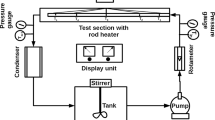
Abstract
In this paper, the heat transfer characteristics of nanofluid nucleate and film boiling are studied experimentally. For this purpose, Al2O3 and SiO2 ethanol-based nanofluids prepared with three volumetric concentrations of 0.1 %, 0.3 %, and 0.5 %. The boiling experiments were conducted on a circular and polished copper surface with a diameter of 25 mm. The results showed that the addition of nanoparticles to the base fluid reduced the heat transfer coefficient of nucleate boiling. The critical heat flux of ethanol-based nanofluids was significantly higher than that of pure ethanol. The Al2O3 ethanol-based nanofluid with a volumetric concentration of 0.5 % had the best performance, with a critical heat flux of 42.36 % higher than that of pure ethanol. The presence of nanoparticles in the ethanol-based nanofluid improved the heat transfer coefficient of film boiling. The results showed that the stable film boiling for nanofluids starts at higher wall superheat temperature difference than pure ethanol. Among the investigated concentrations, volumetric concentration of 0.5 % had the best performance for both nanofluids, so that the minimum heat flux of Al2O3 and SiO2 ethanol-based nanofluids were increased by 45.96 % and 45.67 % compared to pure ethanol, respectively.

























Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Polytetrafluoroethylene.
Abbreviations
- C :
-
Constant coefficient
- c p :
-
Specific heat capacity (J·kg−1·°C−1)
- h :
-
Boiling heat transfer coefficient (W·m−2·°C−1)
- i :
-
Latent heat of evaporation (J·kg−1)
- k :
-
Thermal conductivity (W·m−1·°C−1)
- m :
-
Mass (kg)
- q″ :
-
Heat flux (W·m−2)
- T :
-
Temperature (°C)
- U :
-
Uncertainty
- V :
-
Volume (m3)
- Z :
-
Thermocouples location in cartridge (m)
- µ :
-
Dynamic viscosity (kg·m−1.s−1)
- ρ :
-
Density (kg·m−3)
- σ :
-
Surface tension (N·m−1)
- φ :
-
Volumetric concentration of nanofluid
- f:
-
Saturated liquid
- fb:
-
Film boiling
- l:
-
Liquid
- nf:
-
Nanofluid
- np:
-
Nano particle
- s:
-
Boiling surface
- sat:
-
Saturation
- sf:
-
Solid–Fluid
- v:
-
Vapor
- w:
-
Solid surface (wall)
References
K. Martin, A. Sözen, E. Çiftçi, H.M. Ali, An experimental investigation on aqueous Fe-CuO hybrid nanofluid usage in a plain heat pipe. Int. J. Thermophys. 41, 135 (2020)
Z. Shahmoradi, N. Etesami, M.N. Esfahany, Pool boiling characteristics of nanofluid on flat plate based on heater surface analysis. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 47, 113–120 (2013)
M.R. Raveshi, A. Keshavarz, M.S. Mojarrad, S. Amiri, Experimental investigation of pool boiling heat transfer enhancement of alumina-water-ethylene glycol nanofluids. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 44, 805–814 (2013)
V. Umesh, B. Raja, A study on nucleate boiling heat transfer characteristics of pentane and CuO pentane nanofluid on smooth and milled surfaces. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 64, 23–29 (2015)
P. Naphon, Effect of magnetic fields on the boiling heat transfer characteristics of nanofluids. Int. J. Thermophys. 36, 2810–2819 (2015)
I.S. Kiyomura, L.L. Manetti, A.P. da Cunha, G. Ribatski, E.M. Cardoso, An analysis of the effects of nanoparticles deposition on characteristics of the heating surface and on pool boiling of water. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 106, 666–674 (2017)
W.T. Ji, P.F. Zhao, C.Y. Zhao, J. Ding, W.Q. Tao, Pool boiling heat transfer of water and nanofluid outside the surface with higher roughness and different wettability. Nanoscale Microscale Thermophys. Eng. 22(4), 296–323 (2018)
F.R. Dareh, M. Haghshenasfard, M.N. Esfahany, H.R.S. Jazi, An experimental investigation of pool boiling characteristics of alumina-water nanofluid over micro/nano-structured surfaces. Heat Transf. Eng. 40(20), 1691–1708 (2019)
M. Mohammadi, M. Khayat, Experimental investigation of the effect of one-dimensional roughened surface on the pool boiling of nanofluids. Sci. Iran. 27(6), 2954–2966 (2020)
D. Vasudevan, D. Senthilkumar, S. Surendhiran, Performance and characterization studies of reduced graphene oxides aqua nanofluids for a pool boiling surface. Int. J. Thermophys. 41, 74 (2020)
