Abstract
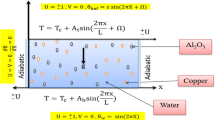
The effects of magnetic field and Joule heating on the heat transfer and fluid flow in a Cu–water nanofluid-filled lid-driven cavity are investigated in this paper. The cavity left side wall is heated by two sinusoidal heat sources, while the other walls have constant temperatures. The top wall of the cavity moves with fixed velocity in + x direction, and the other walls are under no-slip boundary conditions. A constant magnetic flux density is applied to the cavity left side wall. Numerical procedures can be applied to solve the dimensionless equations governing the stream function and temperature at various Reynolds number (Re), Hartmann number (Ha), Eckert number (Ec), magnetic field angle(α) and the solid nanoparticles volume fraction(ϕ). The averaged Nusselt number (Nuavg) is used to specify the rate of the heat transfer. It can be observed that increasing ϕ and also increasing Re result in the significant increase of Nuavg, which enhances convective cooling, and furthermore, Nuavg is varied with α. The increase of Ha within the cavity causes decrease in heat transfer, which enhances conduction heat transfer and also reduces Nuavg. The negative influence of Joule heating on the convection within the cavity is observable in this regard, and the convection is decreased by increasing the value of Ec.















Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- B:
-
Magnetic flux density vector (Wb·m−2)
- C p :
-
Specific heat (J·kg−1·K−1)
- d :
-
Particle size (diameter) (m)
- g :
-
Gravitational acceleration vector (m·s−2)
- h :
-
Grid spacing (m)
- k b :
-
Boltzmann constant (kg·m2·s−2·K−1)
- k :
-
Thermal conductivity (W·m−1·K−1)
- L :
-
Dimension of cavity (m)
- p :
-
Pressure (N·m−2)
- T :
-
Temperature (K)
- U s :
-
Brownian motion velocity (m·s−1)
- ν :
-
Velocity vector (m·s−1)
- x, y, z :
-
Cartesian coordinates (m)
- α :
-
Angle of orientation of the magnetic field
- β :
-
Coefficient of volumetric expansion (K−1)
- ϕ :
-
Nanoparticle volumetric fraction
- μ :
-
Dynamic viscosity (kg·m−1·s−1)
- ρ :
-
Density (kg·m−3)
- σ :
-
Electrical conductivity (mho·m−1)
- Ψ :
-
Stream function (m2·s−1)
- 0:
-
Reference value
- c:
-
Cold
- f :
-
Fluid
- max:
-
Maximum value
- nf:
-
Nanofluid
- s :
-
Nanoparticle
- st :
-
Static
- x, y, z :
-
Component of a vector quantity
- V :
-
Velocity vector
- P :
-
Pressure
- X :
-
Cartesian coordinate in x direction
- Y :
-
Cartesian coordinate in y direction
- Ψ:
-
Stream function
- θ :
-
Temperature
- Ec :
-
Eckert number
- Gr :
-
Grashof number
- Ha :
-
Hartmann number
- Nu :
-
Nusselt number
- Pr :
-
Prandtl number
- Ra :
-
Rayleigh number
- Re :
-
Reynolds number
- Ri :
-
Richardson number
References
G.M. Oreper, J. Szekely, The effect of an externally imposed magnetic field on buoyancy driven flow in a rectangular cavity. J. Cryst. Growth 64, 505–515 (1983)
A.A. Mohamad, R. Viskanta, Transient low Prandtl number fluid convection in a lid-driven cavity. Numer. Heat Transf. A 19, 187–205 (1991)
J.P. Garandet, J.P. Alboussiere, T. Moreau, Buoyancy driven convection in a rectangular cavity with a transverse magnetic field. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 35, 741–748 (1992)
N. Rudraiah, R.M. Barron, M. Venkatachalappa, C.K. Subbaraya, Effect of a magnetic field on free convection in a rectangular enclosure. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 33, 1075–1084 (1995)
N.M. Al-Najem, K.M. Khanafer, M.M. El-Refaee, Numerical study of laminar natural convection in tilted enclosure with transverse magnetic field. Int. J. Numer. Meth. Heat Fluid Flow 8, 651–672 (1998)
I.E. Sarris, S.C. Kakarantzas, A.P. Grecos, N.S. Vlachos, MHD natural convection in a laterally and volumetrically heated square cavity. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 48, 3443–3453 (2005)
P. Kandaswamy, S. Malliga Sundari, N. Nithyadevi, Magnetoconvection in an enclosure with partially active vertical walls. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 51, 1946–1954 (2008)
C.A. Borghi, A. Cristofolini, G. Minak, Numerical methods for the solution of the electrodynamics in magnetohydrodynamic flows. IEEE Trans. Magn. 32, 1010–1013 (1996)
