Abstract
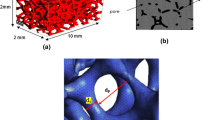
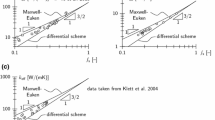
The accurate evaluation of the specific surface area and the effective thermal conductivity (ETC) of high-porosity metal foams is an important prerequisite to study the mechanism of heat transfer enhancement. In this paper, the tetrakaidecahedron, concave triangular prism and equivalent tetrahedron were used to develop the geometry shapes of cell, ligament and node, respectively. The calculation model of the specific surface area characterized by porosity and pore density (PPI) was deduced by considering the shape characteristics. Based on the angle between the two-dimensional plane skeleton layer and the heat flow direction, the ETC analytical calculation model characterized by only the porosity in the three-dimensional space was deduced. Without any other fitting or experimental empirical parameters, these two models are only related to porosity and PPI, which are the most readily available parameters for the metal foams. The results of these models are consistent with the experimental and empirical data in other literature, indicating that these models are both versatile and accurate.










Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- S v :
-
Specific surface area (m−1)
- φ :
-
Porosity
- \( d_{s} \) :
-
Ligament thickness \( \left( {\text{m}} \right) \)
- \( d_{w} \) :
-
Cell pore diameter \( \left( {\text{m}} \right) \)
- \( l \) :
-
Length of the ligament \( \left( {\text{m}} \right) \)
- \( a_{1} \) :
-
Parameter that affects the shape of the ligament cross section
- \( a_{2} \) :
-
Height of the pyramid \( \left( {\text{m}} \right) \)
- \( a_{3} \) :
-
Parameter that controls the shape of the ligament along the axial direction
- \( V \) :
-
Volume \( \left( {{\text{m}}^{3} } \right) \)
- \( S \) :
-
Surface area \( \left( {{\text{m}}^{2} } \right) \)
- \( d_{r} \) :
-
Inscribed circle diameter of cell \( \left( {\text{m}} \right) \)
- \( k \) :
-
Thermal conductivity \( \left( {{\text{W}} \cdot {\text{m}}^{ - 1} \cdot {\text{K}}^{ - 1} } \right) \)
- PPI:
-
Pore number per inch
- \( \Delta T \) :
-
Temperature difference \( \left( {\text{K}} \right) \)
- \( Q \) :
-
Heat \( \left( {\text{J}} \right) \)
- A, B, C:
-
Serial number of plane skeleton layer
- \( H \) :
-
Height of cell \( \left( {\text{m}} \right) \)
- \( A_{l} \) :
-
Cross-sectional area of ligament \( \left( {{\text{m}}^{2} } \right) \)
- \( A_{b} \) :
-
Bottom area of cell \( \left( {{\text{m}}^{2} } \right) \)
- λ :
-
Parameter, \( \lambda = a_{2} /l \)
- α :
-
Angle
- l :
-
Ligament
- n :
-
Node
- cell :
-
Cell
- foam :
-
Metal foams
- max :
-
Maximum
- min :
-
Minimum
- s :
-
Solid phase
- f :
-
Fluid phase
- hex :
-
Hexahedron
- e :
-
Effective
- t :
-
Total
- p :
-
Plane skeleton layer
References
P.S. Liu, Philos. Mag. Lett. 90, 447–453 (2010)
M. Lacroix, P. Nguyen, D. Schweich, C.P. Huu, S. Savin-Poncet, D. Edouard, Chem. Eng. Sci. 62, 3259–3267 (2007)
A. Inayat, H. Freund, T. Zeiser, Chem. Eng. Sci. 66, 1179–1188 (2011)
F.C. Buciuman, B. Kraushaarczarnetzki, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 42, 1863–1869 (2003)
J. Grosse, B. Dietrich, G.I. Garrido, P. Habisreuther, N. Zarzalis, H. Martin, M. Kind, B. Kraushaar-Czarnetzki, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 48, 10395–10401 (2009)
D.L. Duan, R.L. Zhang, X.J. Ding, S. Li, Mater. Sci. Technol. 22, 1364–1367 (2006)
V.V. Calmidi, R.L. Mahajan, J. Heat Trans-T ASME 121, 466–471 (1999)
A. Bhattacharya, V.V. Calmidi, R.L. Mahajan, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 45, 1017–1031 (2002)
L.J. Gibson, M.F. Ashby, Cellular Solids: Structure and Properties, vol. 33 (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1988), pp. 487–488
K. Boomsma, D. Poulikakos, Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 44, 827–836 (2001)
Z. Dai, K. Nawaz, Y.G. Park, J. Bock, A.M. Jacobi, Int. Commun. Heat Mass 37, 575–580 (2010)
S. Kanaun, O. Tkachenko, Int. J. Eng. Sci. 46, 551–571 (2008)
Y. Yao, H. Wu, Z. Liu, Int. J. Therm. Sci. 97, 56–67 (2015)
W. Thomson, Acta Math. 11, 121–134 (1887)
Jagjiwanram, R. Singh, Appl. Therm. Eng. 24, 2727–2735 (2004)
M.S. Phanikumar, R.L. Mahajan, Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 45, 3781–3793 (2002)
E. Sadeghi, S. Hsieh, M. Bahrami, J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 44, 125406 (2009)
J.W. Paek, B.H. Kang, S.Y. Kim, J.M. Hyun, Int. J. Thermophys. 21, 453–464 (2000)
X.H. Yang, J.J. Kuang, J.X. Bai, T.J. Lu, D.F. Jin, J. Xi’an Jiao Tong Univ. 48, 79–84 (2014)
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by National Basic Research Program of China-973 Program 2015CB857100.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shen, H., Ye, Q. & Meng, G. The Simplified Analytical Models for Evaluating the Heat Transfer Performance of High-Porosity Metal Foams. Int J Thermophys 39, 87 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10765-018-2405-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10765-018-2405-0