M.S. Kamel, F. Lezsovits, Experimental investigation on pool boiling heat transfer performance using tungsten oxide WO3 nanomaterial-based water nanofluids. Materials 13(8), 1922 (2020)
J. Gylys, R. Skvorcinskiene, L. Paukstaitis, M. Gylys, A. Adomavicius, Film boiling influence on the spherical body’s cooling in sub-cooled water. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 95, 709–719 (2016)
T. Arai, M. Furuya, Effect of nanofluid on the film boiling behavior at vapor film collapse, in Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (Brussels, Belgium, 2009)
D. Ciloglu, A. Bolukbasi, K. Comakli, Effect of nanofluids on the saturated pool film boiling. World Acad. Sci. Eng. Technol. 6(7), 1112–1124 (2012)
J.Q. Li, L.W. Fan, L. Zhang, Z.T. Yu, An experimental study of boiling heat transfer during quenching of nanofluids with carbon nanotubes of various sizes, in Proceedings of the ASME Heat Transfer Summer Conference (Washington, DC, USA, 2016)
J.Y. Kang, T.K. Kim, G.C. Lee, H.S. Park, M.H. Kim, Minimum heat flux and minimum film-boiling temperature on a completely wettable surface: effect of the Bond number. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 120, 399–410 (2018)
S. Wcislik, A simple economic and heat transfer analysis of the nanoparticles use. Chem. Pap. 71(12), 2395–2401 (2017)
V. Talari, P. Behar, Y. Lu, E. Haryadi, D. Liu, Leidenfrost drops on micro/nanostructured surfaces. Front. Energy 12(1), 22–42 (2018)
A. Kalani, S.G. Kandlikar, Enhanced pool boiling with ethanol at subatmospheric pressures for electronics cooling. J. Heat Transf. 135(11), 111002 (2013)
A. Amiri, M. Shanbedi, H. Amiri, S.Z. Heris, S.N. Kazi, B.T. Chew, H. Eshghi, Pool boiling heat transfer of CNT/water nanofluids. Appl. Therm. Eng. 71(1), 450–459 (2014)
D. Zheng, J. Wang, Z. Chen, J. Baleta, B. Sundén, Performance analysis of a plate heat exchanger using various nanofluids. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 158, 119993 (2020)
A. Ghadimi, R. Saidur, H.S.C. Metselaar, A review of nanofluid stability properties and characterization in stationary conditions. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 54(17–18), 4051–4068 (2011)
J. Shah, M. Ranjan, V. Davariya, S.K. Gupta, Y. Sonvane, Temperature-dependent thermal conductivity and viscosity of synthesized α-alumina nanofluids. Appl. Nanosci. 7, 803–813 (2017)
S.M. Ghiaasiaan, Two Phase Flow, Boiling and Condensation in Conventional and Miniature Systems (Cambridge University Press, New York, 2008).
J.G. Hust, A.B. Lankford, Thermal Conductivity of Aluminum, Copper, Iron, and Tungsten for Temperatures from 1 K to the Melting Point (U.S. Department of Commerce, Malcolm Baldrige, CO, 1984).
R.J. Moffat, Describing the uncertainties in experimental results. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 1(1), 3–17 (1988)
W.M. Rohsenow, A method of correlating heat transfer data for surface boiling liquids. Trans. ASME 74, 969–975 (1952)
B. Shen, T. Hamazaki, W. Ma, N. Iwata, S. Hidaka, A. Takahara, K. Takahashi, Y. Takata, Enhanced pool boiling of ethanol on wettability-patterned surfaces. Appl. Therm. Eng. 149, 325–331 (2019)
N. Zuber, On the stability of boiling heat transfer. Trans. ASME 80, 711–720 (1958)
Z. Liu, L. Liao, Sorption and agglutination phenomenon of nanofluids on a plain heating surface during pool boiling. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 51(9–10), 2593–2602 (2008)
S.M. Kwark, M. Amaya, S.M. You, Experimental pool boiling heat transfer study of the nanoporous coating in various fluids. Int. J. Air-Cond. Refrig. 20(1), 1150001 (2012)
P.J. Berenson, Film-boiling heat transfer from a horizontal surface. J. Heat Transf. 83, 351–356 (1961)
L.A. Bromley, Heat transfer in stable film boiling. Chem. Eng. Prog. Symp. Ser. 46, 221–227 (1950)
R.E. Henry, A correlation for the minimum film boiling temperature. Chem. Eng. Prog. Symp. Ser. 70(138), 81–90 (1974)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Golkar, S.H., Khayat, M. & Zareh, M. Nucleate and Film Boiling Performance of Ethanol-Based Nanofluids on Horizontal Flat Plate: An Experimental Investigation. Int J Thermophys 42, 55 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10765-021-02805-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10765-021-02805-0