C.A. Borghi, M.R. Carraro, A. Cristofolini, Numerical solution of the nonlinear electrodynamics in MHD regimes with magnetic Reynolds number near one. IEEE Trans. Magn. 40, 593–596 (2004)
S.L.L. Verardi, J.R. Cardoso, A solution of two-dimensional magneto-hydrodynamic flow using the finite element method. IEEE Trans. Magn. 34, 3134–3137 (1998)
S.L.L. Verardi, J.R. Cardoso, M.C. Costa, Three-dimensional finite element analysis of MHD duct flow by the penalty function formulation. IEEE Trans. Magn. 37, 3384–3387 (2001)
S.L.L. Verardi, J.M. Machado, J.R. Cardoso, The element-free Galerkin method applied to the study of fully developed magneto-hydrodynamic duct flows. IEEE Trans. Magn. 38, 941–944 (2002)
J.N. Shadid, R.P. Pawlowski, J.W. Banks, L. Chacon, P.T. Lin, R.S. Tuminaro, Towards a scalable fully-implicit fully-coupled resistive MHD formulation with stabilized FE methods. J. Comput. Phys. 229, 7649–7671 (2010)
M.A. Taghikhani, Magnetic field effect on natural convection flow with internal heat generation using fast Ψ–Ω method. J. Appl. Fluid Mech. 8, 189–196 (2015)
M.A. Taghikhani, Numerical study of magneto-convection inside an enclosure using enhanced stream function-vorticity formulation. Scientia Iranica B 22, 854–864 (2015)
M.C. Ece, E. Buyuk, Natural convection flow under magnetic field in an inclined rectangular enclosure heated and cooled on adjacent walls. Fluid Dyn. Res. 38, 564–590 (2006)
M.C. Ece, E. Büyük, Natural convection flow under a magnetic field in an inclined square enclosure differentially heated on adjacent walls. Meccanica 42, 435–449 (2007)
M.M. Rashidi, M. Nasiri, M. Khezerloo, N. Laraqi, Numerical investigation of magnetic field effect on mixed convection heat transfer of nanofluid in a channel with sinusoidal walls. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 401, 159–168 (2016)
G.C. Bourantas, V.C. Loukopoulos, MHD natural-convection flow in an inclined square enclosure filled with a micropolar-nanofluid. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 79, 930–944 (2014)
H. Heidary, R. Hosseini, M. Pirmohammadi, M.J. Kermani, Numerical study of magnetic field effect on nano-fluid forced convection in a channel. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 374, 11–17 (2015)
M. Sheikholeslami, T. Hayat, A. Alsaedi, Numerical study for external magnetic source influence on water based nanofluid convective heat transfer. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 106, 745–755 (2017)
M. Sheikholeslami, D.D. Ganji, Ferrohydrodynamic and magnetohydrodynamic effects on ferrofluid flow and convective heat transfer. Energy 75, 400–410 (2014)
M. Sheikholeslami, M. Gorji Bandpy, R. Ellahi, A. Zeeshan, Simulation of MHD CuO–water nanofluid flow and convective heat transfer considering Lorentz forces. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 369, 69–80 (2014)
F. Selimefendigil, H.F. Oztop, Analysis of MHD mixed convection in a flexible walled and nanofluids filled lid-driven cavity with volumetric heat generation. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 118, 113–124 (2016)
F. Selimefendigil, H.F. Oztop, Mixed convection in a partially heated triangular cavity filled with nanofluid having a partially flexible wall and internal heat generation. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 70, 168–178 (2017)
F. Selimefendigil, H.F. Oztop, Natural convection in a flexible sided triangular cavity with internal heat generation under the effect of inclined magnetic field. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 417, 327–337 (2016)
F. Selimefendigil, H.F. Oztop, Mixed convection of nanofluid filled cavity with oscillating lid under the influence of an inclined magnetic field. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 63, 202–215 (2016)
F. Selimefendigil, H.F. Oztop, A.J. Chamkha, MHD mixed convection and entropy generation of nanofluid filled lid driven cavity under the influence of inclined magnetic fields imposed to its upper and lower diagonal triangular domains. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 406, 266–281 (2016)
M.A. Sheremet, H.F. Oztop, I. Pop, MHD natural convection in an inclined wavy cavity with corner heater filled with a nanofluid. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 416, 37–47 (2016)
