fevotte, C., Bertin, N., & Durrieu, J. (2009). Nonnegative matrix factorization with the itakura-saito divergence: With application to music analysis. Neural Computation, 21(3), 793–830. https://doi.org/10.1162/neco.2008.04-08-771.
Gao, B., Woo, W. L., & Dlay, S. S. (2011). Single-channel source separation using emd-subband variable regularized sparse features. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 19(4), 961–976. https://doi.org/10.1109/TASL.2010.2072500.
Gao, B., Woo, W. L., & Dlay, S. S. (2013). Unsupervised single-channel separation of nonstationary signals using gammatone filterbank and itakura saito nonnegative matrix two-dimensional factorizations. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, 60(3), 662–675. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCSI.2012.2215735.
Hadad, E., Heese, F., Vary, P., & Gannot, S. (2014). Multichannel audio database in various acoustic environments. In 2014 14th international workshop on acoustic signal enhancement (IWAENC), Juan-les-Pins, France (pp. 313–317). https://doi.org/10.1109/IWAENC.2014.6954309.
Huang, P., Kim, M., Hasegawa-Johnson, M., & Smaragdis, P. (2015). Joint optimization of masks and deep recurrent neural networks for monaural source separation. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 23(12), 2136–2147. https://doi.org/10.1109/TASLP.2015.2468583.
Hu, K., & Wang, D. (2013). An unsupervised approach to cochannel speech separation. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 21(1), 122–131. https://doi.org/10.1109/TASL.2012.2215591.
Hyvarinen, A. (1999). Fast and robust fixed-point algorithms for independent component analysis. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 10(3), 626–634. https://doi.org/10.1109/72.761722.
Krishna, P. K. M., & Ramaswamy, K. (2017). Single channel speech separation based on empirical mode decomposition and hilbert transform. IET Signal Processing, 11(5), 579–586. https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-spr.2016.0450.
Li, P., Guan, Y., Xu, B., & Liu, W. (2006). Monaural speech separation based on computational auditory scene analysis and objective quality assessment of speech. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 14(6), 2014–2023. https://doi.org/10.1109/TASL.2006.883258.
Li, W., Wang, L., Zhou, Y., Dines, J., Doss, M. M., Bourlard, H., et al. (2014). Feature mapping of multiple beamformed sources for robust overlapping speech recognition using a microphone array. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 22(12), 2244–2255.
Madhu, N., & Martin, R. (2011). A versatile framework for speaker separation using a model-based speaker localization approach. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech and Language Processing, 19(7), 1900–1912.
Mesgarani, N., & Chang, E. F. (2012). Selective cortical representation of attended speaker in multi-talker speech perception. Nature, 485(5), 233–236.
Molla, M. K. I., & Hirose, K. (2007). Single-mixture audio source separation by subspace decomposition of hilbert spectrum. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 15(3), 893–900. https://doi.org/10.1109/TASL.2006.885254.
Morgan, D. P., George, E. B., Lee, L. T., & Kay, S. M. (1995). Co-channel speaker separation. In 1995 international conference on acoustics, speech, and signal processing, Detroit, Michigan (Vol. 1, pp. 828–831). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICASSP.1995.479822.
Prasanna Kumar, M. K., & Kumaraswamy, R. (2017). Single-channel speech separation using empirical mode decomposition and multi pitch information with estimation of number of speakers. International Journal of Speech Technology, 20(1), 109–125. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10772-016-9392-y.
Rennie, S. J., Hershey, J. R., & Olsen, P. A. (2010). Single-channel multitalker speech recognition. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 27(6), 66–80.
Saruwatari, H., Kawamura, T., Nishikawa, T., Lee, A., & Shikano, K. (2006). Blind source separation based on a fast-convergence algorithm combining ICA and beamforming. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 14(2), 666–678. https://doi.org/10.1109/TSA.2005.855832.
Schmidt, M. N., & Olsson, R. K. (2006). Single-channel speech separation using sparse non-negative matrix factorization. In ISCA international conference on spoken language proceesing, INTERSPEECH, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania.
Shao, Y., & Wang, D. (2003). Co-channel speaker identification using usable speech extraction based on multi-pitch tracking. In ıtIEEE international conference on acoustics, speech, and signal processing, Hong Kong, China (Vol. 2, pp. II–205–8). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICASSP.2003.1202330.
Smaragdis, P. (2007). Convolutive speech bases and their application to supervised speech separation. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 15(1), 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1109/TASL.2006.876726.
Smaragdis, P. (2009). Relative-pitch tracking of multiple arbitary sounds. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 125(5), 3406–3413.
Swamy, R. K., Murty, K. S. R., & Yegnanarayana, B. (2007). Determining number of speakers from multispeaker speech signals using excitation source information. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 14(7), 481–484. https://doi.org/10.1109/LSP.2006.891333.
Taal, C. H., Hendriks, R. C., Heusdens, R., & Jensen, J. (2010). A short-time objective intelligibility measure for time-frequency weighted noisy speech. In IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing, Dallas, Texas, USA (pp. 4214–4217). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICASSP.2010.5495701.
Wang, D., & Chen, J. (2018). Supervised speech separation based on deep learning: An overview. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 26(10), 1702–1726. https://doi.org/10.1109/TASLP.2018.2842159.
Wang, Y., & Wang, D. (2013). Towards scaling up classification-based speech separation. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 21(7), 1381–1390. https://doi.org/10.1109/TASL.2013.2250961.
Wang, Z., & Wang, D. (2019). Combining spectral and spatial features for deep learning based blind speaker separation. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 27(2), 457–468.
Yegnanarayana, B., Swamy, R. K., & Prasanna, S. R. M. (2005). Separation of multispeaker speech using excitation information. NOLISP-2005, Barcelona, Spain (pp. 11–18).
Yegnanarayana, B., Swamy, R. K., & Murty, K. S. R. (2009). Determining mixing parameters from multispeaker data using speech-specific information. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 17(6), 1196–1207. https://doi.org/10.1109/TASL.2009.2016230.
Zhang, X., & Wang, D. (2016). A deep ensemble learning method for monaural speech separation. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 24(5), 967–977. https://doi.org/10.1109/TASLP.2016.2536478.
Funding
Funding was provided by Department of science and Technology, Government of India (Grant No. SR/WOS-A/ET-69/2016).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hemavathi, R., Kumaraswamy, R. A study on unsupervised monaural reverberant speech separation. Int J Speech Technol 23, 451–457 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10772-020-09706-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10772-020-09706-x