Abstract
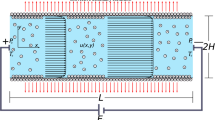
In this paper, heat transfer enhancement in an evaporating thin film along the wall of a microchannel under an imposed inhomogenous electrostatic field is analyzed. The mathematical model, based on the augmented Young–Laplace equation with the inhomogenous electrostatic field taken into consideration, is developed. The 2D inhomogenous electric field with the curved liquid–vapor interface is solved by the lattice Boltzmann method. Numerical solutions for the thin film characteristics are obtained for both constant wall temperature and uniform wall heat flux boundary conditions. The numerical results show that the liquid film becomes thinner and the heat transfer coefficient increases under an imposed electric field. Both of octane and water are chosen as the working mediums, and similar result about the enhancement of heat transfer on evaporating thin film by imposing electric field is obtained. It is found that applying an electric field on the evaporating thin film can enhance evaporative heat transfer in a microchannel.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
F. Holm, S. Goplen, Heat transfer in the meniscus thin-film transition region. J. Heat Transf. 101, 543 (1979)
B.V. Deryagin, S.V. Nerpin, N.V. Churayev, Effect of film heat transfer upon evaporation of liquids from capillaries. Bull. Rilem 29, 93 (1965)
B.V. Deryagin, Modern state of the investigation of long-range surface forces. Langmuir 3, 601 (1987)
M. Potash Jr., P.C. Wayner Jr., Evaporation from a two-dimensional extended meniscus. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 15, 1851 (1972)
P. Wayner Jr., Y. Kao, L. LaCroix, The interline heat-transfer coefficient of an evaporating wetting film. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 19, 487 (1976)
J. Schonberg, P. Wayner Jr., An analytical solution for the integral contact line evaporative heat sink, in Proceedings of the AIAA/ASME 5th Joint Thermophysics and Heat Transfer Conference, Seattle (1990)
K. Park, K.-J. Noh, K.-S. Lee, Transport phenomena in the thin-film region of a micro-channel. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 46, 2381 (2003)
H. Wang, S.V. Garimella, J.Y. Murthy, Characteristics of an evaporating thin film in a microchannel. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 50, 3933 (2007)
H. Wang, Z. Pan, Z. Chen, Thin-liquid-film evaporation at contact line. Front. Energy Power Eng. 3, 141 (2009)
H. Wang, S.V. Garimella, J.Y. Murthy, An analytical solution for the total heat transfer in the thin-film region of an evaporating meniscus. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 51, 6317 (2008)
H.B. Ma, P. Cheng, B. Borgmeyer, Y.X. Wang, Fluid flow and heat transfer in the evaporating thin film region. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 4, 237 (2008)
L. Zheng, Y.-X. Wang, J.L. Plawsky, P.C. Wayner, Accuracy of measurements of curvature and apparent contact angle in a constrained vapor bubble heat exchanger. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 45, 2021 (2002)
C.P. Migliaccio, H.K. Dhavaleswarapu, S.V. Garimella, Temperature measurements near the contact line of an evaporating meniscus V-groove. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf, 54, 1520 (2011)
R.S.R. Gorla, J.E. Gatica, B. Ghorashi, P. In-Eure, L.W. Byrd, Heat transfer in a thin liquid film in the presence of electric field for non-isothermal interfacial condition. Int. J. Fluid Mech. Res. 29, 12 (2002)
D. Landau, E. Lifshitz, Electrodynamics of Continuous Media (Pergamon press, New York, 1960)
S. Chen, G.D. Doolen, Lattice Boltzmann method for fluid flows. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 30, 329 (1998)
Y.H. Qian, D. d’Humieres, P. Lallemand, Lattice BGK models for Navier–Stokes equation. Europhys. Lett. 17, 479 (1992)
X. He, N. Li, Lattice Boltzmann simulation of electrochemical systems. Comput. Phys. Commun. 129, 158 (2000)
J. Zhang, D.Y. Kwok, A 2D lattice Boltzmann study on electrohydrodynamic drop deformation with the leaky dielectric theory. J. Comput. Phys. 206, 150 (2005)
S. Gong, P. Cheng, X. Quan, Lattice Boltzmann simulation of droplet formation in microchannels under an electric field. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 53, 5863 (2010)
G. Liu, L. Ma, J. Liu, Chemical Data Manual (Chemical Industry Press, Beijing, 2002)
K. Park, K.S. Lee, Flow and heat transfer characteristics of the evaporating extended meniscus in a micro-capillary channel. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 46, 4587 (2003)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Dr. Zhuoyao He, Dr. Kunxu Zhu and Dr. Qiang Lin for many helpful discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, X., Hu, C., Li, H. et al. Effects of an Inhomogenous Electric Field on an Evaporating Thin Film in a Microchannel. Int J Thermophys 39, 43 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10765-018-2363-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10765-018-2363-6