O. Ghaffarpasand, Numerical study of MHD natural convection inside a sinusoidally heated lid-driven cavity filled with Fe3O4–water nanofluid in the presence of Joule heating. Appl. Math. Model. 40, 9165–9182 (2016)
S. Hussain, S. Ahmad, K. Mehmood, M. Sagheer, Effects of inclination angle on mixed convective nanofluid flow in a double lid-driven cavity with discrete heat sources. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 106, 847–860 (2017)
S. Hussain, K. Mehmood, M. Sagheer, MHD mixed convection and entropy generation of water-alumina nanofluid flow in a double lid driven cavity with discrete heating. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 419, 140–155 (2016)
V.M. Job, S.R. Gunakala, Mixed convection nanofluid flows through a grooved channel with internal heat generating solid cylinders in the presence of an applied magnetic field. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 107, 133–145 (2017)
A. Karimipour, A. Taghipour, A. Malvandi, Developing the laminar MHD forced convection flow of water/FMWNT carbon nanotubes in a microchannel imposed the uniform heat flux. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 419, 420–428 (2016)
M.A. Ismael, M.A. Mansour, A.J. Chamkha, A.M. Rashad, Mixed convection in a nanofluid filled-cavity with partial slip subjected to constant heat flux and inclined magnetic field. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 416, 25–36 (2016)
A. Aghaei, H. Khorasanizadeh, G.A. Sheikhzadeh, M. Abbaszadeh, Numerical study of magnetic field on mixed convection and entropy generation of nanofluid in a trapezoidal enclosure. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 403, 133–145 (2016)
Z. Mehrez, A. El Cafsi, A. Belghith, P. Le Quéré, MHD effects on heat transfer and entropy generation of nanofluid flow in an open cavity. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 374, 214–224 (2015)
A. Karimi, M. Goharkhah, M. Ashjaee, M.B. Shafii, Thermal conductivity of Fe2O3 and Fe3O4 magnetic nanofluids under the influence of magnetic field. Int. J. Thermophys. 36, 2720–2739 (2015)
P. Naphon, Effect of magnetic fields on the boiling heat transfer characteristics of nanofluids. Int. J. Thermophys. 36, 2810–2819 (2015)
MATLAB Release 2015, Computer Software, The MathWorks Inc., Natick, MA, United States
H.A. Van der Vorst, Bi-CGSTAB: a fast and smoothly converging variant of Bi-CG for the solution of nonsymmetric linear systems. SIAM J. Sci. Stat. Comput. 13, 631–644 (1992)
J. Koo, C. Kleinstreuer, Laminar nanofluid flow in microheat-sinks. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 48, 2652–2661 (2005)
Z.F. Tian, P.X. Yu, An efficient compact difference scheme for solving the streamfunction formulation of the incompressible Navier–Stokes equations. J. Comput. Phys. 230, 6404–6419 (2011)
H.N. Dixit, V. Babu, Simulation of high Rayleigh number natural convection in a square cavity using the lattice Boltzmann method. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 49, 727–739 (2006)
F. Kuznik, J. Vareilles, G. Rusaouen, G. Krauss, A double-population lattice Boltzmann method with non-uniform mesh for the simulation of natural convection in a square cavity. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 28, 862–870 (2007)
H. Moumni, H. Welhezi, R. Djebali, E. Sediki, Accurate finite volume investigation of nanofluid mixed convection in two sided lid driven cavity including discrete heat sources. Appl. Math. Model. 39, 4164–4179 (2015)
R. Djebali, M. El Ganaoui, H. Sammouda, R. Bennacer, Some benchmarks of a side wall heated cavity using lattice Boltzmann approach. Fluid Dyn. Mater. Process. 5, 261–282 (2009)
Z. Tian, Y. Ge, A fourth-order compact finite difference scheme for the steady stream function–vorticity formulation of the Navier–Stokes/Boussinesq equations. Int. J. Numer. Meth. Fluids 41, 495–518 (2003)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Taghikhani, M.A. Cu–Water Nanofluid MHD Mixed Convection in a Lid-Driven Cavity with Two Sinusoidal Heat Sources Considering Joule Heating Effect. Int J Thermophys 40, 44 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10765-019-2507-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10765-019-2507-3